
Santa Cruz is a county in southern Arizona, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population is 47,669. The county seat is Nogales. The county was established in 1899. It borders Pima County to the north and west, Cochise County to the east, and the Mexican state of Sonora to the south.

Sahuarita is a town in Pima County, Arizona, United States. Sahuarita is located south of the Tohono O'odham Nation and abuts the north end of Green Valley, 15 miles (24 km) south of Tucson. The 2022 population estimate was 35,638.

Elgin is a census-designated place (CDP) in Santa Cruz County, Arizona, United States. The population was 161 at the 2010 census.

Patagonia is a town in Santa Cruz County, Arizona, United States. As of the 2010 census it had a population of 913. It developed in the mid-19th century as a trading and supply center for nearby mines and ranches. In the 21st century, it is a tourist destination, retirement community, and arts and crafts center.

Sonoita is a census-designated place (CDP) in Santa Cruz County, Arizona, United States. The population was 803 at the 2020 census.
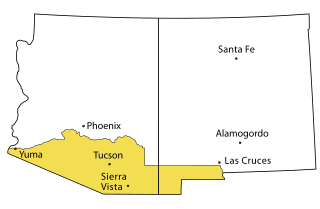
The Gadsden Purchase is a 29,640-square-mile (76,800 km2) region of present-day southern Arizona and southwestern New Mexico that the United States acquired from Mexico by the Treaty of Mesilla, which took effect on June 8, 1854. The purchase included lands south of the Gila River and west of the Rio Grande where the U.S. wanted to build a transcontinental railroad along a deep southern route, which the Southern Pacific Railroad later completed in 1881–1883. The purchase also aimed to resolve other border issues.

Fort Buchanan was a US Army post founded in 1856 three miles southwest of present-day Sonoita in Santa Cruz County, Arizona, on the east slope of what is now called Hog Canyon. At the time, the area was under constant threat from hostile Apaches. Full-scale war with the local Chiricahua Apache was initiated by the Bascom affair in early 1861, during which Lieutenant George Nicholas Bascom and his patrol were based at Fort Buchanan.

Thomas Leonidas Crittenden was an American statesman, politician, soldier and lawyer from the U.S. state of Kentucky. He served as a general for the Union during the Civil War. His family was fairly typical for Kentucky, in that he and his father supported the Union during the war, but his elder brother fought for the Confederacy.

The Fort Apache Indian Reservation is an Indian reservation in Arizona, United States, encompassing parts of Navajo, Gila, and Apache counties. It is home to the federally recognized White Mountain Apache Tribe of the Fort Apache Reservation, a Western Apache tribe. It has a land area of 1.6 million acres and a population of 12,429 people as of the 2000 census. The largest community is in Whiteriver.

Mission San Cayetano de Calabazas, also known as Calabasas, is a Spanish Mission in the Sonoran Desert, located near present-day Tumacacori, Arizona, United States.
Hereford is a populated place in Cochise County along the San Pedro Riparian National Conservation Area in the southern part of the U.S. state of Arizona. It is southeast of Sierra Vista and is a part of the Sierra Vista-Douglas micropolitan area. The elevation is 4,193 feet at the location of the original townsite at the far eastern end of the unincorporated area; the residential area runs for another 8 miles west from this location, blending into the unincorporated area of Nicksville at an elevation of approximately 4800 feet. Hereford Station Post Office is located at the far western end of Nicksville, at the foot of the Huachuca Mountains.
District of Arizona was a subordinate district of the Department of New Mexico territory created on August 30, 1862 and transferred to the Department of the Pacific in March 1865.

The Canelo Hills are a range of low mountains or hills in eastern Santa Cruz County, Arizona. The range consists of a series of northwest–southeast trending ridges extending from the Sonoita Creek valley southwest of Sonoita to the Parker Canyon Lake area in southwest Cochise County, Arizona. The Canelo Hills merge with the Huachuca Mountains to the southeast. The San Rafael Valley lies to the southwest of the range and the Patagonia Mountains lie to the west across the Harshaw Creek valley. The Canelo Hills Cienega Reserve and the ghost town of Canelo, Arizona, are located on the eastern side of the hills.
The Presidio de Calabasas, also known as Fort Calabasas or Camp Calabasas, was a stone fortress built by Mexico in 1837 south of Tumacacori, Arizona. It was built on the land of the Grant of Manuel María Gándara, by Gándara to protect his lands near the Mission San Cayetano de Calabazas from the Apache. Civilians established a small farming settlement called Calabasas, in the area nearby the protection of the Presidio.

The Battle of Fort Buchanan was an Apache attack on the United States Army post of Old Fort Buchanan in southern Arizona Territory, which occurred on February 17, 1865. Though a skirmish, it ended with a significant Apache victory when they forced the small garrison of California Volunteers to retreat to the Santa Rita Mountains. Fort Buchanan was the only American military post conquered during the war against the Chiricahua.
Camp Cameron was a temporary U. S. Army camp located in Madera Canyon in Arizona Territory between 1866 and 1867.

Calabasas is a former populated place or ghost town, within the census-designated place of Rio Rico, a suburb of Nogales in Santa Cruz County, Arizona, United States.
The Willcox AVA is an American Viticultural Area located in southeastern Arizona, centered around the city of Willcox where it is bisected by Interstate 10. Approximately 85% of wine grapes from Arizona are grown within the AVA boundaries. The AVA consists mostly of flat terrain at over 4,000 feet in elevation, including the Aravaipa Valley and much of Sulphur Springs Valley. It is bounded by the Chiricahua Mountains and Dos Cabezas Mountains to the east, the Pinaleño Mountains to the northeast, and the Dragoon Mountains to the west. Sixty miles (97 km) to the southwest is the Sonoita AVA, and the Mimbres Valley AVA is 120 miles (190 km) to the east in New Mexico. The AVA is one of the three major centers of viticulture in Arizona, along with Sonoita and the Verde Valley in central Arizona. Just east of the AVA are Fort Bowie National Historic Site, Chiricahua National Monument, and Coronado National Forest.












