
Internal fertilization is the union of an egg and sperm cell during sexual reproduction inside the female body. Internal fertilization, unlike its counterpart, external fertilization, brings more control to the female with reproduction. For internal fertilization to happen there needs to be a method for the male to introduce the sperm into the female's reproductive tract.

Penis fencing is a mating behavior engaged in by many species of flatworm, such as Pseudobiceros hancockanus. Species which engage in the practice are hermaphroditic; each individual has both egg-producing ovaries and sperm-producing testes.

The Entelegynae or entelegynes are a subgroup of araneomorph spiders, the largest of the two main groups into which the araneomorphs were traditionally divided. Females have a genital plate (epigynum) and a "flow through" fertilization system; males have complex palpal bulbs. Molecular phylogenetic studies have supported the monophyly of Entelegynae.

Sexual conflict or sexual antagonism occurs when the two sexes have conflicting optimal fitness strategies concerning reproduction, particularly over the mode and frequency of mating, potentially leading to an evolutionary arms race between males and females. In one example, males may benefit from multiple matings, while multiple matings may harm or endanger females, due to the anatomical differences of that species. Sexual conflict underlies the evolutionary distinction between male and female.

Traumatic insemination, also known as hypodermic insemination, is the mating practice in some species of invertebrates in which the male pierces the female's abdomen with his aedeagus and injects his sperm through the wound into her abdominal cavity (hemocoel). The sperm diffuse through the female's hemolymph, reaching the ovaries and resulting in fertilization.

Cimex is a genus of insects in the family Cimicidae. Cimex species are ectoparasites that typically feed on the blood of birds and mammals. Two species, Cimex lectularius and Cimex hemipterus, are known as bed bugs and frequently feed on humans, although other species may parasitize humans opportunistically. Species that primarily parasitize bats are known as bat bugs.
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are also important accessories to the reproductive system. Unlike most organ systems, the sexes of differentiated species often have significant differences. These differences allow for a combination of genetic material between two individuals, which allows for the possibility of greater genetic fitness of the offspring.
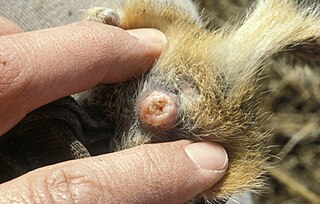
A mating plug, also known as a copulation plug, sperm plug, vaginal plug, or sphragis, is gelatinous secretion used in the mating of some species. It is deposited by a male into a female genital tract, such as the vagina, and later hardens into a plug or glues the tract together. While females can expel the plugs afterwards, the male's sperm still gets a time advantage in getting to the egg, which is often the deciding factor in fertilization.

Harpactea is a genus of woodlouse hunting spiders that was first described by W. S. Bristowe in 1939. They are non-web building predators that forage on the ground and on tree trunks at night, mainly in xerothermic forests. During the day, they hide in silk retreats they build under rocks or bark.

The reproductive system of gastropods varies greatly from one group to another within this very large and diverse taxonomic class of animals. Their reproductive strategies also vary greatly, see Mating of gastropods.
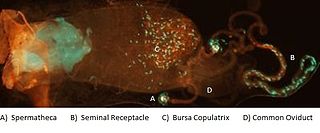
Female sperm storage is a biological process and often a type of sexual selection in which sperm cells transferred to a female during mating are temporarily retained within a specific part of the reproductive tract before the oocyte, or egg, is fertilized. The site of storage is variable among different animal taxa and ranges from structures that appear to function solely for sperm retention, such as insect spermatheca and bird sperm storage tubules, to more general regions of the reproductive tract enriched with receptors to which sperm associate before fertilization, such as the caudal portion of the cow oviduct containing sperm-associating annexins. Female sperm storage is an integral stage in the reproductive process for many animals with internal fertilization. It has several documented biological functions including:

Spiders are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all orders of organisms. Spiders are found worldwide on every continent except for Antarctica, and have become established in nearly every land habitat. As of August 2022, 50,356 spider species in 132 families have been recorded by taxonomists. However, there has been debate among scientists about how families should be classified, with over 20 different classifications proposed since 1900.
Sexual antagonistic co-evolution is the relationship between males and females where sexual morphology changes over time to counteract the opposite's sex traits to achieve the maximum reproductive success. This has been compared to an arms race between sexes. In many cases, male mating behavior is detrimental to the female's fitness. For example, when insects reproduce by means of traumatic insemination, it is very disadvantageous to the female's health. During mating, males will try to inseminate as many females as possible, however, the more times a female's abdomen is punctured, the less likely she is to survive. Females that possess traits to avoid multiple matings will be more likely to survive, resulting in a change in morphology. In males, genitalia is relatively simple and more likely to vary among generations compared to female genitalia. This results in a new trait that females have to avoid in order to survive.
This glossary describes the terms used in formal descriptions of spiders; where applicable these terms are used in describing other arachnids.

Dryomyza anilis is a common fly from the family Dryomyzidae. The fly is found through various areas in the Northern hemisphere and has brown and orange coloration with distinctive large red eyes. The life span of the fly is not known, but laboratory-reared males can live 28–178 days. D. anilis has recently been placed back in the genus Dryomyza, of which it is the type species. Dryomyzidae were previously part of Sciomyzidae but are now considered a separate family with two subfamilies.
Most insects reproduce oviparously, i.e. by laying eggs. The eggs are produced by the female in a pair of ovaries. Sperm, produced by the male in one testis or more commonly two, is transmitted to the female during mating by means of external genitalia. The sperm is stored within the female in one or more spermathecae. At the time of fertilization, the eggs travel along oviducts to be fertilized by the sperm and are then expelled from the body ("laid"), in most cases via an ovipositor.
Cryptic female choice is a form of mate choice which occurs both in pre and post copulatory circumstances when females in certain species use physical or chemical mechanisms to control a male's success of fertilizing their ova or ovum; i.e. by selecting whether sperm are successful in fertilizing their eggs or not. It occurs in internally-fertilizing species and involves differential use of sperm by females when sperm are available in the reproductive tract.
Macrostomum hystrix is a free-living flatworm in the family Macrostomidae. It is small, transparent, and a simultaneous hermaphrodite.

Philodromus cespitum is a species of running crab spider in the family Philodromidae. It is found in North America, Europe, North Africa, and parts of the Middle East and Asia. P. cespitum is a foliage-dweller, and is the most abundant species found in European fruit orchards. It acts as a biological control by preying on orchard pests. P. cespitum is a diurnal ambush hunter and preys on aphids, insects, and occasionally competitor spider species. Males court females by tapping on the females’ bodies with their forelegs. They then insert a genital plug into the female during copulation. Unlike in many other spider species, subsequent males can mate with plugged females by removing part of the plug prior to copulation. Males discriminate among females based on virginity and plug size, and can determine these factors using the females’ draglines and plug samples.

Self-insemination is a mating behavior engaged in by individuals of multiple flatworm species, such as the free-living Macrostomum hystrix. Species that engage in this method of reproduction are hermaphroditic, meaning they possess both male and female reproductive organs. Selfing is referred to as a conditional reproductive strategy in this species, which means that there is a preference to reproduce with a mate.













