Related Research Articles
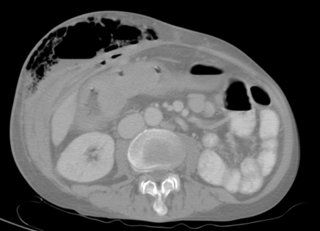
A fistula in anatomy is an abnormal connection between two hollow spaces, such as blood vessels, intestines, or other hollow organs. Types of fistula can be described by their location. Anal fistulas connect between the anal canal and the perianal skin. Anovaginal or rectovaginal fistulas occur when a hole develops between the anus or rectum and the vagina. Colovaginal fistulas occur between the colon and the vagina. Urinary tract fistulas are abnormal openings within the urinary tract or an abnormal connection between the urinary tract and another organ such as between the bladder and the uterus in a vesicouterine fistula, between the bladder and the vagina in a vesicovaginal fistula, and between the urethra and the vagina in urethrovaginal fistula. When occurring between two parts of the intestine, it is known as an enteroenteral fistula, between the small intestine and the skin as an enterocutaneous fistula, and between the colon and the skin as a colocutaneous fistula.

A thyroglossal cyst is a fibrous cyst that forms from a persistent thyroglossal duct. Thyroglossal cysts can be defined as an irregular neck mass or a lump which develops from cells and tissues left over after the formation of the thyroid gland during developmental stages.
Mirizzi's syndrome is a rare complication in which a gallstone becomes impacted in the cystic duct or neck of the gallbladder causing compression of the common hepatic duct, resulting in obstruction and jaundice. The obstructive jaundice can be caused by direct extrinsic compression by the stone or from fibrosis caused by chronic cholecystitis (inflammation). A cholecystocholedochal fistula can occur.

Colorectal surgery is a field in medicine dealing with disorders of the rectum, anus, and colon. The field is also known as proctology, but this term is now used infrequently within medicine and is most often employed to identify practices relating to the anus and rectum in particular. The word proctology is derived from the Greek words πρωκτός proktos, meaning "anus" or "hindparts", and -λογία -logia, meaning "science" or "study".
A seton or seton stitch is a procedure used to aid the healing of fistulae.

Blood in stool looks different depending on how early it enters the digestive tract—and thus how much digestive action it has been exposed to—and how much there is. The term can refer either to melena, with a black appearance, typically originating from upper gastrointestinal bleeding; or to hematochezia, with a red color, typically originating from lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Evaluation of the blood found in stool depends on its characteristics, in terms of color, quantity and other features, which can point to its source, however, more serious conditions can present with a mixed picture, or with the form of bleeding that is found in another section of the tract. The term "blood in stool" is usually only used to describe visible blood, and not fecal occult blood, which is found only after physical examination and chemical laboratory testing.
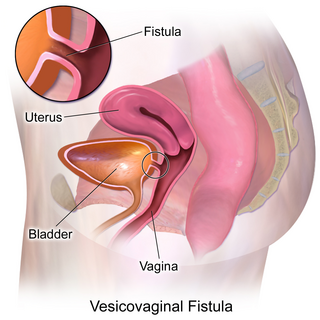
Vesicovaginal fistula (VVF) is a subtype of female urogenital fistula (UGF).

Anal fistula is a chronic abnormal communication between the epithelialised surface of the anal canal and usually the perianal skin. An anal fistula can be described as a narrow tunnel with its internal opening in the anal canal and its external opening in the skin near the anus. Anal fistulae commonly occur in people with a history of anal abscesses. They can form when anal abscesses do not heal properly.

A biliary fistula is a type of fistula in which bile flows along an abnormal connection from the bile ducts into nearby hollow structure. Types of biliary fistula include:

Anorectal abscess is an abscess adjacent to the anus. Most cases of perianal abscesses are sporadic, though there are certain situations which elevate the risk for developing the disease, such as diabetes mellitus, Crohn's disease, chronic corticosteroid treatment and others. It arises as a complication of paraproctitis. Ischiorectal, inter- and intrasphincteric abscesses have been described.
Goodsall's rule relates the external opening of an anal fistula to its internal opening. It states that if the perianal skin opening is posterior to the transverse anal line, the fistulous tract will open into the anal canal in the midline posteriorly, sometimes taking a curvilinear course. A perianal skin opening anterior to the transverse anal line is usually associated with a radial fistulous tract.

