
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that is specific for one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can tag a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly.

Colchicine is a medication used to treat gout and Behçet's disease. In gout, it is less preferred to NSAIDs or steroids. Other uses for colchicine include the management of pericarditis and familial Mediterranean fever. Colchicine is taken by mouth.

Amyloids are aggregates of proteins characterised by a fibrillar morphology of typically 7–13 nm in diameter, a β-sheet secondary structure and ability to be stained by particular dyes, such as Congo red. In the human body, amyloids have been linked to the development of various diseases. Pathogenic amyloids form when previously healthy proteins lose their normal structure and physiological functions (misfolding) and form fibrous deposits within and around cells. These protein misfolding and deposition processes disrupt the healthy function of tissues and organs.

Phagocytes are cells that protect the body by ingesting harmful foreign particles, bacteria, and dead or dying cells. Their name comes from the Greek phagein, "to eat" or "devour", and "-cyte", the suffix in biology denoting "cell", from the Greek kutos, "hollow vessel". They are essential for fighting infections and for subsequent immunity. Phagocytes are important throughout the animal kingdom and are highly developed within vertebrates. One litre of human blood contains about six billion phagocytes. They were discovered in 1882 by Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov while he was studying starfish larvae. Mechnikov was awarded the 1908 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discovery. Phagocytes occur in many species; some amoebae behave like macrophage phagocytes, which suggests that phagocytes appeared early in the evolution of life.

Ferritin is a universal intracellular protein that stores iron and releases it in a controlled fashion. The protein is produced by almost all living organisms, including archaea, bacteria, algae, higher plants, and animals. It is the primary intracellular iron-storage protein in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, keeping iron in a soluble and non-toxic form. In humans, it acts as a buffer against iron deficiency and iron overload.

Colostrum, or first milk, is the first form of milk produced by the mammary glands of humans and other mammals immediately following delivery of the newborn. It may be called beestings when referring to the first milk of a cow or similar animal. Most species will begin to generate colostrum just prior to giving birth. Colostrum has an especially high amount of bioactive compounds compared to mature milk to give the newborn the best possible start to life. Specifically, colostrum contains antibodies to protect the newborn against disease and infection, and immune and growth factors and other bioactives that help to activate a newborn's immune system, jumpstart gut function, and seed a healthy gut microbiome in the first few days of life. The bioactives found in colostrum are essential for a newborn's health, growth and vitality. Colostrum strengthens a baby's immune system and is filled with white blood cells to protect it from infection.

Lactoferrin (LF), also known as lactotransferrin (LTF), is a multifunctional protein of the transferrin family. Lactoferrin is a globular glycoprotein with a molecular mass of about 80 kDa that is widely represented in various secretory fluids, such as milk, saliva, tears, and nasal secretions. Lactoferrin is also present in secondary granules of PMNs and is secreted by some acinar cells. Lactoferrin can be purified from milk or produced recombinantly. Human colostrum has the highest concentration, followed by human milk, then cow milk (150 mg/L).
Amatoxin is the collective name of a subgroup of at least nine related toxic compounds found in three genera of poisonous mushrooms and one species of the genus Conocybe. Amatoxins are lethal in even small doses, as little as half a mushroom, including the immature "egg" form which appears quite different from the fully-grown mushroom.

β-Lactoglobulin (BLG) is the major whey protein of cow and sheep's milk, and is also present in many other mammalian species; a notable exception being humans. Its structure, properties and biological role have been reviewed many times. BLG is considered to be a milk allergen.

Ochratoxin A—a toxin produced by different Aspergillus and Penicillium species — is one of the most-abundant food-contaminating mycotoxins. It is also a frequent contaminant of water-damaged houses and of heating ducts. Human exposure can occur through consumption of contaminated food products, particularly contaminated grain and pork products, as well as coffee, wine grapes, and dried grapes. The toxin has been found in the tissues and organs of animals, including human blood and breast milk. Ochratoxin A, like most toxic substances, has large species- and sex-specific toxicological differences.

Osteocalcin, also known as bone gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein (BGLAP), is a small (49-amino-acid) noncollagenous protein hormone found in bone and dentin, first identified as a calcium-binding protein.

Milk allergy is an adverse immune reaction to one or more proteins in cow's milk. Symptoms may take hours to days to manifest, with symptoms including atopic dermatitis, inflammation of the esophagus, enteropathy involving the small intestine and proctocolitis involving the rectum and colon. However, rapid anaphylaxis is possible, a potentially life-threatening condition that requires treatment with epinephrine, among other measures.

