
Chromium is a chemical element; it has symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.

Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials that results in a significant, observable magnetic permeability, and in many cases, a significant magnetic coercivity, allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagnetic materials are familiar metals that are noticeably attracted to a magnet, a consequence of their substantial magnetic permeability. Magnetic permeability describes the induced magnetization of a material due to the presence of an external magnetic field. This temporarily induced magnetization, for example, inside a steel plate, accounts for its attraction to the permanent magnet. Whether or not that steel plate acquires a permanent magnetization itself depends not only on the strength of the applied field but on the so-called coercivity of the ferromagnetic material, which can vary greatly.
Spintronics, also known as spin electronics, is the study of the intrinsic spin of the electron and its associated magnetic moment, in addition to its fundamental electronic charge, in solid-state devices. The field of spintronics concerns spin-charge coupling in metallic systems; the analogous effects in insulators fall into the field of multiferroics.

In materials that exhibit antiferromagnetism, the magnetic moments of atoms or molecules, usually related to the spins of electrons, align in a regular pattern with neighboring spins pointing in opposite directions. This is, like ferromagnetism and ferrimagnetism, a manifestation of ordered magnetism. The phenomenon of antiferromagnetism was first introduced by Lev Landau in 1933.
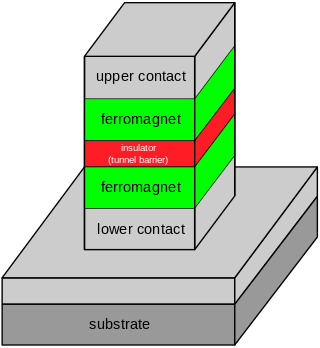
Tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) is a magnetoresistive effect that occurs in a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ), which is a component consisting of two ferromagnets separated by a thin insulator. If the insulating layer is thin enough, electrons can tunnel from one ferromagnet into the other. Since this process is forbidden in classical physics, the tunnel magnetoresistance is a strictly quantum mechanical phenomenon, and lies in the study of spintronics.
Colossal magnetoresistance (CMR) is a property of some materials, mostly manganese-based perovskite oxides, that enables them to dramatically change their electrical resistance in the presence of a magnetic field. The magnetoresistance of conventional materials enables changes in resistance of up to 5%, but materials featuring CMR may demonstrate resistance changes by orders of magnitude.

Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) is a quantum mechanical magnetoresistance effect observed in multilayers composed of alternating ferromagnetic and non-magnetic conductive layers. The 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Albert Fert and Peter Grünberg for the discovery of GMR, which also sets the foundation for the study of spintronics.
Magnetic semiconductors are semiconductor materials that exhibit both ferromagnetism and useful semiconductor properties. If implemented in devices, these materials could provide a new type of control of conduction. Whereas traditional electronics are based on control of charge carriers, practical magnetic semiconductors would also allow control of quantum spin state. This would theoretically provide near-total spin polarization, which is an important property for spintronics applications, e.g. spin transistors.
Multiferroics are defined as materials that exhibit more than one of the primary ferroic properties in the same phase:
Exchange bias or exchange anisotropy occurs in bilayers of magnetic materials where the hard magnetization behavior of an antiferromagnetic thin film causes a shift in the soft magnetization curve of a ferromagnetic film. The exchange bias phenomenon is of tremendous utility in magnetic recording, where it is used to pin the state of the readback heads of hard disk drives at exactly their point of maximum sensitivity; hence the term "bias."

Heusler compounds are magnetic intermetallics with face-centered cubic crystal structure and a composition of XYZ (half-Heuslers) or X2YZ (full-Heuslers), where X and Y are transition metals and Z is in the p-block. The term derives from the name of German mining engineer and chemist Friedrich Heusler, who studied such a compound (Cu2MnAl) in 1903. Many of these compounds exhibit properties relevant to spintronics, such as magnetoresistance, variations of the Hall effect, ferro-, antiferro-, and ferrimagnetism, half- and semimetallicity, semiconductivity with spin filter ability, superconductivity, topological band structure and are actively studied as Thermoelectric materials. Their magnetism results from a double-exchange mechanism between neighboring magnetic ions. Manganese, which sits at the body centers of the cubic structure, was the magnetic ion in the first Heusler compound discovered. (See the Bethe–Slater curve for details of why this happens.)
Spin-polarized scanning tunneling microscopy (SP-STM) is a type of scanning tunneling microscope (STM) that can provide detailed information of magnetic phenomena on the single-atom scale additional to the atomic topography gained with STM. SP-STM opened a novel approach to static and dynamic magnetic processes as precise investigations of domain walls in ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic systems, as well as thermal and current-induced switching of nanomagnetic particles.

