Related Research Articles

Ophthalmology is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders.

Near-sightedness, also known as myopia and short-sightedness, is an eye disease where light focuses in front of, instead of on, the retina. As a result, distant objects appear blurry while close objects appear normal. Other symptoms may include headaches and eye strain. Severe near-sightedness is associated with an increased risk of retinal detachment, cataracts, and glaucoma.

A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and difficulty seeing at night. This may result in trouble driving, reading, or recognizing faces. Poor vision caused by cataracts may also result in an increased risk of falling and depression. Cataracts cause 51% of all cases of blindness and 33% of visual impairment worldwide.

Chorioretinitis is an inflammation of the choroid and retina of the eye. It is a form of posterior uveitis. If only the choroid is inflamed, not the retina, the condition is termed choroiditis. The ophthalmologist's goal in treating these potentially blinding conditions is to eliminate the inflammation and minimize the potential risk of therapy to the patient.

Peripheral vision, or indirect vision, is vision as it occurs outside the point of fixation, i.e. away from the center of gaze or, when viewed at large angles, in the "corner of one's eye". The vast majority of the area in the visual field is included in the notion of peripheral vision. "Far peripheral" vision refers to the area at the edges of the visual field, "mid-peripheral" vision refers to medium eccentricities, and "near-peripheral", sometimes referred to as "para-central" vision, exists adjacent to the center of gaze.

The Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung is a German newspaper founded in 1949. It is published daily in Frankfurt. Its Sunday edition is the Frankfurter Allgemeine Sonntagszeitung.
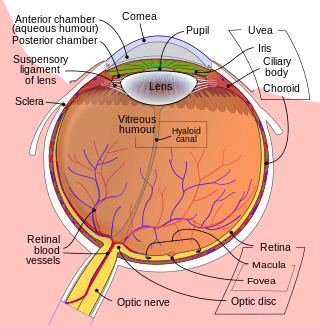
The fovea centralis is a small, central pit composed of closely packed cones in the eye. It is located in the center of the macula lutea of the retina.

The human eye is a sensory organ, part of the sensory nervous system, that reacts to visible light and allows humans to use visual information for various purposes including seeing things, keeping balance, and maintaining circadian rhythm.

Ophthalmology was one of the foremost branches in medieval Islamic medicine. The oculist or kahhal (کحال), a somewhat despised professional in Galen’s time, was an honored member of the medical profession by the Abbasid period, occupying a unique place in royal households. Medieval Islamic scientists considered it normal to combine theory and practice, including the crafting of precise instruments, and therefore found it natural to combine the study of the eye with the practical application of that knowledge. The specialized instruments used in their operations ran into scores. Innovations such as the “injection syringe”, a hollow needle, invented by Ammar ibn Ali of Mosul, which was used for the extraction by suction of soft cataracts, were quite common.

Govindappa Venkataswamy, popularly known as Dr V., was an Indian ophthalmologist who dedicated his life to eliminate needless blindness. He was the founder and former chairman of Aravind Eye Hospitals. He is best known for developing a high quality, high volume, low-cost service delivery model that has restored sight to millions of people. Since inception, Aravind Eye Care System has seen over 55 million patients, and performed over 6.8 million surgeries. Over 50% of the organisation's patients pay either nothing or highly subsidised rates. Its scale and self-sustainability prompted a 1993 Harvard Business Case Study on the Aravind model.
The Egmore Eye Hospital, officially the Regional Institute of Ophthalmology and Government Ophthalmic Hospital, is a public eye hospital in Chennai, India. Considered the oldest eye hospital in Asia, the institute was established in 1819 and is the second oldest hospital of its kind, next only to the Moorfields Eye Hospital in the United Kingdom.
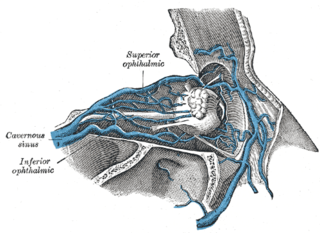
The central retinal vein is a vein that drains the retina of the eye. It travels backwards through the centre of the optic nerve accompanied by the central retinal artery before exiting the optic nerve together with the central retinal artery to drain into either the superior ophthalmic vein or the cavernous sinus.


Orbital lymphoma is a common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that occurs near or on the eye. Common symptoms include decreased vision and uveitis. Orbital lymphoma can be diagnosed via a biopsy of the eye and is usually treated with radiotherapy or in combination with chemotherapy.
Cyclotropia is a form of strabismus in which, compared to the correct positioning of the eyes, there is a torsion of one eye about the eye's visual axis. Consequently, the visual fields of the two eyes appear tilted relative to each other. The corresponding latent condition – a condition in which torsion occurs only in the absence of appropriate visual stimuli – is called cyclophoria.

Perifovea is a region in the retina that circumscribes the parafovea and fovea and is a part of the macula lutea. The perifovea is a belt that covers a 10° radius around the fovea and is 1.5 mm wide. The perifovea ends when the Henle's fiber layer disappears and the ganglion cells are one-layered.

Yog Raj Sharma is an Indian ophthalmologist and ex-chief of Dr. Rajendra Prasad Centre for Ophthalmic Sciences of the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi, the apex body of the National Programme for the Control of Blindness, a Government of India initiative to reduce the prevalence of blindness in India. He is the Chairman of the Task Force on Prevention and Control of Diabetic Retinopathy Group and the Co-Chairman of the National Task Force on Prevention of Blindness from Retinopathy of Prematurity under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare of the Government of India. An advisor to the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, India. Sharma was honored by the Government of India in 2015 with Padma Shri, the fourth highest Indian civilian award. In 2005, Yog Raj Sharma's published article on "Pars plana vitrectomy vs scleral buckling in rhegmatogenous retinal detachment" in Acta Ophthalmologica Scandinavica and in November 2021, American society of retina specialists cited it as top 100 publications on retinal detachment management in the last ~121 years. Of these top hundred publications, only nineteen countries contributed, three of the contributing countries were Asian and from India this study was the sole contribution. Dr Sharma called it 'the singular biggest achievement of his career" in an article published in Daily Excelsior, Jammu in December 2021.
Mahipal S. Sachdev is an Indian ophthalmologist and the Chairman of Centre for Sight, a chain of Eye Hospitals in India. He is known as one of the pioneers of Phacoemulsification procedure in India. He is the co-author of A Practical Guide to Phacoemulsification, the first Indian book on the topic. The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian honour of the Padma Shri, in 2007, for his contributions to Indian medicine. He is the Chairman Scientific Committee of the Intraocular Implant and Refractive Society of India, IIRSI.

Atul Kumar is an Indian ophthalmologist who is currently the Chief & Professor of Ophthalmology at Dr. Rajendra Prasad Centre for Ophthalmic Sciences (RPC-AIIMS), the national apex ophthalmic centre at All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Delhi. He was awarded the Padma Shri award in January 2007 for his services to the medical field. He specializes in vitreoretinal surgery and also heads the Vitreo-Retinal, Uvea and ROP services at RPC-AIIMS.

The Singapore National Eye Centre (SNEC) is a national eye specialty centre in Singapore.