
Fort Adams is a former United States Army post in Newport, Rhode Island that was established on July 4, 1799 as a First System coastal fortification, named for President John Adams who was in office at the time. Its first commander was Captain John Henry who was later instrumental in starting the War of 1812. The current Fort Adams was built 1824–57 under the Third System of coastal forts; it is part of Fort Adams State Park today.

Fort Hancock is a former United States Army fort at Sandy Hook in Atlantic Highlands New Jersey. The coastal artillery base defended the Atlantic coast and the entrance to New York Harbor, with its first gun batteries operational in 1896. The fort served from then until 1950 as part of the Harbor Defenses of New York and predecessor organizations. Between 1874 and 1919, the adjacent US Army Sandy Hook Proving Ground was operated in conjunction with Fort Hancock. It is now part of Fort Hancock Memorial Park. It was preceded by the Fort at Sandy Hook, built 1857–1867 and demolished beginning in 1885.

Several boards have been appointed by US presidents or Congress to evaluate the US defensive fortifications, primarily coastal defenses near strategically important harbors on the US shores, its territories, and its protectorates.

The 16 inch gun M1919 (406 mm) was a large coastal artillery piece installed to defend the United States' major seaports between 1920 and 1946. It was operated by the United States Army Coast Artillery Corps. Only a small number were produced and only seven were mounted; in 1922 and 1940 the US Navy surplussed a number of their own 16-inch/50 guns, which were mated to modified M1919 carriages and filled the need for additional weapons.

Fort H. G. Wright was a United States military installation on Fishers Island in the town of Southold, New York, just two miles off the coast of southeastern Connecticut, but technically in New York. It was part of the Harbor Defenses of Long Island Sound, along with Fort Terry, Fort Michie, and Camp Hero. These forts defended the eastern entrance of Long Island Sound and thus Connecticut's ports and the north shore of Long Island. The fort was named for Union General Horatio G. Wright, a former Chief of Engineers who was born in Clinton, Connecticut.

Seacoast defense was a major concern for the United States from its independence until World War II. Before airplanes, many of America's enemies could only reach it from the sea, making coastal forts an economical alternative to standing armies or a large navy. After the 1940s, it was recognized that fixed fortifications were obsolete and ineffective against aircraft and missiles. However, in prior eras foreign fleets were a realistic threat, and substantial fortifications were built at key locations, especially protecting major harbors.
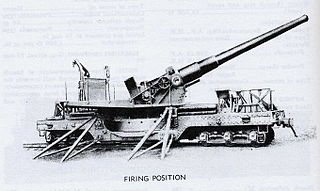
The 8-inch Navy gun Mk.VI M3A2 on railway mount M1A1 was a World War II improved replacement for the World War I-era 8-inch M1888 gun and was used by the US Army's Coast Artillery Corps in US harbor defenses. The guns were also mounted in fixed emplacements on the barbette carriage M1A1. These guns were US Navy surplus 8"/45 caliber guns from battleships scrapped under the 1922 Washington Naval Treaty. Mark VI was the Navy designation. The Army designation for this gun was "8-inch Navy gun Mk.VI M3A2".

The 8-inch gun M1888 (203 mm) was a U.S. Army Coast Artillery Corps gun, initially deployed 1898–1908 in about 75 fixed emplacements, usually on a disappearing carriage. During World War I, 37 or 47 of these weapons were removed from fixed emplacements or from storage to create a railway gun version, the 8-inch Gun M1888MIA1 Barbette carriage M1918 on railway car M1918MI, converted from the fixed coast defense mountings and used during World War I and World War II.

The 12-inch coastal defense gun M1895 (305 mm) and its variants the M1888 and M1900 were large coastal artillery pieces installed to defend major American seaports between 1895 and 1945. For most of their history they were operated by the United States Army Coast Artillery Corps. Most were installed on disappearing carriages, with early installations on low-angle barbette mountings. From 1919, 19 long-range two-gun batteries were built using the M1895 on an M1917 long-range barbette carriage. Almost all of the weapons not in the Philippines were scrapped during and after World War II.

Fort Williams is a former United States Army fort in Cape Elizabeth, Maine which operated from 1872 to 1964. It was part of the Coast Defenses of Portland, later renamed the Harbor Defenses of Portland, a command which protected Portland's port and naval anchorage 1904–1950. After its closure, it was redeveloped into Fort Williams Park.