In humans, the anus is the external opening of the rectum, located inside the intergluteal cleft and separated from the genitals by the perineum. Two sphincters control the exit of feces from the body during an act of defecation, which is the primary function of the anus. These are the internal anal sphincter and the external anal sphincter, which are circular muscles that normally maintain constriction of the orifice and which relaxes as required by normal physiological functioning. The inner sphincter is involuntary and the outer is voluntary. It is located behind the perineum which is located behind the vagina or scrotum.
Urogynecology or urogynaecology is a surgical sub-specialty of urology and gynecology.
LIFT technique is the novel modified approach through the intersphincteric plane for the treatment of fistula-in-ano, known as LIFT procedure. LIFT procedure is based on secure closure of the internal opening and removal of infected cryptoglandular tissue through the intersphincteric approach. Essential steps of the procedure include, incision at the intersphincteric groove, identification of the intersphincteric tract, ligation of intersphincteric tract close to the internal opening and removal of intersphincteric tract, scraping out all granulation tissue in the rest of the fistulous tract, and suturing of the defect at the external sphincter muscle. The procedure was developed by Thai colorectal surgeon, Arun Rojanasakul, Colorectal Division Department of Surgery, Chulalongkorn University in Bangkok, Thailand. The first report of preliminary healing result from the procedure were 94% in 2007

Anorectal disorders include conditions involving the anorectal junction as seen in the image. They are painful but common conditions like hemorrhoids, tears, fistulas, or abscesses that affect the anal region. Most people experience some form of anorectal disorder during their lifetime. Primary care physicians can treat most of these disorders, however, high-risk individuals include those with HIV, roughly half of whom need surgery to remedy the disorders. Likelihood of malignancy should also be considered in high risk individuals. This is why it is important to perform a full history and physical exam on each patient. Because these disorders affect the rectum, people are often embarrassed or afraid to confer with a medical professional.
A keyhole defect may refer to a groove in the anal canal wall, which can occur after posterior midline fissurectomy or fistulotomy, or with lateral internal anal sphincter defects. The keyhole defect is associated with minor degrees of fecal incontinence, allowing seepage of liquid stool or mucus.
Fistulectomy is a surgical procedure where a fistulous tract is excised completely. This is compared with fistulotomy, where the fistulous tract is merely laid open to heal.
A rectovestibular fistula, also referred to simply as a vestibular fistula, is an anorectal congenital disorder where an abnormal connection (fistula) exists between the rectum and the vulval vestibule of the female genitalia.

Pradeep Kumar Chowbey is an Indian surgeon, known for laparoscopic and bariatric surgeries. He is the incumbent Executive vice chairman of the Max Healthcare, Chairman of the Minimal Access, Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery and Allied Surgical Specialities of the Max Healthcare Institute, New Delhi. He is the founder of the Minimal Access, Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery Centre at the Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi and has served as the Honorary Surgeon to the President of India, Dalai Lama and the Indian Armed Forces (AFMS). The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian honour of the Padma Shri in 2002.
A urogenital fistula is an abnormal tract that exists between the urinary tract and bladder, ureters, or urethra. A urogenital fistula can occur between any of the organs and structures of the pelvic region. A fistula allows urine to continually exit through and out the urogenital tract. This can result in significant disability, interference with sexual activity, and other physical health issues, the effects of which may in turn have a negative impact on mental or emotional state, including an increase in social isolation. Urogenital fistulas vary in etiology. Fistulas are usually caused by injury or surgery, but they can also result from malignancy, infection, prolonged and obstructed labor and deliver in childbirth, hysterectomy, radiation therapy or inflammation. Of the fistulas that develop from difficult childbirth, 97 percent occur in developing countries. Congenital urogenital fistulas are rare; only ten cases have been documented. Abnormal passageways can also exist between the vagina and the organs of the gastrointestinal system, and these may also be termed fistulas.
References
- ↑ Jain, Bhupendra Kumar; Vaibhaw, Kumar; Garg, Pankaj Kumar; Gupta, Sanjay; Mohanty, Debajyoti (April 2012). "Comparison of a Fistulectomy and a Fistulotomy with Marsupialization in the Management of a Simple Anal Fistula: A Randomized, Controlled Pilot Trial". Journal of the Korean Society of Coloproctology. 28 (2): 78–82. doi:10.3393/jksc.2012.28.2.78. ISSN 2093-7822. PMC 3349814 . PMID 22606646.