
The Battle of Richmond, Kentucky, fought August 29–30, 1862, was one of the most complete Confederate victories in the war by Major General Edmund Kirby Smith against Union major general William "Bull" Nelson's forces, which were defending the town. It was the first major battle in the Kentucky Campaign. The battle took place on and around what is now the grounds of the Blue Grass Army Depot, outside Richmond, Kentucky.

Shiloh National Military Park preserves the American Civil War Shiloh and Corinth battlefields. The main section of the park is in the unincorporated town of Shiloh, about nine miles (14 km) south of Savannah, Tennessee, with an additional area located in the city of Corinth, Mississippi, 23 miles (37 km) southwest of Shiloh. The Battle of Shiloh began a six-month struggle for the key railroad junction at Corinth. Afterward, Union forces marched from Pittsburg Landing to take Corinth in a May siege, then withstood an October Confederate counter-attack.

Poison Springs Battleground State Park is an Arkansas state park located southeast of Bluff City. It commemorates the Battle of Poison Spring in the American Civil War, which was part of the 1864 Camden Expedition, an element of a Union Army initiative to gain control of Shreveport, Louisiana and get a foothold in Texas.
The Battle of Greenbrier River, also known as the Battle of Camp Bartow, took place on October 3, 1861 in Pocahontas County, Virginia as part of the Operations in Western Virginia Campaign during the American Civil War.
The Battle of Averasborough or the Battle of Averasboro, fought March 16, 1865, in Harnett and Cumberland counties, North Carolina, as part of the Carolinas Campaign of the American Civil War, was a prelude to the climactic Battle of Bentonville, which began three days later.

The Battle of Hatchie's Bridge, also known as Battle of Davis Bridge or Matamora, was fought on October 5, 1862, in Hardeman County and McNairy County, Tennessee, as the final engagement of the Iuka–Corinth Campaign of the American Civil War. Confederate Major General Earl Van Dorn's army successfully evaded capture by the Union Army, following his defeat at the Battle of Corinth.

The Battle of Middle Creek was an engagement fought January 10, 1862, in Eastern Kentucky during the American Civil War. It was the only battle personally commanded by future president James A. Garfield, then a colonel in the Union Army.
The Battle of White Oak Road, also known as The Battle of Hatcher's Run, Gravelly Run, Boydton Plank Road, White Oak Ridge was fought on March 31, 1865, during the American Civil War at the end of the Richmond-Petersburg Campaign and in the beginning stage of the Appomattox Campaign. Along with the Battle of Dinwiddie Court House which was fought simultaneously on March 31, the battle involved the last offensive action by General Robert E. Lee's Confederate Army of Northern Virginia to stop the progress of Lieutenant General Ulysses S. Grant's Union Army. Grant's forces were moving to cut the remaining Confederate supply lines and to force the Confederates to extend their defensive lines at Petersburg, Virginia and Richmond, Virginia to the breaking point, if not to force them into a decisive open field battle.

The Battle of Champion Hill of May 16, 1863, was the pivotal battle in the Vicksburg Campaign of the American Civil War (1861–1865). Union Army commander Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant and the Army of the Tennessee pursued the retreating Confederate States Army under Lt. Gen. John C. Pemberton and defeated it twenty miles to the east of Vicksburg, Mississippi, leading inevitably to the siege of Vicksburg and surrender. The battle is also known as Baker's Creek.

Wilson's Creek National Battlefield, located near Republic, Missouri, preserves the site of the Battle of Wilson's Creek. Fought on August 10, 1861, the battle was the first major American Civil War engagement west of the Mississippi River. In the battle, a Confederate army commanded by Benjamin McCulloch and Sterling Price defeated a smaller Union army commanded by Nathaniel Lyon. However, the Confederates were unable to hold much of Missouri, and a Confederate defeat at the Battle of Pea Ridge effectively solidified Union control of the state. Major features include a five-mile automobile tour loop, the restored 1852 Ray House, and "Bloody Hill", the site of the final stage of the battle. The site is located near Republic in southwestern Missouri just southwest of the city of Springfield. It has been a unit of the National Park Service since 1960, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1966.

The Battle of Peebles's Farm was the western part of a simultaneous Union offensive against the Confederate works guarding Petersburg and Richmond, Virginia, during the Siege of Petersburg in the American Civil War.

The Prairie D'Ane Battlefield, also known as Prairie D'Ann Battlefield or Prairie De Ann Battlefield in anglicized forms, was the site of the Civil War Battle of Prairie D'Ane, one of the engagements in southwestern Arkansas of the Union's Camden Expedition of 1864. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974, and, with other sites, is part of the Camden Expedition Sites National Historic Landmark. It was declared part of the National Historic Landmark in 1994.
The Port Gibson Battlefield is the site near Port Gibson, Mississippi where the 1863 Battle of Port Gibson was fought during the American Civil War. The battlefield covers about 3,400 acres (1,400 ha) of land west of the city, astride Rodney Road, where Union Army forces were establishing a beachhead after crossing the Mississippi River in a bid to take the Confederate fortress of Vicksburg. The Union victory secured that beachhead and paved the way for the eventual fall of Vicksburg. A 2,080-acre (840 ha) area surrounding part of the site was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1972, and a larger area was designated a National Historic Landmark in 2005. In 2009, the battlefield was designated by the Civil War Preservation Trust as one of its Top 10 most endangered Civil War battlefields. In 2011, the Civil War Preservation Trust was renamed the Civil War Trust, which in 2018 became a division of the American Battlefield Trust. The Trust and its partners have acquired and preserved 644 acres (2.61 km2) of the Port Gibson battlefield.

