
A résumé, sometimes spelled resume, is a document created and used by a person to present their background, skills, and accomplishments. Résumés can be used for a variety of reasons, but most often they are used to secure new employment.
Freelance, freelancer, or freelance worker, are terms commonly used for a person who is self-employed and not necessarily committed to a particular employer long-term. Freelance workers are sometimes represented by a company or a temporary agency that resells freelance labor to clients; others work independently or use professional associations or websites to get work.

Recruitment is the overall process of identifying, sourcing, screening, shortlisting, and interviewing candidates for jobs within an organization. Recruitment also is the process involved in choosing people for unpaid roles. Managers, human resource generalists, and recruitment specialists may be tasked with carrying out recruitment, but in some cases, public-sector employment, commercial recruitment agencies, or specialist search consultancies such as Executive search in the case of more senior roles, are used to undertake parts of the process. Internet-based recruitment is now widespread, including the use of artificial intelligence (AI).

LinkedIn is a business and employment-focused social media platform that works through websites and mobile apps. It was launched on May 5, 2003 by Reid Hoffman and Eric Ly. Since December 2016, LinkedIn has been a wholly owned subsidiary of Microsoft. The platform is primarily used for professional networking and career development, and allows jobseekers to post their CVs and employers to post jobs. From 2015, most of the company's revenue came from selling access to information about its members to recruiters and sales professionals. LinkedIn has more than 1 billion registered members from over 200 countries and territories.
Ad blocking or ad filtering is a software capability for blocking or altering online advertising in a web browser, an application or a network. This may be done using browser extensions or other methods.
Online advertising, also known as online marketing, Internet advertising, digital advertising or web advertising, is a form of marketing and advertising that uses the Internet to promote products and services to audiences and platform users. Online advertising includes email marketing, search engine marketing (SEM), social media marketing, many types of display advertising, and mobile advertising. Advertisements are increasingly being delivered via automated software systems operating across multiple websites, media services and platforms, known as programmatic advertising.
Indeed, Inc. is an American worldwide employment website for job listings launched in November 2004. It is an independent subsidiary of multinational Recruit Holdings.It is headquartered in Austin, Texas, and Stamford, Connecticut, with additional offices around the world. As a single topic search engine, its central functionality is also an example of vertical search. Indeed is currently available in over 60 countries and 28 languages. In October 2010, Indeed.com surpassed Monster.com to become the highest-traffic job website in the United States.
An employment website is a website that deals specifically with employment or careers. Many employment websites are designed to allow employers to post job requirements for a position to be filled and are commonly known as job boards. Other employment sites offer employer reviews, career and job-search advice, and describe different job descriptions or employers. Through a job website, a prospective employee can locate and fill out a job application or submit resumes over the Internet for the advertised position.
Lionbridge Technologies, Inc is an American company that provides translation and localization services. Based in Waltham, Massachusetts, the company has operations in 26 countries.

Andersen Corporation is an international window and door manufacturing enterprise employing 12,000 people at more than thirty manufacturing facilities, logistics centers, and company owned retail locations. Andersen is a private company headquartered in Bayport, Minnesota.
Employment fraud is the attempt to defraud people seeking employment by giving them false hope of better employment, offering better working hours, more respectable tasks, future opportunities, or higher wages. They often advertise at the same locations as genuine employers and may ask for money in exchange for the opportunity to apply for a job.
Recruitment advertising, also known as Recruitment communications and Recruitment agency, includes all communications used by an organization to attract talent to work within it. Recruitment advertisements may be the first impression of a company for many job seekers. In turn, the strength of employer branding in job postings can directly impact interest in job openings.
Craigslist is a privately held American company operating a classified advertisements website with sections devoted to jobs, housing, for sale, items wanted, services, community service, gigs, résumés, and discussion forums.

Ghost Trick: Phantom Detective is a 2010 puzzle adventure video game developed and published by Capcom. The story follows Sissel, an amnesiac ghost with supernatural powers, and his journey to rediscover his identity. Players solve environmental puzzles, interact with eccentric characters, and uncover the truth of Sissel's death over the course of one night. Gameplay is split into two sections: gathering information by navigating through the city, and saving lives by traveling back in time.
Fiverr is an Israeli multinational online marketplace for freelance services. Fiverr's platform connects freelancers (sellers) to people or businesses looking to hire (buyers), encouraging a wide range of services in a free market. Fiverr takes its name from the $5 asking price attached to all tasks when the company was founded in 2010 in Tel Aviv, though many sellers now charge more.
An Internet water army is a group of users who are paid to post online comments with vested interest on Chinese language websites. Internet water armies started in the early 2010s. They post news, comments, gossip and disinformation on online platforms like Weibo, WeChat and Taobao, China's eBay-like platform. In this astroturfing technique for public relations and media manipulation, online Chinese companies employ people to post on social media to change public opinion. It has been developed into an industry in which a company specializing in internet water armies can earn 7.6 million yuan within three months and has made over 2500 transactions. The private Internet water army operations parallel the official 50 Cent Party internet commentators hired by the government of the People's Republic of China or the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) to spread propaganda and disinformation.
Social spam is unwanted spam content appearing on social networking services, social bookmarking sites, and any website with user-generated content. It can be manifested in many ways, including bulk messages, profanity, insults, hate speech, malicious links, fraudulent reviews, fake friends, and personally identifiable information.
Glassdoor is an American website where current and former employees anonymously review companies, operated by the company of the same name.

A technical support scam, or tech support scam, is a type of scam in which a scammer claims to offer a legitimate technical support service. Victims contact scammers in a variety of ways, often through fake pop-ups resembling error messages or via fake "help lines" advertised on websites owned by the scammers. Technical support scammers use social engineering and a variety of confidence tricks to persuade their victim of the presence of problems on their computer or mobile device, such as a malware infection, when there are no issues with the victim's device. The scammer will then persuade the victim to pay to fix the fictitious "problems" that they claim to have found. Payment is made to the scammer through ways which are hard to trace and have fewer consumer protections in place which could allow the victim to claim their money back, usually through gift cards.
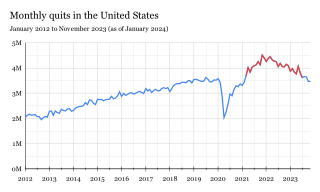
The Great Resignation, also known as the Big Quit and the Great Reshuffle, was a mainly American economic trend in which employees voluntarily resigned from their jobs en masse, beginning in early 2021 during the COVID-19 pandemic. Among the most cited reasons for resigning included wage stagnation amid rising cost of living, limited opportunities for career advancement, hostile work environments, lack of benefits, inflexible remote-work policies, and long-lasting job dissatisfaction. Most likely to quit were workers in hospitality, healthcare, and education. In addition, many of the resigning workers were retiring seniors. Collectively, the Baby Boomers are one of the largest demographic cohorts in the United States.







