Transport in Bhutan uses about 8,000 kilometres (5,000 mi) of roads and four airports, three of which are operational and interconnected. Paro Airport is the only airport which accommodates international flights. As part of Bhutan's infrastructure modernization programs, its road system has been under development since the 1960s. There are no railways, and as Bhutan is a landlocked country with no major waterways, there are no ports.

Northeast India, officially known as the North Eastern Region(NER) is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political administrative division of the country. It comprises eight states—Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura (commonly known as the "Seven Sisters"), and the "brother" state of Sikkim.

The Royal Bhutan Army is a branch of the armed forces of the Kingdom of Bhutan responsible for maintaining the country's territorial integrity and sovereignty against security threats. The King of Bhutan is the Supreme Commander in Chief of the RBA. The Chief Operations Officer is Goonglon Gongma Batoo Tshering.

The Insurgency in Northeast India involves multiple separatist militant groups operating in some of India's northeastern states, which are connected to the rest of India by the Siliguri Corridor, a strip of land as narrow as 14.29 miles (23.00 km) wide.

Drukair Corporation Limited, operating as Drukair — Royal Bhutan Airlines, is the flag carrier of the Kingdom of Bhutan, headquartered in the western dzongkhag of Paro.

Tawang is a town and administrative headquarter of Tawang district in the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. It lies on NH-13 section of Trans-Arunachal Highway. The town was once the capital of the Tawang Tract, which is now divided into the Tawang district and the West Kameng district. Tawang continues as the headquarters of the former. Tawang is the number one tourist destination of Arunachal Pradesh.

Bhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked South Asian country situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainous country, Bhutan is known locally as "Druk Yul" or "Land of the Thunder Dragon", a name reflecting the cultural heritage of the country. The exonym Bhutan likely derives from the Prakrit hybrid word Bhŏṭṭaṃta, a name referring to its geographical proximity to Tibet (Bhŏṭṭa). Nepal and Bangladesh are located near Bhutan but do not share a border with it. The country has a population of over 727,145 and a territory of 38,394 square kilometres (14,824 sq mi) and ranks 133rd in land area and 160th in population. Bhutan is a constitutional monarchy with a king as the head of state and a prime minister as the head of government. Vajrayana Buddhism is the state religion and the Je Khenpo is the head of the state religion.

Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck is the Druk Gyalpo, the monarch of the Kingdom of Bhutan. After his father Jigme Singye Wangchuck abdicated the throne, he became the monarch on 9 December 2006. A public coronation ceremony was held on 6 November 2008, a year that marked 100 years of monarchy in Bhutan.

Chirang District is an administrative district in the Bodoland Territorial Region of Assam state in the North-East of India.
The Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region is a Government of India ministry, established in September 2001, which functions as the nodal Department of the Central Government to deal with matters related to the socio-economic development of the eight States of Northeast India: Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura and Sikkim. It acts as a facilitator between the Central Ministries/ Departments and the State Governments of the North Eastern Region in the economic development including removal of infrastructural bottlenecks, provision of basic minimum services, creating an environment for private investment and to remove impediments to lasting peace and security in the North Eastern Region.
Gelephu, also spelled as Gelyephug, Gelegphu, Gaylegphug, or Gaylephug, is a town or Thromde in Sarpang District in Bhutan. It is located on the Indian border, about 30 km to the east of Sarpang, the Dzongkhag (District) headquarters, and has a population of 9,858 as per the 2017 census. It is one of the road entry points into Bhutan from India; Phuntsholing to its west and Samdrup Jongkhar to its east are two other road entry points into Bhutan.

The bilateral relations between the Himalayan Kingdom of Bhutan and the Republic of India have been traditionally close and both countries share a "special relationship", making Bhutan a protected state, but not a protectorate, of India. India remains influential over Bhutan's foreign policy, defence and commerce. Bhutan is the largest beneficiary of India's foreign aid.

