
A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial or textual form. A discrete monitor comprises a visual display, support electronics, power supply, housing, electrical connectors, and external user controls.

A 19-inch rack is a standardized frame or enclosure for mounting multiple electronic equipment modules. Each module has a front panel that is 19 inches (482.6 mm) wide. The 19 inch dimension includes the edges or ears that protrude from each side of the equipment, allowing the module to be fastened to the rack frame with screws or bolts. Common uses include computer servers, telecommunications equipment and networking hardware, audiovisual production gear, music production equipment, and scientific equipment.

Digital Visual Interface (DVI) is a video display interface developed by the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG). The digital interface is used to connect a video source, such as a video display controller, to a display device, such as a computer monitor. It was developed with the intention of creating an industry standard for the transfer of uncompressed digital video content.
Extended Display Identification Data (EDID) and Enhanced EDID (E-EDID) are metadata formats for display devices to describe their capabilities to a video source. The data format is defined by a standard published by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA).

The D-subminiature or D-sub is a common type of electrical connector. They are named for their characteristic D-shaped metal shield. When they were introduced, D-subs were among the smallest connectors used on computer systems.

The bottom bracket on a bicycle connects the crankset (chainset) to the bicycle and allows the crankset to rotate freely. It contains a spindle to which the crankset attaches, and the bearings that allow the spindle and crankset to rotate. The chainrings and pedals attach to the cranks. Bottom bracket bearings fit inside the bottom bracket shell, which connects the seat tube, down tube and chain stays as part of the bicycle frame.

In photography and cinematography, a filter is a camera accessory consisting of an optical filter that can be inserted into the optical path. The filter can be of a square or oblong shape and mounted in a holder accessory, or, more commonly, a glass or plastic disk in a metal or plastic ring frame, which can be screwed into the front of or clipped onto the camera lens.

A hole punch, also known as hole puncher, or paper puncher, is an office tool that is used to create holes in sheets of paper, often for the purpose of collecting the sheets in a binder or folder. A hole punch can also refer to similar tools for other materials, such as leather, cloth, or plastic or metal sheets.

The wheel size for a motor vehicle or similar wheel has a number of parameters.
The following are common definitions related to the machine vision field.

VESA Plug and Display is a video connector that carries digital signals for monitors, such as flat panel displays and video projectors, ratified by Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) in 1997. Introduced around the same time as the competing connectors for the Digital Visual Interface and VESA's own Digital Flat Panel, it was marketed as a replacement for the VESA Enhanced Video Connector. Unlike DVI, it never achieved widespread implementation.

Computer case screws are the hardware used to secure parts of a PC to the case. Although there are numerous manufacturers of computer cases, they have generally used three thread sizes. The Unified Thread Standard (UTS) originates from the United States, while the ISO metric screw thread is standardized worldwide. In turn, these thread standards define preferred size combinations that are based on generic units—some on the inch and others on the millimetre.

Drum hardware is the set of parts of a drum or drum kit that are used to tension, position, and otherwise support the instruments themselves.

Asus EeeBox PC is a nettop computer line from ASUSTeK Computer Incorporated, and a part of the Asus Eee product family. First released on August 11, 2008, the Asus EeeBox PC series is marketed as a small, light, inexpensive and energy-efficient counterpart to the Asus Eee PC netbook / subnotebook laptop series. Its motherboard employs Splashtop technology called Express Gate by Asus.
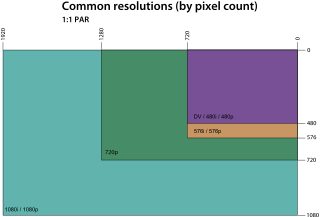
A display resolution standard is a commonly used width and height dimension of an electronic visual display device, measured in pixels. This information is used for electronic devices such as a computer monitor. Certain combinations of width and height are standardized and typically given a name and an initialism which is descriptive of its dimensions. A graphics display resolution can be used in tandem with the size of the graphics display to calculate pixel density. An increase in the pixel density often correlates with a decrease in the size of individual pixels on a display.

TETRIX Robotics consists of two robotic kits by Pitsco Education. The two sets are the TETRIX MAX building system and the TETRIX PRIME building system. They are intended to be used as educational robotics and for competitions such as the FIRST Tech Challenge.

In electronics, a chip carrier is one of several kinds of surface-mount technology packages for integrated circuits. Connections are made on all four edges of a square package; compared to the internal cavity for mounting the integrated circuit, the package overall size is large.
A monitor mount is a supportive bracket or arm designed to hold up a computer monitor, laptop, notebook or other display screen. Monitor arm and monitor bracket are other common terms for this device.

Scope mounts are rigid implements used to attach (typically) a telescopic sight or other types of optical sights onto a firearm. The mount can be made integral to the scope body or, more commonly, an external fitting that clamp onto the scope tube via screw-tightened rings. The scope and mount are then fastened onto compatible interfaces on the weapon. Words such as mounts and bases are used somewhat loosely, and can refer to several different parts which are either used together or in place of each other as ways to mount optical sights to firearms.

















