Related Research Articles

Lester Garfield Maddox Sr. was an American politician who served as the 75th governor of Georgia from 1967 to 1971. A populist Southern Democrat, Maddox came to prominence as a staunch segregationist when he refused to serve black customers in his Atlanta restaurant, the Pickrick, in violation of the Civil Rights Act of 1964. As he was ineligible to run for a second consecutive gubernatorial term, he sought and won election as lieutenant governor, serving alongside his successor as governor, Jimmy Carter.

Herman Eugene Talmadge was an American politician who served as governor of Georgia in 1947 and from 1948 to 1955 and as a U.S. senator from Georgia from 1957 to 1981. A Democrat, Talmadge served during a time of political transition, both in Georgia and nationally. He began his career as a staunch segregationist known for his opposition to civil rights, ordering schools to be closed rather than desegregated. But by the later stages of his career, following the enactment of the Voting Rights Act, which gave substance to the Fifteenth Amendment enacted nearly one hundred years before, Talmadge, like many other Southern politicians of that period, had modified his views. His life eventually encapsulated the emergence of his native Georgia from entrenched white supremacy into a political culture where white voters regularly elect black members of Congress.

Eugene Talmadge was an attorney and American politician who served three terms as the 67th governor of Georgia, from 1933 to 1937, and then again from 1941 to 1943. Elected to a fourth term in November 1946, he died before his inauguration, scheduled for January 1947. Only Talmadge and Joe Brown, in the mid-19th century, have been elected four times as governor of Georgia.

Melvin Ernest Thompson was an American educator and politician from Millen in the U.S. state of Georgia. Generally known as M.E. Thompson during his political career, he served as the 70th Governor of Georgia from 1947 to 1948 and was elected as the first Lieutenant Governor of Georgia in 1946.

Ellis Gibbs Arnall was an American politician who served as the 69th Governor of Georgia from 1943 to 1947. A liberal Democrat, he helped lead efforts to abolish the poll tax and to reduce Georgia's voting age to 18. Following his departure from office, he became a highly successful attorney and businessman.

Samuel Ernest Vandiver Jr. was an American Democratic Party politician who was the 73rd governor of Georgia from 1959 to 1963.

Carl Edward Sanders Sr. was an American attorney and politician who served as the 74th governor of Georgia from 1963 to 1967.

George Bell Timmerman Jr. was an American politician and World War II veteran who served as the 105th governor of South Carolina from 1955 to 1959. A member of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the state's 76th lieutenant governor from 1947 to 1955.
The Richard B. Russell Library for Political Research and Studies is an archive of political and historical primary documents relating to the modern American political system. The Russell Library is one of three Special Collections Libraries located in the Richard B. Russell Building on the campus of the University of Georgia in Athens. The address is 300 S. Hull Street. The Russell Library is a department within the University of Georgia Libraries that reports to the University Librarian.

Garland Turk Byrd was United States Democratic politician from Georgia, who served as the fourth Lieutenant Governor of Georgia from 1959 to 1963, and as Senator from the 17th District in 1963-4.

The 1966 Georgia gubernatorial election was held on November 8, 1966. After an election that exposed divisions within the Georgia Democratic Party, segregationist Democrat Lester Maddox was elected Governor of Georgia. The voting also brought future President Jimmy Carter to statewide prominence for the first time. The election was very close; Republican candidate Bo Callaway won a plurality of the popular vote, but lost the contingent election in the Georgia General Assembly to Maddox.

An Appeal for Human Rights is a civil rights manifesto initially printed as an advertisement in Atlanta newspapers on March 9, 1960 that called for ending racial inequality in Atlanta, Georgia, United States. The manifesto was written by students of Atlanta's six historically black colleges and universities that comprise the Atlanta University Center. It was drafted by Roslyn Pope and other students of the Atlanta University Center after the students, led by Lonnie King and Julian Bond, were encouraged by the six presidents of the Atlanta University Center to draft a document stating their goals. The students, organized as the Committee on Appeal for Human Rights (COAHR), published An Appeal for Human Rights working within and as part of the Civil Rights Movement.