Lanthanum strontium manganite (LSM or LSMO) is an oxide ceramic material with the general formula La1−xSrxMnO3, where x describes the doping level.
Molecule-based magnets (MBMs) or molecular magnets are a class of materials capable of displaying ferromagnetism and other more complex magnetic phenomena. This class expands the materials properties typically associated with magnets to include low density, transparency, electrical insulation, and low-temperature fabrication, as well as combine magnetic ordering with other properties such as photoresponsiveness. Essentially all of the common magnetic phenomena associated with conventional transition-metal magnets and rare-earth magnets can be found in molecule-based magnets. Prior to 2011, MBMs were seen to exhibit "magnetic ordering with Curie temperature (Tc) exceeding room temperature".
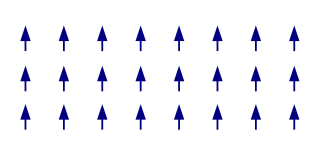
The term magnetic structure of a material pertains to the ordered arrangement of magnetic spins, typically within an ordered crystallographic lattice. Its study is a branch of solid-state physics.

Superexchange or Kramers–Anderson superexchange interaction, is a prototypical indirect exchange coupling between neighboring magnetic moments by virtue of exchanging electrons through a non-magnetic anion known as the superexchange center. In this way, it differs from direct exchange, in which there is direct overlap of electron wave function from nearest neighboring cations not involving an intermediary anion or exchange center. While direct exchange can be either ferromagnetic or antiferromagnetic, the superexchange interaction is usually antiferromagnetic, preferring opposite alignment of the connected magnetic moments. Similar to the direct exchange, superexchange calls for the combined effect of Pauli exclusion principle and Coulomb's repulsion of the electrons. If the superexchange center and the magnetic moments it connects to are non-collinear, namely the atomic bonds are canted, the superexchange will be accompanied by the antisymmetric exchange known as the Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction, which prefers orthogonal alignment of neighboring magnetic moments. In this situation, the symmetric and antisymmetric contributions compete with each other and can result in versatile magnetic spin textures such as magnetic skyrmions.

Chromium(III) boride, also known as chromium monoboride (CrB), is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrB. It is one of the six stable binary borides of chromium, which also include Cr2B, Cr5B3, Cr3B4, CrB2, and CrB4. Like many other transition metal borides, it is extremely hard (21-23 GPa), has high strength (690 MPa bending strength), conducts heat and electricity as well as many metallic alloys, and has a high melting point (~2100 °C). Unlike pure chromium, CrB is known to be a paramagnetic, with a magnetic susceptibility that is only weakly dependent on temperature. Due to these properties, among others, CrB has been considered as a candidate material for wear resistant coatings and high-temperature diffusion barriers.

Bipolar magnetic semiconductors (BMSs) are a special class of magnetic semiconductors characterized by a unique electronic structure, where valence band maximum (VBM) and conduction band minimum (CBM) are fully spin polarized in the opposite spin direction. BMSs can be described by three energy gaps, the spin-flip gap Δ2 in valence band (VB), band gap Δ1 and spin-flip gap Δ3 in conduction band (CB). Up to now, bipolar magnetic semiconductors, together with half-metal and spin gapless semiconductor, have been viewed as three important classes of spintronic materials.
Mohindar Singh Seehra is an Indian-American Physicist, academic and researcher. He is Eberly Distinguished Professor Emeritus at West Virginia University (WVU).

Gang Cao is an American condensed matter physicist, academic, author, and researcher. He is a professor of physics at the University of Colorado Boulder. and Director of Center for Experiments on Quantum Materials.