Sashastra Seema Bal is a border guarding force of India deployed along its borders with Nepal and Bhutan. It is one of the seven Central Armed Police Forces under the administrative control of the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
The following is a timeline of the Premiership of Narendra Modi from his inauguration as Prime Minister of India on 26 May 2014 till now. The following are the highlights of the major events that took place under his premiership.
Arunachal Frontier Highway (AFH), officially notified as the National Highway NH-913 and also called Bomdila-Vijaynagar Highway (BVH), connecting Bomdila Airstrip ALG & HQ in northwest to Vijaynagar Airstrip ALG & HQ in southeast via Nafra HQ-Sarli HQ-Huri Helipad ALG & HQ-Nacho HQ-Mechuka Airstrip ALG & HQ-Monigong HQ-Jido -Hunli HQ-Hayuliang Airstrip ALG HQ-Chenquenty-Hawai HQ-Miao HQ including 800 km greenfield section and network of new tunnels & bridges, is a 2-lane paved-shoulder under-construction national highway along the India-China LAC-McMahon Line border in the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. The 1,748 km-long (1,086 mi) highway itself will cost ₹27,000 crore and total cost including 6 additional inter-corridors is ₹40,000 crore. In some places, this highway will run as close as 20 km from the LAC. To be constructed by MoRTH in 9 packages, all packages will be approved by the end of fy 2024-25 and construction will be completed in 2 years by 31 March 2027. Of the total route, 800km is greenfield, rest brownfield will be upgraded and tunnels will be built. This highway in the north & east Arunachal along the China border, would complement the Trans-Arunachal Highway and the Arunachal East-West Corridor as major highways spanning the whole state, pursuing the Look East connectivity policy.

Neighborhood First Policy of India, a core component of India's foreign policy, focuses on peaceful relations and collaborative synergetic co-development with its South Asian neighbours of the Indian subcontinent encompassing a diverse range of topics, such as economic, technology, research, education, connectivity, space program, defence security, environment, and climate challenge. This policy creates new avenues as well as leverages existing regional cooperation initiatives, such as SAARC, SASEC, BBIN, and BIMSTEC. It compliments India's Look East policy focused on Southeast Asia and Look West Policy focused on Middle East.
A special administrative region is a designation for types of administrative division in China, East Timor, and North Korea.
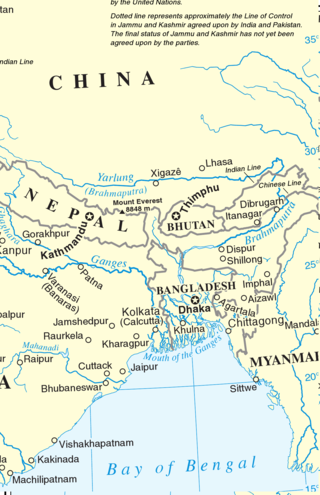
Eastern South Asia is a geographical area in the Southern Asian subregion, precisely the eastern region of the subcontinent. It includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal and India. Geographically, it lies between the Eastern Himalayas and the Bay of Bengal. Two of the world's largest rivers, the Ganges and the Brahmaputra, flow into the sea through the Bengal region. The region includes the world's highest mountainous terrain and the world's largest delta, and has a climate ranging from alpine and subalpine to subtropical and tropical. Since Nepal, Bhutan, and northeast India are landlocked, the coastlines of Bangladesh and East India serve as the principal gateways to the region.
The Republic of India shares borders with several sovereign countries; it shares land borders with China, Bhutan, Nepal, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Myanmar. Bangladesh Myanmar and Pakistan share both land borders as well as maritime borders, while Sri Lanka shares only a maritime border through Ram Setu. India's Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia.
Assam Global Investors' Summit or Advantage Assam Global Investors' Summit on 3–4 February 2018 was an economic summit organised by the Government of Assam. The main aim of the summit is to increase the trade and other relations with Southeast Asia. Members and Delegates from ASEAN and BBIN countries along with industrialists and business leaders of India and around the world are invited in this summit. The Summit aims at highlighting the geo-strategic advantages offered to investors by Assam. The summit will also focus on India's Act East Policy which will help in achieving balanced and fast-paced growth of the north-eastern region and development of MSME sector.