The Henry Grady Hotel was a hotel in downtown Atlanta, Georgia, United States. The building, designed by architect G. Lloyd Preacher, was completed in 1924 at the intersection of Peachtree Street and Cain Street, on land owned by the government of Georgia that had previously been occupied by the official residence of the governor. The hotel, which was named after journalist Henry W. Grady, was owned by the state and leased to operators. During the mid-1900s, the hotel typically served as the residence of state legislators during the legislative sessions, and it was an important location for politicking, with President Jimmy Carter later saying, "[m]ore of the state's business was probably conducted in the Henry Grady than in the state capitol". In the late 1960s, the government decided to not renew the building's lease when it expired in 1972, and it was demolished that year. The land was sold to developers and the Peachtree Plaza Hotel was built on the site. At the time of its completion in 1976, it was the tallest hotel building in the world.

The three governors controversy was a political crisis in the U.S. state of Georgia from 1946 to 1947. On December 21, 1946, Eugene Talmadge, the governor-elect of Georgia, died before taking office. The state constitution did not specify who would assume the governorship in such a situation, so three men made claims to the governorship: Ellis Arnall, the outgoing governor; Melvin E. Thompson, the lieutenant governor-elect; and Herman Talmadge, Eugene Talmadge's son. Eventually a ruling by the Supreme Court of Georgia settled the matter in favor of Thompson. Georgia's Secretary of State Ben Fortson hid the state seal in his wheelchair so no official business could be conducted until the controversy was settled.

Gridiron Secret Society is a collegiate secret society at the University of Georgia. Gridiron has been called "the highest honor a male student may receive on the University of Georgia campus.". It has also been recognized as one of the "Top 10 Secret Member's Clubs" in the world.
The county unit system was a voting system used by the U.S. state of Georgia to determine a victor in statewide primary elections from 1917 until 1962.
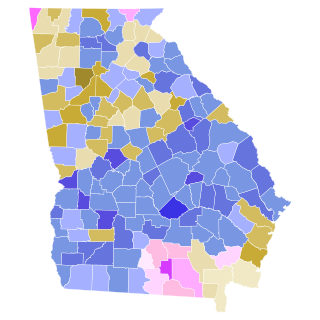
The 1946 Georgia gubernatorial election took place on November 5, 1946, in order to elect the Governor of Georgia.

Josephine Mathewson Wilkins was an American social activist, president of the Georgia State League of Women Voters. She is a 2022 inductee into the Georgia Women of Achievement.
Roy Vincent Harris was an American politician and newspaper publisher in the U.S. state of Georgia during the mid-1900s. From the 1920s until the 1940s, Harris served several terms in both the Georgia House of Representatives and the Georgia State Senate, and he served as the speaker of the house from 1937 to 1940 and again from 1943 to 1946. Historian Harold Paulk Henderson has called Harris "one of Georgia's most capable behind-the-scenes politicians".
References
- ↑ "Harold Paulk (Hal) Henderson, Sr. oral history collection - The Civil Rights History Project: Survey of Collections and Repositories (The American Folklife Center, Library of Congress)". www.loc.gov.
- ↑ "Harold Paulk (Hal) Henderson, Sr. Oral History Collection". russelldoc.galib.uga.edu.
- ↑ Cook, James (2001). "Reviewed work: Ernest Vandiver, Governor of Georgia, Harold Paulk Henderson". The Georgia Historical Quarterly. 85 (1): 161–163. JSTOR 40584396.
- ↑ Henderson, Harold Paulk (June 1, 2008). Ernest Vandiver, Governor of Georgia. University of Georgia Press. ISBN 9780820330600 – via Google Books.
- ↑ "Georgia Press".
- ↑ "Articles by hhenderson".