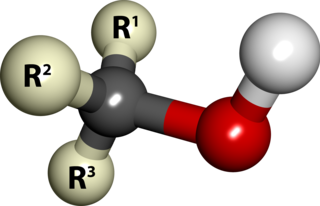
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sugar alcohols and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of hydrocarbons, conferring hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur.

In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as R−COOH or R−CO2H, sometimes as R−C(O)OH with R referring to an organyl group, or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion.

In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure R−C(=O)−R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group −C(=O)−. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula (CH3)2CO. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.

In organic chemistry, an aldehyde is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure R−CH=O. The functional group itself can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are a common motif in many chemicals important in technology and biology.

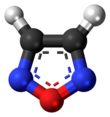
Acridine is an organic compound and a nitrogen heterocycle with the formula C13H9N. Acridines are substituted derivatives of the parent ring. It is a planar molecule that is structurally related to anthracene with one of the central CH groups replaced by nitrogen. Like the related molecules pyridine and quinoline, acridine is mildly basic. It is an almost colorless solid, which crystallizes in needles. There are few commercial applications of acridines; at one time acridine dyes were popular, but they are now relegated to niche applications, such as with acridine orange. The name is a reference to the acrid odour and acrid skin-irritating effect of the compound.

Manganese dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula MnO
2. This blackish or brown solid occurs naturally as the mineral pyrolusite, which is the main ore of manganese and a component of manganese nodules. The principal use for MnO
2 is for dry-cell batteries, such as the alkaline battery and the zinc–carbon battery. MnO
2 is also used as a pigment and as a precursor to other manganese compounds, such as KMnO
4. It is used as a reagent in organic synthesis, for example, for the oxidation of allylic alcohols. MnO
2 has an α-polymorph that can incorporate a variety of atoms in the "tunnels" or "channels" between the manganese oxide octahedra. There is considerable interest in α-MnO
2 as a possible cathode for lithium-ion batteries.

In organic chemistry, an oxime is an organic compound belonging to the imines, with the general formula RR’C=N−OH, where R is an organic side-chain and R' may be hydrogen, forming an aldoxime, or another organic group, forming a ketoxime. O-substituted oximes form a closely related family of compounds. Amidoximes are oximes of amides with general structure R1C(=NOH)NR2R3.

Phthalic anhydride is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2O. It is the anhydride of phthalic acid. Phthalic anhydride is a principal commercial form of phthalic acid. It was the first anhydride of a dicarboxylic acid to be used commercially. This white solid is an important industrial chemical, especially for the large-scale production of plasticizers for plastics. In 2000, the worldwide production volume was estimated to be about 3 million tonnes per year.
Thiophene is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4S. Consisting of a planar five-membered ring, it is aromatic as indicated by its extensive substitution reactions. It is a colorless liquid with a benzene-like odor. In most of its reactions, it resembles benzene. Compounds analogous to thiophene include furan (C4H4O), selenophene (C4H4Se) and pyrrole (C4H4NH), which each vary by the heteroatom in the ring.
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups. An aliphatic diol is also called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified. They are used as protecting groups of carbonyl groups, making them essential in synthesis of organic chemistry.
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.
In organic chemistry, a nitrile is any organic compound that has a −C≡N functional group. The name of the compound is composed of a base, which includes the carbon of the −C≡N, suffixed with "nitrile", so for example CH3CH2C≡N is called "propionitrile". The prefix cyano- is used interchangeably with the term nitrile in industrial literature. Nitriles are found in many useful compounds, including methyl cyanoacrylate, used in super glue, and nitrile rubber, a nitrile-containing polymer used in latex-free laboratory and medical gloves. Nitrile rubber is also widely used as automotive and other seals since it is resistant to fuels and oils. Organic compounds containing multiple nitrile groups are known as cyanocarbons.
Cyclohexene is a hydrocarbon with the formula (CH2)4C2H2. It is an example of a cycloalkene. At room temperature, cyclohexene a colorless liquid with a sharp odor. It has few practical applications.

Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) is a yellow-orange salt with the formula [C5H5NH]+[CrO3Cl]−. It is a reagent in organic synthesis used primarily for oxidation of alcohols to form carbonyls. A variety of related compounds are known with similar reactivity. PCC offers the advantage of the selective oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes or ketones, whereas many other reagents are less selective.

Periodate is an anion composed of iodine and oxygen. It is one of a number of oxyanions of iodine and is the highest in the series, with iodine existing in oxidation state +7. Unlike other perhalogenates, such as perchlorate, it can exist in two forms: metaperiodateIO−
4 and orthoperiodateIO5−
6. In this regard it is comparable to the tellurate ion from the adjacent group. It can combine with a number of counter ions to form periodates, which may also be regarded as the salts of periodic acid.

1,4-Benzoquinone, commonly known as para-quinone, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H4O2. In a pure state, it forms bright-yellow crystals with a characteristic irritating odor, resembling that of chlorine, bleach, and hot plastic or formaldehyde. This six-membered ring compound is the oxidized derivative of 1,4-hydroquinone. The molecule is multifunctional: it exhibits properties of a ketone, being able to form oximes; an oxidant, forming the dihydroxy derivative; and an alkene, undergoing addition reactions, especially those typical for α,β-unsaturated ketones. 1,4-Benzoquinone is sensitive toward both strong mineral acids and alkali, which cause condensation and decomposition of the compound.

Sulfolene, or butadiene sulfone is a cyclic organic chemical with a sulfone functional group. It is a white, odorless, crystalline, indefinitely storable solid, which dissolves in water and many organic solvents. The compound is used as a source of butadiene.
In organic chemistry, a homologation reaction, also known as homologization, is any chemical reaction that converts the reactant into the next member of the homologous series. A homologous series is a group of compounds that differ by a constant unit, generally a methylene group. The reactants undergo a homologation when the number of a repeated structural unit in the molecules is increased. The most common homologation reactions increase the number of methylene units in saturated chain within the molecule. For example, the reaction of aldehydes or ketones with diazomethane or methoxymethylenetriphenylphosphine to give the next homologue in the series.
In chemistry, decarbonylation is a type of organic reaction that involves the loss of carbon monoxide (CO). It is often an undesirable reaction, since it represents a degradation. In the chemistry of metal carbonyls, decarbonylation describes a substitution process, whereby a CO ligand is replaced by another ligand.

Hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid (HOSA) or aminosulfuric acid is the inorganic compound with molecular formula H3NO4S that is formed by the sulfonation of hydroxylamine with oleum. It is a white, water-soluble and hygroscopic, solid, commonly represented by the condensed structural formula H2NOSO3H, though it actually exists as a zwitterion and thus is more accurately represented as +H3NOSO3−. It is used as a reagent for the introduction of amine groups (–NH2), for the conversion of aldehydes into nitriles and alicyclic ketones into lactams (cyclic amides), and for the synthesis of variety of nitrogen-containing heterocycles.