
The Maritimes, also called the Maritime provinces, is a region of Eastern Canada consisting of three provinces: New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. The Maritimes had a population of 1,899,324 in 2021, which makes up 5.1% of Canada's population. Together with Canada's easternmost province, Newfoundland and Labrador, the Maritime provinces make up the region of Atlantic Canada.
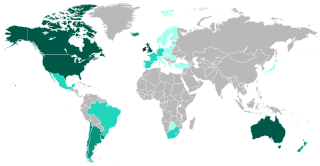
The Irish diaspora refers to ethnic Irish people and their descendants who live outside the island of Ireland.

The United States is a country primarily located in North America. Demographics of the United States concern matters of population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations, and other aspects regarding the population.

United Empire Loyalist is an honorific title which was first given by the 1st Lord Dorchester, the Governor of Quebec and Governor General of the Canadas, to American Loyalists who resettled in British North America during or after the American Revolution. At that time, the demonym Canadian or Canadien was used to refer to the indigenous First Nations groups and the descendants of New France settlers inhabiting the Province of Quebec.

Irish people in Great Britain or British Irish are immigrants from the island of Ireland living in Great Britain as well as their British-born descendants.

Canada ranks 37th by population among countries of the world, comprising about 0.5% of the world's total, with 40 million Canadians. Despite being the second-largest country by total area, the vast majority of the country is sparsely inhabited, with most of its population south of the 55th parallel north. Just over 60 percent of Canadians live in just two provinces: Ontario and Quebec. Though Canada's overall population density is low, many regions in the south, such as the Quebec City–Windsor Corridor, have population densities higher than several European countries. Canada has six population centres with more than one million people: Toronto, Montreal, Vancouver, Calgary, Edmonton and Ottawa.

Irish Canadians are Canadian citizens who have full or partial Irish heritage including descendants who trace their ancestry to immigrants who originated in Ireland. 1.2 million Irish immigrants arrived from 1825 to 1970, and at least half of those in the period from 1831 to 1850. By 1867, they were the second largest ethnic group, and comprised 24% of Canada's population. The 1931 national census counted 1,230,000 Canadians of Irish descent, half of whom lived in Ontario. About one-third were Catholic in 1931 and two-thirds Protestant.

Irish Quebecers are residents of the Canadian province of Quebec who have Irish ancestry. In 2016, there were 446,215 Quebecers who identified themselves as having partial or exclusive Irish descent in Quebec, representing 5.46% of the population.

According to the 2021 Canadian census, immigrants in Canada number 8.3 million persons and make up approximately 23 percent of Canada's total population. This represents the eighth-largest immigrant population in the world, while the proportion represents one of the highest ratios for industrialized Western countries.

The Royal Decree of Graces of 1815 is a real cédula approved by the Spanish Crown in the early half of the 19th century to encourage Spaniards and, later, Europeans of non-Spanish origin, to settle in and populate the colony of Puerto Rico.

The history of New Brunswick covers the period from the arrival of the Paleo-Indians thousands of years ago to the present day. Prior to European colonization, the lands encompassing present-day New Brunswick were inhabited for millennia by the several First Nations groups, most notably the Maliseet, Mi'kmaq, and the Passamaquoddy.

The history of immigration to Canada details the movement of people to modern-day Canada. The modern Canadian legal regime was founded in 1867, but Canada also has legal and cultural continuity with French and British colonies in North America that go back to the 17th century, and during the colonial era, immigration was a major political and economic issue with Britain and France competing to fill their colonies with loyal settlers. Until then, the land that now makes up Canada was inhabited by many distinct Indigenous peoples for thousands of years. Indigenous peoples contributed significantly to the culture and economy of the early European colonies to which was added several waves of European immigration. More recently, the source of migrants to Canada has shifted away from Europe and towards Asia and Africa. Canada's cultural identity has evolved constantly in tandem with changes in immigration patterns.

Scottish Canadians are people of Scottish descent or heritage living in Canada. As the third-largest ethnic group in Canada and amongst the first Europeans to settle in the country, Scottish people have made a large impact on Canadian culture since colonial times. According to the 2016 Census of Canada, the number of Canadians claiming full or partial Scottish descent is 4,799,010, or 13.93% of the nation's total population. Prince Edward Island has the highest population of Scottish descendants at 41%.

The history of immigration to the United States details the movement of people to the United States from the colonial era to the present day. Throughout U.S. history, the country experienced successive waves of immigration, particularly from Europe and later on from Asia and Latin America. Colonial-era immigrants often repaid the cost of transoceanic transportation by becoming indentured servants in which the new employer paid the ship's captain. In the late 19th century, immigration from China and Japan was restricted. In the 1920s, restrictive immigration quotas were imposed but political refugees had special status. Numerical restrictions ended in 1965. In recent years, the largest numbers of immigrants to the United States have come from Asia and Central America.

European emigration is the successive emigration waves from the European continent to other continents. The origins of the various European diasporas can be traced to the people who left the European nation states or stateless ethnic communities on the European continent.
British Canadians primarily refers to Canadians who were either born in or can trace their ancestry to the British Isles, which includes the nations of England, Ireland, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland.

Canadians are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being Canadian.
European Canadians, or Euro-Canadians, are Canadians who were either born in or can trace their ancestry to the continent of Europe. They form the largest panethnic group within Canada.

The history of Saint John, New Brunswick is one that extends back thousands of years, with the area being inhabited by the Maliseet and Miꞌkmaq First Nations prior to the arrival of European colonists. During the 17th century, a French settlement was established in Saint John. During the Acadian Civil War, Saint John served as the seat for the administration under Charles de Saint-Étienne de la Tour. The French position in Saint John was abandoned in 1755, with British forces taking over the area shortly afterwards.
Since the founding of Montreal in 1642, there has been a strong Irish presence in the city. The earlier Irish immigrants gradually assimilated into Montreal society. Irish people arrived in greater numbers as a result of the Great Irish Famine of 1845–49, and although these encountered considerable hostility, many people of Irish descent have continued to live in Montreal.














