
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery to end users or its storage, using for example, the pumped-storage method.

General Electric Company (GE) was an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, incorporated in the state of New York and headquartered in Boston. The company had several divisions, including aerospace, energy, healthcare, and finance.

Alstom SA is a French multinational rolling stock manufacturer which operates worldwide in rail transport markets. It is active in the fields of passenger transportation, signaling, and locomotives, producing high-speed, suburban, regional and urban trains along with trams.

A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electrical grid.

General Electric Company, doing business as GE Aerospace, is an American aircraft engine supplier that is headquartered in Evendale, Ohio, outside Cincinnati. It is the legal successor to the original General Electric Company founded in 1892, which split into three separate companies between November 2021 and April 2024, adopting the trade name GE Aerospace after divesting its healthcare and energy divisions.

Areva S.A. is a French multinational group specializing in nuclear power headquartered in Courbevoie, France. Before its 2016 corporate restructuring, Areva was majority-owned by the French state through the French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (54.37%), Banque publique d'investissement (3.32%), and Agence des participations de l'État (28.83%). Électricité de France, of which the French government has a majority ownership stake, owned 2.24%; Kuwait Investment Authority owned 4.82% as the second largest shareholder after the French state.

Électricité de France SA, commonly known as EDF, is a French multinational electric utility company owned by the government of France. Headquartered in Paris, with €139.7 billion in sales in 2023, EDF operates a diverse portfolio of at least 120 gigawatts of generation capacity in Europe, South America, North America, Asia, the Middle East, and Africa.

EDF Energy is a British integrated energy company, wholly owned by the French state-owned EDF, with operations spanning electricity generation and the sale of natural gas and electricity to homes and businesses throughout the United Kingdom. It employs 11,717 people, and handles 5.22 million business and residential customer accounts.

Ansaldo Energia S.p.A. is an Italian power engineering company based in Genoa, Italy. The absorbed parent company, Gio. Ansaldo & C., was started in 1853 before it merged with Leonardo S.p.A. In 2011, Leonardo S.p.A. sold a 45% stake in Ansaldo Energia to First Reserve Corporation. In 2013, Fondo Strategico Italiano acquired an 85% share of the company. It then sold a 40% share to Shanghai Electric Corporation.
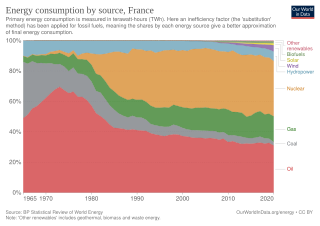
According to the International Energy Agency, France has historically generated a very low level of carbon dioxide emissions compared to other G7 economies due to its reliance on nuclear energy. Energy in France was generated from five primary sources: nuclear power, natural gas, liquid fuels, renewables and coal. In 2020, nuclear power made up the largest portion of electricity generation, at around 78%. Coal energy is declining and due to cease. Renewables accounted for 19.1% of energy consumption in 2020. France has the largest share of nuclear electricity in the world. The country is also among the world's biggest net exporters of electricity. The country is increasingly investing in renewable energy and has set a target of 32% by 2030.
The Siemens Energy Sector was one of the four sectors of German industrial conglomerate Siemens. Founded on January 1, 2009, it generated and delivered power from numerous sources including the extraction, conversion and transport of oil and natural gas in addition to renewable and alternative energy sources. As of October 1, 2014, the sector level has been eliminated, including the Siemens Energy Sector.

GE Power was an American energy technology company owned by General Electric (GE). In April 2024, GE completed the spin-off of GE Power into a separate company, GE Vernova. Following this, General Electric ceased to exist as a conglomerate and pivoted to aviation, rebranding as GE Aerospace.
GE Offshore Wind is a joint venture with Alstom and a subsidiary of GE Vernova, created in 2015 when most of Alstom's electrical power and generation assets were acquired by General Electric. GE's stake in the joint venture is 50% plus 1 share.

GE Wind is a division of GE Vernova. The company manufactures and sells wind turbines to the international market. In 2018, GE Wind was the fourth largest wind turbine manufacturer in the world. Vic Abate is the CEO of GE Vernova’s Wind businesses.
Atomenergomash JSC (AEM Group) (Russian: Атомэнергомаш, AEM Holding company) is a Russian power engineering company, a supplier of products for nuclear and thermal power plants, natural gas and petrochemical industry, shipbuilding, and special steel markets. It is the mechanical engineering division of Rosatom. Together with its subsidiaries it employees more than 17,000 people.

GE Digital is a subsidiary of American energy conglomerate GE Vernova. Headquartered in San Ramon, California, the company provides software and industrial internet of things (IIoT) services to industrial companies.

GE Renewable Energy is a manufacturing and services division of the American company General Electric. It is headquartered in Boulogne-Billancourt, near Paris, France and focuses on the production of energy systems that use renewable sources. Its products include wind, hydroelectric and solar power generating facilities.
Vera Silva is a Portuguese engineer and the chief strategy and technology officer (CSO/CTO) at General Electric (GE) GE Vernova Electrification Systems division. She is one of the few women to hold a chief technology officer position in one of the top three players in the electricity transmission and distribution space. She works on electricity grids technology and renewable energy integration.

Arabelle Solutions, formerly GEAST, for ‘GE-Alstom’, most of which was spun off from GE Steam Power, is a French multinational specialising in nuclear activities related to steam turbines (Arabelle) for the conventional island, present in nearly 16 countries including China, Finland, India, Romania and the United Kingdom, and headquartered in Boulogne-Billancourt, France. At Belfort, it is developing the Arabelle nuclear turbine, the most powerful in the world.
