Egg allergy is an immune hypersensitivity to proteins found in chicken eggs, and possibly goose, duck, or turkey eggs. Symptoms can be either rapid or gradual in onset. The latter can take hours to days to appear. The former may include anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening condition which requires treatment with epinephrine. Other presentations may include atopic dermatitis or inflammation of the esophagus.

Cylindrospermopsin is a cyanotoxin produced by a variety of freshwater cyanobacteria. CYN is a polycyclic uracil derivative containing guanidino and sulfate groups. It is also zwitterionic, making it highly water soluble. CYN is toxic to liver and kidney tissue and is thought to inhibit protein synthesis and to covalently modify DNA and/or RNA. It is not known whether cylindrospermopsin is a carcinogen, but it appears to have no tumour initiating activity in mice.

Etifoxine, sold under the trade name Stresam among others, is a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic agent, primarily indicated for short-term management of adjustment disorder, specifically instances of situational depression accompanied by anxiety, such as stress-induced anxiety. Administration is by mouth. Side effects associated with etifoxine use include slight drowsiness, headache, skin eruptions, and allergic reactions. In rare cases, etifoxine has been linked to severe skin and liver toxicity, as well as menstrual bleeding between periods. Unlike benzodiazepines, etifoxine does not cause sedation or lack of coordination. Etifoxine acts as a GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator and as a ligand for translocator proteins. Both mechanisms are conjectured to contribute to its anxiolytic properties.
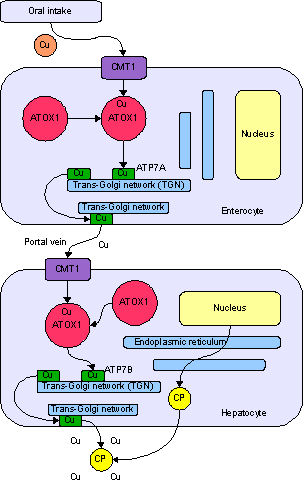
Copper is an essential trace element that is vital to the health of all living things. In humans, copper is essential to the proper functioning of organs and metabolic processes. The human body has complex homeostatic mechanisms which attempt to ensure a constant supply of available copper, while eliminating excess copper whenever this occurs. However, like all essential elements and nutrients, too much or too little nutritional ingestion of copper can result in a corresponding condition of copper excess or deficiency in the body, each of which has its own unique set of adverse health effects.
AI-10-49 is a small molecule inhibitor of leukemic oncoprotein CBFβ-SMHHC developed by the laboratory of John Bushweller with efficacy demonstrated by the laboratories of Lucio H. Castilla and Monica Guzman. AI-10-49 allosterically binds to CBFβ-SMMHC and disrupts protein-protein interaction between CBFβ-SMMHC and tumor suppressor RUNX1. This inhibitor is under development as an anti-leukemic drug.

Fish allergy is an immune hypersensitivity to proteins found in fish. Symptoms can be either rapid or gradual in onset. The latter can take hours to days to appear. The former may include anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening condition which requires treatment with epinephrine. Other presentations may include atopic dermatitis or inflammation of the esophagus. Fish is one of the eight common food allergens which are responsible for 90% of allergic reactions to foods: cow's milk, eggs, wheat, shellfish, peanuts, tree nuts, fish, and soy beans.

Shellfish allergy is among the most common food allergies. "Shellfish" is a colloquial and fisheries term for aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs such as clams, mussels, oysters and scallops, crustaceans such as shrimp, lobsters and crabs, and cephalopods such as squid and octopus. Shellfish allergy is an immune hypersensitivity to proteins found in shellfish. Symptoms can be either rapid or gradual in onset. The latter can take hours to days to appear. The former may include anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening condition which requires treatment with epinephrine. Other presentations may include atopic dermatitis or inflammation of the esophagus. Shellfish is one of the eight common food allergens, responsible for 90% of allergic reactions to foods: cow's milk, eggs, wheat, shellfish, peanuts, tree nuts, fish, and soy beans.
Protein nanotechnology is a burgeoning field of research that integrates the diverse physicochemical properties of proteins with nanoscale technology. This field assimilated into pharmaceutical research to give rise to a new classification of nanoparticles termed protein nanoparticles (PNPs). PNPs garnered significant interest due to their favorable pharmacokinetic properties such as high biocompatibility, biodegradability, and low toxicity Together, these characteristics have the potential to overcome the challenges encountered with synthetic NPs drug delivery strategies. These existing challenges including low bioavailability, a slow excretion rate, high toxicity, and a costly manufacturing process, will open the door to considerable therapeutic advancements within oncology, theranostics, and clinical translational research.


















