
Clarke County is a county located in the southwestern part of the U.S. state of Alabama. As of the 2020 census, the population was 23,087. The county seat is Grove Hill. The county's largest city is Jackson. The county was created by the legislature of the Mississippi Territory in 1812. It is named in honor of General John Clarke of Georgia, who was later elected governor of that state.

Fort Stoddert, also known as Fort Stoddard, was a stockade fort in the U.S. Mississippi Territory, in what is today Alabama. It was located on a bluff of the Mobile River, near modern Mount Vernon, close to the confluence of the Tombigbee and Alabama Rivers. It served as the western terminus of the Federal Road which ran through Creek lands to Fort Wilkinson in Georgia. The fort, built in 1799, was named for Benjamin Stoddert, the secretary to the Continental Board of War during the American Revolution and Secretary of the Navy during the Quasi War. Fort Stoddert was built by the United States to keep the peace by preventing its own settlers in the Tombigbee District from attacking the Spanish in the Mobile District. It also served as a port of entry and was the site of a Court of Admiralty. While under the command of Captain Edmund P. Gaines, Aaron Burr was held as a prisoner at the fort after his arrest at McIntosh in 1807 for treason against the United States. In July 1813, General Ferdinand Claiborne brought the Mississippi Militia to Fort Stoddert as part of the Creek War. The 3rd Infantry Regiment was commanded by General Thomas Flournoy to Fort Stoddert following the Fort Mims massacre. The site declined rapidly in importance after the capture of Mobile by the United States in 1813 and the establishment of the Mount Vernon Arsenal in 1828.

Fort Williams was a supply depot built in early 1814 in preparation for the Battle of Horseshoe Bend. It was located in Alabama on the southeast shore where Cedar Creek meets the Coosa River, near Talladega Springs.

The Alston–Cobb House, now formally known as the Clarke County Historical Museum, is a historic house and local history museum in Grove Hill, Alabama. It was built in 1854 by Dr. Lemuel Lovett Alston as a Greek Revival I-house, a vernacular style also known in the South as Plantation Plain. It is one of only four examples of an I-house to survive intact in Clarke County. The Alston–Cobb House was added to the Alabama Register of Landmarks and Heritage on September 1, 1978, and to the National Register of Historic Places on April 30, 1979.

Fort Sinquefield is the historic site of a wooden stockade fortification in Clarke County, Alabama, near the modern town of Grove Hill. It was built by early Clarke County pioneers as protection during the Creek War and was attacked in 1813 by Creek warriors.

Fort Strother was a stockade fort at Ten Islands in the Mississippi Territory, in what is today St. Clair County, Alabama. It was located on a bluff of the Coosa River, near the modern Neely Henry Dam in Ragland, Alabama. The fort was built by General Andrew Jackson and several thousand militiamen in November 1813, during the Creek War and was named for Captain John Strother, Jackson's chief cartographer.

The Canoe Fight was a skirmish between Mississippi Territory militiamen led by Captain Samuel Dale and Red Stick warriors that took place on November 12, 1813 as part of the Creek War. The skirmish was fought largely from canoes and was a victory for the militiamen, who only had one member wounded. The victory held little military value in the overall Creek War but its participants gained widespread notoriety for their actions during the fight. The fight has been depicted in multiple illustrations, but only a historical marker currently exists near the site of the fight.

Fort Claiborne was a stockade fort built in 1813 in present-day Monroe County, Alabama during the Creek War.

Suggsville is an unincorporated community in Clarke County, Alabama.
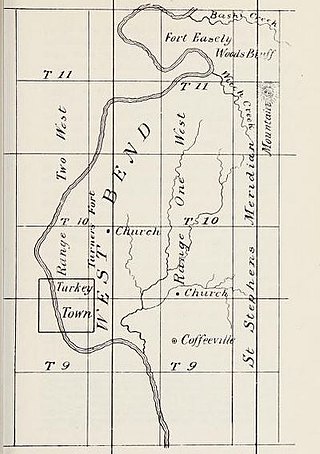
The Bashi Skirmish in the Creek War was fought in what became Failetown, Alabama. A Clarke County historical marker which stands on Woods Bluff Road between Alabama 69 and Cassidy Hill marks the location of the incident which resulted in the death of 4 Americans.
Ferdinand Leigh Claiborne was an American military officer most notable for his command of the militia of the Mississippi Territory during the Creek War and the War of 1812.
Fort Bibb was a stockade fort built in present-day Butler County, Alabama during the First Seminole War.
Fort Carney was a stockade fort built in 1813 in present-day Clarke County, Alabama during the Creek War.

Fort Dale was a stockade fort built in present-day Butler County, Alabama by Alabama Territory settlers. The fort was constructed in response to Creek Indian attacks on settlers in the surrounding area.

Fort Easley was a stockade fort built in 1813 in present-day Clarke County, Alabama during the Creek War.

Fort Glass was a stockade fort built in July 1813 in present-day Clarke County, Alabama during the Creek War.

Fort Hampton was a collection of log buildings and stables built in present-day Limestone County, Alabama, on a hill near the Elk River. It was named for Brigadier General Wade Hampton by Alexander Smyth, and once complete in the winter of 1810 both men visited the site. The fort was originally built to deter Americans from settling in Chickasaw territory, then was garrisoned during the War of 1812. Later, it was used for United States governmental functions prior to being abandoned.

Fort Hull was an earthen fort built in present-day Macon County, Alabama in 1814 during the Creek War. After the start of hostilities, the United States decided to mount an attack on Creek territory from three directions. The column advancing west from Georgia built Fort Mitchell and then clashed with the Creeks. After a pause in operations, the column from Georgia continued its march and built Fort Hull. The fort was used as a supply point and was soon abandoned after the end of the Creek War.

Fort Madison was a stockade fort built in August 1813 in present-day Clarke County, Alabama, during the Creek War, which was part of the larger War of 1812. The fort was built by the United States military in response to attacks by Creek warriors on encroaching American settlers. The fort shared many similarities to surrounding stockade forts in its construction but possessed a number of differences in its defenses. The fort housed members of the United States Army and settlers from the surrounding area, and it was used as a staging area for raids on Creek forces and supply point on further military expeditions. Fort Madison was subsequently abandoned at the conclusion of the Creek War and only a historical marker exists at the site today.

Turner's Fort, also known as Fort Turner, was a stockade fort built in 1813 in present-day Clarke County, Alabama during the Creek War. Turner's Fort, like many other forts built around the same time, was built in response to Red Stick attacks on settlers in the surrounding area.















