Related Research Articles

Cyc is a long-term artificial intelligence project that aims to assemble a comprehensive ontology and knowledge base that spans the basic concepts and rules about how the world works. Hoping to capture common sense knowledge, Cyc focuses on implicit knowledge that other AI platforms may take for granted. This is contrasted with facts one might find somewhere on the internet or retrieve via a search engine or Wikipedia. Cyc enables semantic reasoners to perform human-like reasoning and be less "brittle" when confronted with novel situations.

The International Mathematical Union (IMU) is an international organization devoted to international cooperation in the field of mathematics across the world. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC) and supports the International Congress of Mathematicians (ICM). Its members are national mathematics organizations from more than 80 countries.

Wolfram Mathematica is a software system with built-in libraries for several areas of technical computing that allow machine learning, statistics, symbolic computation, data manipulation, network analysis, time series analysis, NLP, optimization, plotting functions and various types of data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other programming languages. It was conceived by Stephen Wolfram, and is developed by Wolfram Research of Champaign, Illinois. The Wolfram Language is the programming language used in Mathematica. Mathematica 1.0 was released on June 23, 1988 in Champaign, Illinois and Santa Clara, California.
Information science is an academic field which is primarily concerned with analysis, collection, classification, manipulation, storage, retrieval, movement, dissemination, and protection of information. Practitioners within and outside the field study the application and the usage of knowledge in organizations in addition to the interaction between people, organizations, and any existing information systems with the aim of creating, replacing, improving, or understanding the information systems.
PlanetMath is a free, collaborative, mathematics online encyclopedia. Intended to be comprehensive, the project is currently hosted by the University of Waterloo. The site is owned by a US-based nonprofit corporation, "PlanetMath.org, Ltd".
Question answering (QA) is a computer science discipline within the fields of information retrieval and natural language processing (NLP) that is concerned with building systems that automatically answer questions that are posed by humans in a natural language.
MathWorld is an online mathematics reference work, created and largely written by Eric W. Weisstein. It is sponsored by and licensed to Wolfram Research, Inc. and was partially funded by the National Science Foundation's National Science Digital Library grant to the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign.

Wolfram Research, Inc. is an American multinational company that creates computational technology. Wolfram's flagship product is the technical computing program Wolfram Mathematica, first released on June 23, 1988. Other products include WolframAlpha, Wolfram SystemModeler, Wolfram Workbench, gridMathematica, Wolfram Finance Platform, webMathematica, the Wolfram Cloud, and the Wolfram Programming Lab. Wolfram Research founder Stephen Wolfram is the CEO. The company is headquartered in Champaign, Illinois, United States.
Eric Wolfgang Weisstein is an American scientist, mathematician, and encyclopedist who created and maintains the encyclopedias MathWorld and ScienceWorld. In addition, he is the author of the CRC Concise Encyclopedia of Mathematics. He works for Wolfram Research.
Simple Knowledge Organization System (SKOS) is a W3C recommendation designed for representation of thesauri, classification schemes, taxonomies, subject-heading systems, or any other type of structured controlled vocabulary. SKOS is part of the Semantic Web family of standards built upon RDF and RDFS, and its main objective is to enable easy publication and use of such vocabularies as linked data.
The International Commission on Mathematical Instruction (ICMI) is a commission of the International Mathematical Union and is an internationally acting organization focussing on mathematics education. ICMI was founded in 1908 at the International Congress of Mathematicians (ICM) in Rome and aims to improve teaching standards around the world, through programs, workshops and initiatives and publications. It aims to work a great deal with developing countries, to increase teaching standards and education which can improve life quality and aid the country.
Michael Kohlhase is a German computer scientist and professor at University of Erlangen–Nuremberg, where he is head of the KWARC research group.
Digital curation is the selection, preservation, maintenance, collection, and archiving of digital assets. Digital curation establishes, maintains, and adds value to repositories of digital data for present and future use. This is often accomplished by archivists, librarians, scientists, historians, and scholars. Enterprises are starting to use digital curation to improve the quality of information and data within their operational and strategic processes. Successful digital curation will mitigate digital obsolescence, keeping the information accessible to users indefinitely. Digital curation includes digital asset management, data curation, digital preservation, and electronic records management.
Computational thinking (CT) refers to the thought processes involved in formulating problems so their solutions can be represented as computational steps and algorithms. In education, CT is a set of problem-solving methods that involve expressing problems and their solutions in ways that a computer could also execute. It involves automation of processes, but also using computing to explore, analyze, and understand processes.

Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.

In natural language processing, entity linking, also referred to as named-entity linking (NEL), named-entity disambiguation (NED), named-entity recognition and disambiguation (NERD) or named-entity normalization (NEN) is the task of assigning a unique identity to entities mentioned in text. For example, given the sentence "Paris is the capital of France", the idea is to determine that "Paris" refers to the city of Paris and not to Paris Hilton or any other entity that could be referred to as "Paris". Entity linking is different from named-entity recognition (NER) in that NER identifies the occurrence of a named entity in text but it does not identify which specific entity it is.
LaTeXML is a free public domain software package which converts LaTeX documents to XML, HTML, EPUB, JATS and TEI.
Patrick D. F. Ion is an American mathematician whose main interest is in mathematical knowledge management.
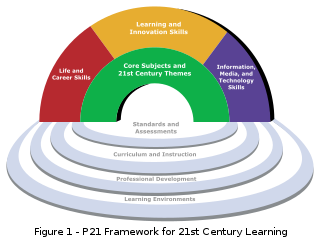
21st century skills comprise skills, abilities, and learning dispositions identified as requirements for success in 21st century society and workplaces by educators, business leaders, academics, and governmental agencies. This is part of an international movement focusing on the skills required for students to prepare for workplace success in a rapidly changing, digital society. Many of these skills are associated with deeper learning, which is based on mastering skills such as analytic reasoning, complex problem solving, and teamwork, which differ from traditional academic skills as these are not content knowledge-based.
References
- ↑ "The Global Digital Mathematical Library Working Group (GDML WG) - "The World Digital Mathematics Library" (WDML)". Archived from the original on 2016-02-20. Retrieved 2016-02-05.
- ↑ Council, National Research (18 March 2014). "Developing a 21st Century Global Library for Mathematics Research". doi:10.17226/18619. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "Fields Institute - Semantic Representation of Mathematical Knowledge Workshop". Archived from the original on 2016-02-03. Retrieved 2016-02-22.
- ↑ "Computable Archive of Mathematics: Wolfram Foundation Project (or Program)". Archived from the original on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2016-02-22.