HMS Canopus was a pre-dreadnought battleship of the British Royal Navy and the lead ship of the Canopus class. Intended for service in Asia, Canopus and her sister ships were smaller and faster than the preceding Majestic-class battleships, but retained the same battery of four 12-inch (305 mm) guns. She also carried thinner armour, but incorporated new Krupp steel, which was more effective than the Harvey armour used in the Majestics. Canopus was laid down in January 1897, launched in October that year, and commissioned into the fleet in December 1899.

HMS Ocean was a pre-dreadnought battleship of the British Royal Navy and a member of the Canopus class. Intended for service in Asia, Ocean and her sister ships were smaller and faster than the preceding Majestic-class battleships, but retained the same battery of four 12-inch (305 mm) guns. She also carried thinner armour, but incorporated new Krupp steel, which was more effective than the Harvey armour used in the Majestics. Ocean was laid down in December 1897, launched in July 1898, and commissioned into the fleet in February 1900.

The Duncan class was a class of six pre-dreadnought battleships built for the Royal Navy in the early 1900s. The six ships—HMS Duncan, HMS Albemarle, HMS Cornwallis, HMS Exmouth, HMS Montagu, and HMS Russell—were ordered in response to Russian naval building, specifically the fast second-class battleships of the Peresvet class, which they were specifically to counter. The foremost design consideration was a high top speed to match the rumoured top speed of 19 knots of the Russian ships while maintaining the same battery of 12-inch (300 mm) guns and keeping displacement from growing. This forced significant compromises in armour protection, though the ships adopted a revised system of protection for the bow, which was copied in other designs like the London class.

HMS Goliath was a pre-dreadnought battleship of the British Royal Navy and a member of the Canopus class. Intended for service in Asia, Goliath and her sister ships were smaller and faster than the preceding Majestic-class battleships, but retained the same battery of four 12-inch (305 mm) guns. She also carried thinner armour, but incorporated new Krupp steel, which was more effective than the Harvey armour used in the Majestics. Goliath was laid down in January 1897, launched in March 1898, and commissioned into the fleet in March 1900.

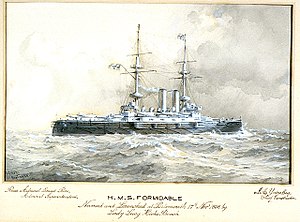
The Formidable class of battleships were a three-ship class of pre-dreadnoughts designed by Sir William White and built for the Royal Navy in the late 1890s. The class comprised Formidable, Irresistible, and Implacable. They were armed with a battery of four 12-inch (305 mm) guns, they had top speed of 18 knots, and they marked the adoption of Krupp armour in British battleship designs. The class formed the basis for the nearly identical London class of five ships, and those ships are sometimes included in the Formidable class. Formidable, Irresistible, and Implacable were built between 1898 and 1901 at the Portsmouth, Chatham, and Devonport Dockyards, respectively.

HMS Irresistible—the fourth British Royal Navy ship of the name—was a Formidable-class pre-dreadnought battleship. The Formidable-class ships were developments of earlier British battleships, featuring the same battery of four 12-inch (305 mm) guns—albeit more powerful 40-calibre versions—and top speed of 19 knots of the preceding Canopus class, while adopting heavier armour protection. The ship was laid down in April 1898, was launched in December that year, and was completed in October 1901. Commissioned in 1902, she initially served with the Mediterranean Fleet until April 1908, when she was transferred to the Channel Fleet. Now outclassed with the emergence of the dreadnought class of ships, she entered service with the Home Fleet in 1911 following a refit. In 1912, she was assigned to the 5th Battle Squadron.

HMS Prince of Wales was a London-class pre-dreadnought battleship built for the Royal Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. She was one of two ships of the London- or Queen sub-class. Shortly after completion the ship was assigned to the Mediterranean Fleet and then to the Atlantic in 1909 and Home Fleets three year later. Prince of Wales often served as a flagship during her career.

