Related Research Articles

Valens was Roman emperor from 364 to 378. Following a largely unremarkable military career, he was named co-emperor by his elder brother Valentinian I, who gave him the eastern half of the Roman Empire to rule. In 378, Valens was defeated and killed at the Battle of Adrianople against the invading Goths, which astonished contemporaries and marked the beginning of barbarian encroachment into Roman territory.

Gratian was emperor of the Western Roman Empire from 367 to 383. The eldest son of Valentinian I, Gratian accompanied his father on several campaigns along the Rhine and Danube frontiers and was raised to the rank of Augustus in 367. Upon the death of Valentinian in 375, Gratian took over government of the west while his half-brother Valentinian II was also acclaimed emperor in Pannonia. Gratian governed the western provinces of the empire, while his uncle Valens was already the emperor over the east.

Valentinian I, sometimes called Valentinian the Great, was Roman emperor along with his brother Valens from 364 to 375. During his reign, he fought successfully against the Alamanni, Quadi, and Sarmatians, strengthening the border fortifications and conducting campaigns across the Rhine and Danube. His general Theodosius defeated a revolt in Africa and the Great Conspiracy, a coordinated assault on Roman Britain by Picts, Scoti, and Saxons. Valentinian founded the Valentinianic dynasty, with his sons Gratian and Valentinian II succeeding him in the western half of the empire.
Flavius Theodosius, also known as Count Theodosius or Theodosius the Elder, was a senior military officer serving Valentinian I and the western Roman empire during Late Antiquity. Under his command the Roman army defeated numerous threats, incursions, and usurpations. Theodosius was patriarch of the imperial Theodosian dynasty and father of the emperor Theodosius the Great.

The Theodosian dynasty was a Roman imperial family that produced five Roman emperors during Late Antiquity, reigning over the Roman Empire from 379 to 457. The dynasty's patriarch was Theodosius the Elder, whose son Theodosius the Great was made Roman emperor in 379. Theodosius's two sons both became emperors, while his daughter married Constantius III, producing a daughter that became an empress and a son also became emperor. The dynasty of Theodosius married into, and reigned concurrently with, the ruling Valentinianic dynasty, and was succeeded by the Leonid dynasty with the accession of Leo the Great.

The six-volume work The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire by the English historian Edward Gibbon (1737–1794) has been reprinted many times over the years in various editions.

The Valentinianic or Valentinian dynasty was a ruling house of five generations of dynasts, including five Roman emperors during Late Antiquity, lasting nearly a hundred years from the mid fourth to the mid fifth century. They succeeded the Constantinian dynasty and reigned over the Roman Empire from 364 to 392 and from 425 to 455, with an interregnum (392–423), during which the Theodosian dynasty ruled and eventually succeeded them. The Theodosians, who intermarried into the Valentinian house, ruled concurrently in the east after 379.
Justina was a Roman empress. She was initially the wife of the rebel emperor Magnentius and was then married to Valentinian I, with whom she had four children, including the emperor Valentinian II and the empress Galla.
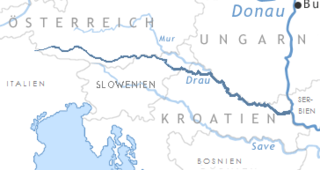
The Battle of the Save was fought in 388 between the forces of Roman usurper Magnus Maximus and the Eastern Roman Empire. Emperor Theodosius I defeated Magnus Maximus's army in battle. Later Maximus was captured and executed at Aquileia.
The Gildonic War was a rebellion in the year 398 led by Comes Gildo against Roman emperor Honorius. The revolt was subdued by Stilicho, the magister militum of the Western Roman empire.
Gildo was a Roman Berber general in the province of Mauretania Caesariensis. He revolted against Honorius and the Western Roman Empire, but was defeated and possibly killed himself or was assassinated.

Roman Tunisia initially included the early ancient Roman province of Africa, later renamed Africa Vetus. As the Roman empire expanded, the present Tunisia also included part of the province of Africa Nova.

Mauri was the Latin designation for the Berber population of Mauretania, located in the west side of North Africa on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea, Mauretania Tingitana and Mauretania Caesariensis, in present-day Morocco and northwestern Algeria.
Flavius Merobaudes was a Roman army officer of Frankish origin. He was appointed magister peditum around 375, and consul twice in 377 and 383. Ancient sources record that he was put to death that year for his support of the imperial usurper Magnus Maximus, but an inscription records that he became consul a third time in 388.

The Vandal Kingdom or Kingdom of the Vandals and Alans was a confederation of Vandals and Alans, which is one of the barbarian kingdoms established under Gaiseric, a Vandal warrior. It ruled in North Africa and the Mediterranean from 435 to 534 AD.
Mascezel was briefly ruler of Roman North Africa after the defeat of his brother Gildo during the Gildonic war in 398 AD.
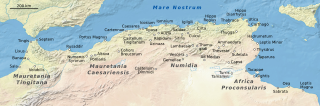
Igilgili was a Berber town and a Phoenician, Carthaginian, and Roman colony in located in present-day Jijel, Algeria.

Cartennae or Cartenna was an ancient Berber, Carthaginian, and Roman port at present-day Ténès, Algeria. Under the Romans, it was part of the province of Mauretania Caesariensis.
Vaga, Vecca and lately Theodorias is an ancient city in Tunisia built by the Berbers and ruled sequentially by the Carthaginians, the Numidians, the Romans, the Vandals and the Byzantines until it was captured by the Arabs who changed its name to the present day Béja. The town was the capital of the Numidian Kingdom during the rule of Jugurtha.
References
- ↑ Camps, G. (1998), "Firmus", Encyclopédie berbère (in French), Éditions Peeters, vol. 19 | Filage – Gastel, pp. 2845–2855, ISBN 2857449941 , retrieved 2020-07-11
- ↑ Historicus, Zosimus. "Historia Nova, Book 4".
- ↑ Edward Gibbon, The Decline And Fall Of The Roman Empire, (The Modern Library, 1932), chap. XXV., p. 883
- ↑ Gibbon, Ibid. Gibbon makes the comparison to Jugurtha
- ↑ Gibbon, Ibid. p. 883, 884
- ↑ Gibbon, Ibid.
- ↑ Piredda 2015: 234-267
- Roberts, Walter, "Firmus (ca.372-ca.375 A.D.)", De Imperatoribus Romanis site
- Piredda, A.M.G.(2015). "Passio sanctae Salsae" in Fialon, S. and Meyers, J. La Passio sanctae Salsae (BHL 7467) : Recherches sur une passion tardive d’Afrique du Nord. Ausonius (Bordeaux). pp. 234–267.