Tandy Corporation was an American family-owned leather-goods company based in Fort Worth, Texas, United States. Tandy Leather was founded in 1919 as a leather supply store. By the end of the 1950s, under the tutelage of then-CEO Charles Tandy, the company expanded into the hobby market, making leather moccasins and coin purses, making huge sales among Scouts, leading to a fast growth in sales.

A laptop computer or notebook computer, also known as a laptop or notebook, is a small, portable personal computer (PC). Laptops typically have a clamshell form factor with a flat-panel screen on the inside of the upper lid and an alphanumeric keyboard and pointing device on the inside of the lower lid. Most of the computer's internal hardware is fitted inside the lower lid enclosure under the keyboard, although many modern laptops have a built-in webcam at the top of the screen, and some even feature a touchscreen display. In most cases, unlike tablet computers which run on mobile operating systems, laptops tend to run on desktop operating systems, which were originally developed for desktop computers.

A portable computer is a computer designed to be easily moved from one place to another, as opposed to those designed to remain stationary at a single location such as desktops and workstations. These computers usually include a display and keyboard that are directly connected to the main case, all sharing a single power plug together, much like later desktop computers called all-in-ones (AIO) that integrate the system's internal components into the same case as the display. In modern usage, a portable computer usually refers to a very light and compact personal computer such as a laptop, subnotebook or handheld PC, while touchscreen-based handheld ("palmtop") devices such as tablet, phablet and smartphone are called mobile devices instead.

A touchpad or trackpad is a type of pointing device. Its largest component is a tactile sensor: an electronic device with a flat surface, that detects the motion and position of a user's fingers, and translates them to 2D motion, to control a pointer in a graphical user interface on a computer screen. Touchpads are common on laptop computers, contrasted with desktop computers, where mice are more prevalent. Trackpads are sometimes used on desktops, where desk space is scarce. Because trackpads can be made small, they can be found on personal digital assistants (PDAs) and some portable media players. Wireless touchpads are also available, as detached accessories.
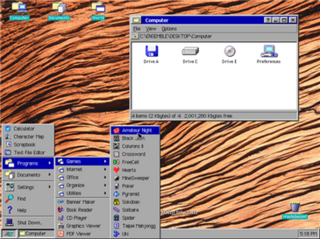
GEOS is a computer operating environment, graphical user interface (GUI), and suite of application software. Originally released as PC/GEOS, it runs on DOS-based, IBM PC compatible computers. Versions for some handheld platforms were also released and licensed to some companies.

The TRS-80 Model 100 is a notebook-sized portable computer introduced in April 1983. It was the first commercially successful notebook computer, as well as one of the first notebook computers ever released. It features a keyboard and liquid-crystal display, in a battery-powered package roughly the size and shape of a notepad or large book. The 224-page, spiral-bound User Manual is nearly the same size as the computer itself.

William Grant Moggridge, RDI was an English designer, author and educator who cofounded the design company IDEO and was director of Cooper Hewitt, Smithsonian Design Museum in New York. He was a pioneer in adopting a human-centred approach in design, and championed interaction design as a mainstream design discipline. Among his achievements, he designed the first laptop computer, the GRiD Compass, was honoured for Lifetime Achievement from the National Design Awards, and given the Prince Philip Designers Prize. He was quoted as saying, "If there is a simple, easy principle that binds everything I have done together, it is my interest in people and their relationship to things."

A clamshell design is a kind of form factor for electronic devices in the shape of a clamshell. Mobile phones, handheld game consoles, and especially laptops, are often designed like clamshells. Clamshell devices are usually made of two sections connected by a hinge, each section containing either a flat panel display or an alphanumeric keyboard/keypad, which can fold into contact together like a bivalve shell.

The Gavilan SC is an early laptop computer first released by the Gavilan Computer Corporation in April 1984. The computer ran on an Intel 8088 microprocessor running at 5 MHz and sported a touchpad for a pointing device, one of the first computers to do so. The laptop was developed by Manuel "Manny" Fernandez, founder of the Gavilan Computer Corporation, and unveiled in May 1983.

The Grid Compass is a family of laptop computers introduced in 1982 by the Grid Systems Corporation. The design for the Compass was rendered by Bill Moggridge. Owing to its clamshell design—the first in a portable computer—some historians credit the original Compass as the first ever laptop.

The Sharp PC-5000 was a pioneering laptop computer, announced by Sharp Corporation of Japan in November 1983. It employed a clamshell design in which the display closes over the keyboard, like the earlier GRiD Compass and contemporary Gavilan SC.

Pen computing refers to any computer user-interface using a pen or stylus and tablet, over input devices such as a keyboard or a mouse.

The history of laptops describes the efforts, begun in the 1970s, to build small, portable Personal Computers that combine the components, inputs, outputs and capabilities of a Desktop Computer in a small chassis.

GRiDPad was a trademarked name for a series of pen computing tablets and hybrid laptops built by Grid Systems Corporation.

GridCase is a line of rugged tablets and laptops by Grid Systems Corporation released as a successor of the GRiD Compass line. The first model was released in 1985.
The history of tablet computers and the associated special operating software is an example of pen computing technology, and thus the development of tablets has deep historical roots. The first patent for a system that recognized handwritten characters by analyzing the handwriting motion was granted in 1914. The first publicly demonstrated system using a tablet and handwriting recognition instead of a keyboard for working with a modern digital computer dates to 1956.
John Ellenby was a British businessman. He was the founder of Grid Systems Corporation, maker of the Grid Compass, one of the first commercially successful laptop computers. He also co-founded GeoVector, an early augmented reality company.
To date, two methods have been used to make a personal computer, not offered by Apple, but able to run a Mac operating system: either create a Macintosh conversion or build a Macintosh clone.
The Olivetti company, an Italian manufacturer of computers, tablets, smartphones, printers and other such business products as calculators and fax machines, was founded as a typewriter manufacturer by Camillo Olivetti in 1908 in the Turin commune of Ivrea, Italy. Olivetti was a pioneer in computer development, starting with the mainframe systems in the 1950s, and continuing into the 1990s with PC-compatible laptops and desktops.

The Executive Partner is an IBM PC-compatible portable computer that was introduced by the Panasonic Corporation in 1985. The portable computer is AC-powered exclusively, weighs between 28 and 30 pounds (14 kg), and features a built-in printer. The Executive Partner was one of the first affordable portable computers with a plasma display.


