Fort Revere is an 8-acre (3.2 ha) historic site situated on a small peninsula located in Hull, Massachusetts. It is situated on Telegraph Hill in Hull Village and contains the remains of two seacoast fortifications, one from the American Revolution and one that served 1898–1947. There are also a water tower with an observation deck, a military history museum and picnic facilities. It is operated as Fort Revere Park by the Metropolitan Park System of Greater Boston.

The 3-inch gun M1903 and its predecessors the M1898 and M1902 were rapid fire breech-loading artillery guns with a 360-degree traverse. In some references they are called "15-pounders" due to their projectile weight. They were originally emplaced from 1899 to 1917 and served until shortly after World War II. These 3-inch guns were placed to provide fire to protect underwater mines and nets against minesweepers, and also to protect against motor torpedo boats. In some documentation they are called "mine defense guns". The 3-inch guns were mounted on pedestal mounts that bolted into a concrete emplacement that provided cover and safety for the gun's crew.

Fort Stark is a former military fortification in New Castle, New Hampshire, United States. Located at Jerry's Point on the southeastern tip of New Castle Island, most of the surviving fort was developed in the early 20th century, following the Spanish–American War, although there were several earlier fortifications on the site, portions of which survive. The fort was named for John Stark, a New Hampshire officer who distinguished himself at the Battle of Bennington in the American Revolution. The purpose of Fort Stark was to defend the harbor of nearby Portsmouth and the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard. The fort remained in active use through the Second World War, after which it was used for reserve training by the US Navy. The property was partially turned over to the state of New Hampshire in 1979, which established Fort Stark Historic Site, and the remainder of the property was turned over in 1983. The grounds are open to the public during daylight hours.

The 10-inch Gun M1895 (254 mm) and its variants the M1888 and M1900 were large coastal artillery pieces installed to defend major American seaports between 1895 and 1945. For most of their history they were operated by the United States Army Coast Artillery Corps. Most were installed on disappearing carriages, with early installations on barbette mountings. All of the weapons not in the Philippines were scrapped during World War II. Two of the surviving weapons were relocated from the Philippines to Fort Casey in Washington state in the 1960s.

The 14-inch Gun M1907 (356 mm) and its variants the M1907MI, M1909, and M1910 were large coastal artillery pieces installed to defend major American seaports between 1895 and 1945. They were operated by the United States Army Coast Artillery Corps. Most were installed on single gun disappearing carriages; the only installation with four guns in twin turrets was built at the unique Fort Drum in Manila Bay, Philippines. All of the weapons not in the Philippines were scrapped during World War II.

The 6-inch gun M1897 (152 mm) and its variants the M1900, M1903, M1905, M1908, and M1 were coastal artillery pieces installed to defend major American seaports between 1897 and 1945. For most of their history they were operated by the United States Army Coast Artillery Corps. They were installed on disappearing carriages or pedestal mountings, and during World War II many were remounted on shielded barbette carriages. Most of the weapons not in the Philippines were scrapped within a few years after World War II.

The 5-inch gun M1897 (127 mm) and its variant the M1900 were coastal artillery pieces installed to defend major American seaports between 1897 and 1920. For most of their history they were operated by the United States Army Coast Artillery Corps. They were installed on balanced pillar or pedestal mountings; generally the M1897 was on the balanced pillar mounting and the M1900 was on the pedestal mounting. All of these weapons were scrapped within a few years after World War I.

The 16-inch howitzer M1920 (406 mm) was a coastal artillery piece installed to defend major American seaports between 1922 and 1947. They were operated by the United States Army Coast Artillery Corps. They were installed on high-angle barbette mountings to allow plunging fire. Only four of these weapons were deployed, all at Fort Story, Virginia. All were scrapped within a few years after World War II.

The Harbor Defenses of Long Island Sound was a United States Army Coast Artillery Corps harbor defense command. It coordinated the coast defenses of Long Island Sound and Connecticut from 1895 to 1950, beginning with the Endicott program. These included both coast artillery forts and underwater minefields. The area defended included the approach via the Sound to New York City, the port cities and manufacturing centers of New London, New Haven, and Bridgeport, and eventually included the submarine base and shipyard in Groton. The command originated circa 1900 as an Artillery District, was renamed Coast Defenses of Long Island Sound in 1913, and again renamed Harbor Defenses of Long Island Sound in 1925.




