HMS Albemarle was a pre-dreadnought Duncan-class battleship of the Royal Navy, named after George Monck, 1st Duke of Albemarle. Built to counter a group of fast Russian battleships, Albemarle and her sister ships were capable of steaming at 19 knots, making them the fastest battleships in the world. The Duncan-class battleships were armed with a main battery of four 12-inch (305 mm) guns and they were broadly similar to the London-class battleships, though of a slightly reduced displacement and thinner armour layout. As such, they reflected a development of the lighter second-class ships of the Canopus-class battleship. Albemarle was built between her keel laying in January 1900 and her completion in November 1903.

HMS Venerable (1899) was a member of the London class of pre-dreadnought battleships built for the British Royal Navy. The Londons were near repeats of the preceding Formidable-class battleships, but with modified armour protection. Venerable's main battery consisted of four 12-inch (305-mm) guns, and she had top speed of 18 knots. The ship was laid down in January 1899, was launched in November that year, and was completed in November 1902. Commissioned that month, Venerable served in the Mediterranean Fleet until 1908, and was subsequently recommissioned into the Channel Fleet. Following a major refit in 1909, she served with the Atlantic and Home Fleets.

HMS Britannia was a King Edward VII-class pre-dreadnought battleship of the Royal Navy. She was named after Britannia, the Latin name of Great Britain under Roman rule. The ship was built by Portsmouth Dockyard between 1904 and 1906. Armed with a battery of four 12-inch (305 mm) and four 9.2 in (234 mm) guns, she and her sister ships marked a significant advance in offensive power compared to earlier British battleship designs that did not carry the 9.2 in guns.

HMS Implacable was a Formidable-class battleship of the British Royal Navy, the second ship of the name. The Formidable-class ships were developments of earlier British battleships, featuring the same battery of four 12-inch (305 mm) guns—albeit more powerful 40-calibre versions—and top speed of 19 knots of the preceding Canopus class, while adopting heavier armour protection. The ship was laid down in July 1898, was launched in March 1899, and was completed in July 1901. Commissioned in September 1901, she was assigned to the Mediterranean Fleet and served with the fleet until 1908. After a refit, she transferred to the Channel Fleet, then onto the Atlantic Fleet in May 1909. By now rendered obsolete by the emergence of the dreadnought class ships, she was assigned to the 5th Battle Squadron and attached to the Home Fleet in 1912.

HMS Cornwallis was a Duncan-class pre-dreadnought battleship of the Royal Navy. Built to counter a group of fast Russian battleships, Cornwallis and her sister ships were capable of steaming at 19 knots, making them the fastest battleships in the world. The Duncan-class battleships were armed with a main battery of four 12-inch (305 mm) guns and they were broadly similar to the London-class battleships, though of a slightly reduced displacement and thinner armour layout. As such, they reflected a development of the lighter second-class ships of the Canopus-class battleship. Cornwallis was built between her keel laying in July 1899 and her completion in February 1904.

HMS London was the lead ship of the London class of pre-dreadnought battleships built for the British Royal Navy. The Londons were near repeats of the preceding Formidable-class battleships, but with modified armour protection. The ship was laid down in December 1898, was launched in September 1899, and was completed in June 1902. Commissioned the same month, she served with the Mediterranean Fleet until early 1907. She was assigned to the Nore Division of the Home Fleet for nearly a year before transferring to the Channel Fleet. Rendered obsolete with the emergence of the new dreadnoughts in late 1906, she underwent an extensive refit in 1909, after which she served with the Atlantic Fleet. She was assigned to the Second Home Fleet in 1912 as part of the 5th Battle Squadron, and was temporarily fitted with a makeshift ramp for experiments with naval aircraft until 1913.

HMS Queen was a member of the London class of pre-dreadnought battleships built for the British Royal Navy. The Londons were near repeats of the preceding Formidable-class battleships, but with modified armour protection. Due to slight differences between Queen and HMS Prince of Wales and the other Londons, they are sometimes referred to as the Queen class. The ship's main battery consisted of four 12-inch (305-mm) guns, and she had top speed of 18 knots. The ship was laid down in March 1901, was launched in March 1902, and was completed in March 1904. After commissioning in April 1904, she served with the Mediterranean Fleet until 1906, when she returned to Britain before embarking on another stint with the Mediterranean Fleet later that year. Queen was transferred back to the United Kingdom in 1908 and thereafter served in the Atlantic Fleet, the Home Fleet, and finally the 5th Battle Squadron of the Second Fleet in 1914.