Bentonville Battlefield is a North Carolina state historic site at 5466 Harper House Road in Johnston County, North Carolina. It belongs to the North Carolina Department of Natural and Cultural Resources and is the site of the 1865 Battle of Bentonville, fought in the waning days of the American Civil War. It was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1996.

The Petersburg Breakthrough Battlefield is a historic district in Dinwiddie County, near Petersburg, Virginia. It was the location of the Third Battle of Petersburg, in which the Union Army broke through Confederate Army lines protecting Petersburg and Richmond on April 2, 1865, during the American Civil War. The success of the breakthrough led to abandonment of Richmond by General Robert E. Lee, a general retreat, and surrender at Appomattox Court House one week later. Portions of the area were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2003, and a different portion was designated a National Historic Landmark in 2006. Much of the battlefield area is part of Pamplin Historical Park, a private park open to the public that interprets the battle. The park includes a full-service visitor center, trails, displays, interpretive signs and history programs. The Civil War Trust and its partners have acquired and preserved 407 acres (1.65 km2) of the Breakthrough battlefield in five transactions since 2004.

Sayler's Creek Battlefield, near Farmville, Virginia, was the site of the Battle of Sayler's Creek of the American Civil War. Confederate general Robert E. Lee's army was retreating from the Richmond to the Petersburg line. Here, on April 6, 1865, Union general Philip Sheridan cut off and beat back about a quarter of Lee's depleted army. Eight Confederate generals surrendered, and 7,700 men were lost. Confederate Major General George Washington Custis Lee, eldest son of Robert E. Lee, was forcibly captured on the battlefield by Private David Dunnels White of the 37th Massachusetts Regiment. The battle was the last major engagement of the war in Virginia; Lee's surrender at Appomattox occurred three days later. A portion of the landmarked battlefield area is included in Sailor's Creek Battlefield Historical State Park. The Civil War Trust and its partners have acquired and preserved 885 acres (3.58 km2) of the battlefield in five transactions since 1996.
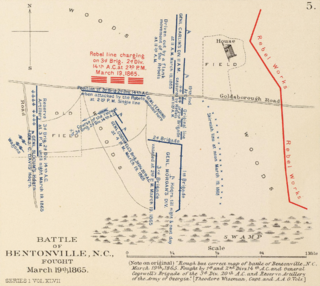
The Battle of Bentonville was fought in Johnston County, North Carolina, near the village of Bentonville, as part of the Western Theater of the American Civil War. It was the last battle between the armies of Union Maj. Gen. William T. Sherman and Confederate Gen. Joseph E. Johnston.

Burnt Quarter is a historic plantation house located near Dinwiddie, Dinwiddie County, Virginia. It was built in stages starting about 1750, and consists of a two-story, hipped roof central section flanked by 1+1⁄2-story wings. On April 1, 1865, the property became the scene of the decisive Battle of Five Forks. During the battle the house served both as headquarters for Union General Merritt and as a military hospital. On the grounds is a monument to six unknown Confederate soldiers killed in the Battle of Five Forks.

Pamplin Historical Park is a 424-acre private sector historical park located near Petersburg, Virginia. The park preserves open space near Richmond, Virginia in Dinwiddie County, Virginia and serves the dual use of preserving a significant fragment of the Petersburg Breakthrough Battlefield, a National Historic Landmark, and key components of the Third Battle of Petersburg. The park also provides a footprint location for the National Museum of the Civil War Soldier, which is located within the park.
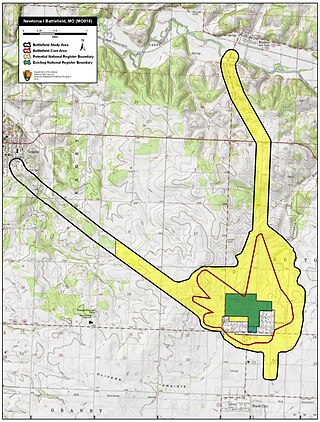
The First Battle of Newtonia Historic District, near Newtonia, Missouri, is a National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) site that preserves the location of the First Battle of Newtonia, an 1862 battle during the American Civil War. The battle saw Confederate troops under Colonels Douglas H. Cooper and Joseph O. Shelby defeat a Union force commanded by Brigadier General Frederick Salomon. The historic district contains some Civil War-period structures, as well as the Mathew H. Ritchey House, which is listed separately on the NRHP.

















