
In aviation, instrument flight rules (IFR) is one of two sets of regulations governing all aspects of civil aviation aircraft operations; the other is visual flight rules (VFR).
In aviation, visual flight rules (VFR) are a set of regulations under which a pilot operates an aircraft in weather conditions generally clear enough to allow the pilot to see where the aircraft is going. Specifically, the weather must be better than basic VFR weather minima, i.e., in visual meteorological conditions (VMC), as specified in the rules of the relevant aviation authority. The pilot must be able to operate the aircraft with visual reference to the ground, and by visually avoiding obstructions and other aircraft.

Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled airspace. The primary purpose of ATC worldwide is to prevent collisions, organize and expedite the flow of air traffic, and provide information and other support for pilots.

Westchester County Airport is a county-owned airport in Westchester County, New York, three miles (6 km) northeast of downtown White Plains, with territory in the towns of North Castle and Harrison, New York, and village of Rye Brook, New York. It is sometimes referred to as the White Plains Airport and is so identified by the Official Airline Guide (OAG).
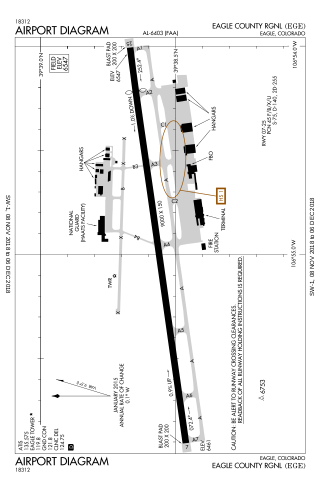
Eagle County Regional Airport is in Gypsum, Colorado, United States, 4 miles from Eagle and 37 miles from Vail. It covers 632 acres (256 ha) and has one runway. The History Channel rated Eagle County Regional Airport as #8 on its list of Most Extreme Airports in July 2010 due to the elevation, weather, approach through mountainous terrain and challenging departure procedures. In 2008–09 the airport completed a runway repaving and extension project, increasing the runway length to 9,000 feet.
Airspace is the portion of the atmosphere controlled by a country above its territory, including its territorial waters or, more generally, any specific three-dimensional portion of the atmosphere. It is not the same as outer space which is the expanse or space outside the Earth and aerospace which is the general term for Earth's atmosphere and the outer space within the planet's vicinity. History:

A fixed-base operator (FBO) is an organization granted the right by an airport to operate at the airport and provide aeronautical services such as fueling, hangaring, tie-down and parking, aircraft rental, aircraft maintenance, flight instruction, and similar services. In common practice, an FBO is the primary provider of support services to general aviation operators at a public-use airport and is on land leased from the airport, or, in rare cases, adjacent property as a "through the fence operation". In many smaller airports serving general aviation in remote or modest communities, the town itself may provide fuel services and operate a basic FBO facility. Most FBOs doing business at airports of high to moderate traffic volume are non-governmental organizations, either privately or publicly held companies.

Centennial Airport is a public use airport owned by the Arapahoe County Public Airport Authority in the Denver-Aurora metropolitan area, 15 nautical miles southeast of downtown Denver, Colorado, United States. Located in Dove Valley, a census designated place in Arapahoe County, the airport's runways extend into Douglas County.
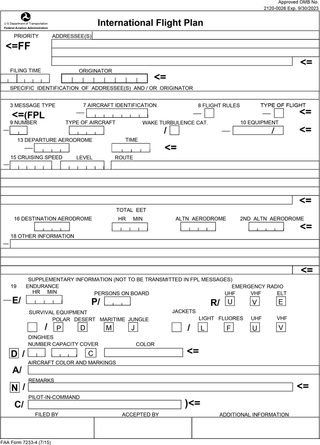
Flight plans are documents filed by a pilot or flight dispatcher with the local Air Navigation Service Provider prior to departure which indicate the plane's planned route or flight path. Flight plan format is specified in ICAO Doc 4444. They generally include basic information such as departure and arrival points, estimated time en route, alternate airports in case of bad weather, type of flight, the pilot's information, number of people on board, and information about the aircraft itself. In most countries, flight plans are required for flights under IFR, but may be optional for flying VFR unless crossing international borders. Flight plans are highly recommended, especially when flying over inhospitable areas such as water, as they provide a way of alerting rescuers if the flight is overdue. In the United States and Canada, when an aircraft is crossing the Air Defense Identification Zone (ADIZ), either an IFR or a special type of VFR flight plan called a DVFR flight plan must be filed. For IFR flights, flight plans are used by air traffic control to initiate tracking and routing services. For VFR flights, their only purpose is to provide needed information should search and rescue operations be required, or for use by air traffic control when flying in a "Special Flight Rules Area."