HMS Russell was a Duncan-class pre-dreadnought battleship of the Royal Navy commissioned in 1903. Built to counter a group of fast Russian battleships, Russell and her sister ships were capable of steaming at 19 knots, making them the fastest battleships in the world. The Duncan-class battleships were armed with a main battery of four 12-inch (305 mm) guns and they were broadly similar to the London-class battleships, though of a slightly reduced displacement and thinner armour layout. As such, they reflected a development of the lighter second-class ships of the Canopus-class battleship. Russell was built between her keel laying in March 1899 and her completion in February 1903.

HMS Vengeance was a pre-dreadnought battleship of the British Royal Navy and a member of the Canopus class. Intended for service in Asia, Vengeance and her sister ships were smaller and faster than the preceding Majestic-class battleships, but retained the same battery of four 12-inch (305 mm) guns. She also carried thinner armour, but incorporated new Krupp steel, which was more effective than the Harvey armour used in the Majestics. Vengeance was laid down in August 1898, launched in July 1899, and commissioned into the fleet in April 1902.

HMS Duncan was the lead ship of the six-ship Duncan class of Royal Navy pre-dreadnought battleships. Built to counter a group of fast Russian battleships, Duncan and her sister ships were capable of steaming at 19 knots, making them the fastest battleships in the world. The Duncan-class battleships were armed with a main battery of four 12-inch (305 mm) guns and they were broadly similar to the London-class battleships, though of a slightly reduced displacement and thinner armour layout. As such, they reflected a development of the lighter second-class ships of the Canopus-class battleship. Duncan was built between her keel laying in July 1899 and her completion in October 1903.

HMS Exmouth was a Duncan-class pre-dreadnought battleship of the Royal Navy. Built to counter a group of fast Russian battleships, Exmouth and her sister ships were capable of steaming at 19 knots, making them the fastest battleships in the world. The Duncan-class battleships were armed with a main battery of four 12-inch (305 mm) guns and they were broadly similar to the London-class battleships, though of a slightly reduced displacement and thinner armour layout. As such, they reflected a development of the lighter second-class ships of the Canopus-class battleship. Exmouth was laid down by Laird Brothers at Birkenhead in August 1899, launched in August 1901, and completed in May 1903.

The London class was a group of five predreadnought battleships built for the British Royal Navy in the late 1890s and early 1900s. The class comprised London, Bulwark, Venerable, Queen, and Prince of Wales. The ships of the London class were very similar to the preceding Formidable class, with the main differences being their armour layout. They were armed with a battery of four 12-inch (305 mm) guns and they had top speed of 18 knots. They are sometimes referred to as being part of the Formidable class due to their similarity, or as being a class of three ships, with the last two forming their own Queen class. The five ships were built between 1898 and 1904 at the Portsmouth, Devonport, and Chatham Dockyards.

HMS Topaze was a Topaze-class protected or third-class cruiser which served in the Royal Navy during the First World War. The vessel was the lead ship of the class, also known as the Gem class, which had a more powerful armament and were faster than preceding protected cruisers. Launched on 23 June 1904, Topaze joined the Channel Fleet and often acted as a flotilla leader for the destroyers of the Navy. At the beginning of the First World War, the cruiser operated with the Fifth Battle Squadron, but was transferred to the Mediterranean Fleet in 1915. There, the cruiser operated with ships of the Italian Regia Marina to enforce the blockade on Albania and to escort ships carrying Italian troops and supplies across the Adriatic Sea. Topaze escorted shipping in the Indian Ocean and captured the Ottoman Army garrison on the island of Kamaran in 1917, but returned to the Mediterranean before the end of the year. After the Armistice in 1918, the cruiser returned to the United Kingdom and was decommissioned on 7 October 1919.