Patrick Leahy Burlington International Airport is a joint-use civil-military airport serving Burlington, Vermont's most populous city, and surrounding areas. Owned by the City of Burlington, the airport itself is located in neighboring South Burlington, just three nautical miles (6 km) east of Burlington's central business district.
An instrument rating is an authorization required for a pilot to fly under instrument flight rules (IFR). In the United States, the rating is issued by the Federal Aviation Administration.

A flight service station (FSS) is an air traffic facility that provides information and services to aircraft pilots before, during, and after flights, but unlike air traffic control (ATC), is not responsible for giving instructions or clearances or providing separation. They do, however, relay clearances from ATC for departure or approaches. The people who communicate with pilots from an FSS are referred to as flight service specialists.
Taunton Municipal Airport, also known as King Field, is a public use airport located three nautical miles (6 km) east of the central business district of Taunton, a city in Bristol County, Massachusetts. It is located in the East Taunton neighborhood of the city. The city-owned airport is maintained and operated by the Taunton Airport Commission. According to the FAA's National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2009–2013, it is categorized as a general aviation airport.

FlightAware is an American multi-national technology company that provides real-time, historical, and predictive flight tracking data and products. As of 2019, it is the world's largest flight tracking platform, with a network of over 32,000 ADS-B ground stations in 200 countries. FlightAware also provides aviation data and predicted ETAs to airlines, airport operators, and software developers. FlightAware is a subsidiary of Collins Aerospace, with headquarters in Eleven Greenway Plaza in Houston and sales offices in New York City, Austin, Singapore, and London.
In aviation, a standard terminal arrival (STAR) is a published flight procedure followed by aircraft on an instrument flight rules (IFR) flight plan just before reaching a destination airport.
The Capstone Program was a United States government-funded aviation safety program for the state of Alaska, primarily focusing on rural areas of the state. This joint effort – between the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), the Alaska Pilot's Association, commercial operators, the University of Alaska, MITRE Corporation, some avionics manufacturers and individual pilots – cut the accident rate in the eastern part of Alaska by around 40%.
Destin Executive Airport, also known as Coleman Kelly Field, is a public use airport owned by and located in Okaloosa County, Florida. The airport is one nautical mile (2 km) east of the central business district of Destin, Florida. It is included in the National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2021–2025, which categorized it as a general aviation facility.
The Next Generation Air Transportation System (NextGen) is an ongoing United States Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) project to modernize the National Airspace System (NAS). The FAA began work on NextGen improvements in 2007 and plans to finish the final implementation segment by 2030. The goals of the modernization include using new technologies and procedures to increase the safety, efficiency, capacity, access, flexibility, predictability, and resilience of the NAS while reducing the environmental impact of aviation.

Automatic Dependent Surveillance–Broadcast (ADS-B) is an aviation surveillance technology and form of Electronic Conspicuity in which an aircraft determines its position via satellite navigation or other sensors and periodically broadcasts its position and other related data, enabling it to be tracked. The information can be received by air traffic control ground-based or satellite-based receivers as a replacement for secondary surveillance radar (SSR). Unlike SSR ADS-B does not require an interrogation signal from the ground or other aircraft to activate its transmissions. ADS-B can also received point-to-point by other nearby equipped "ADS-B In" equipped aircraft to provide traffic situational awareness and support self-separation. ADS-B is "automatic" in that it requires no pilot or external input to trigger its transmissions. It is "dependent" in that it depends on data from the aircraft's navigation system to provide the transmitted data.

The 1971 Colorado Aviation Aero Commander 680 crash claimed the life of decorated American World War II veteran Audie Murphy and five other people on May 28, 1971. The aircraft's passengers were on a business trip from Atlanta, Georgia, to Martinsville, Virginia, aboard an Aero Commander 680 Super twin-engined aircraft owned and operated by Colorado Aviation Co, Inc. The aircraft crashed into the side of Brush Mountain, 14 nautical miles northwest of Roanoke, Virginia, during conditions of poor visibility.












