
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance or energy. Pollutants, the components of pollution, can be either foreign substances/energies or naturally occurring contaminants.

Indoor air quality (IAQ) is the air quality within and around buildings and structures. IAQ is known to affect the health, comfort, and well-being of building occupants. Poor indoor air quality has been linked to sick building syndrome, reduced productivity, and impaired learning in schools. Common pollutants of indoor air include: secondhand tobacco smoke, air pollutants from indoor combustion, radon, molds and other allergens, carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds, legionella and other bacteria, asbestos fibers, carbon dioxide, ozone and particulates. Source control, filtration, and the use of ventilation to dilute contaminants are the primary methods for improving indoor air quality.
Environmental Defense Fund or EDF is a United States-based nonprofit environmental advocacy group. The group is known for its work on issues including global warming, ecosystem restoration, oceans, and human health, and advocates using sound science, economics and law to find environmental solutions that work. It is nonpartisan, and its work often advocates market-based solutions to environmental problems.

Mountaintop removal mining (MTR), also known as mountaintop mining (MTM), is a form of surface mining at the summit or summit ridge of a mountain. Coal seams are extracted from a mountain by removing the land, or overburden, above the seams. This process is considered to be safer compared to underground mining because the coal seams are accessed from above instead of underground. In the United States, this method of coal mining is conducted in the Appalachian Mountains in the eastern United States. Explosives are used to remove up to 400 vertical feet of mountain to expose underlying coal seams. Excess rock and soil is dumped into nearby valleys, in what are called "holler fills" or "valley fills".
A Patient Safety Organization (PSO) is a group, institution, or association that improves medical care by reducing medical errors. Common functions of patient safety organizations are data collection and analysis, reporting, education, funding, and advocacy. A PSO differs from a Federally designed Patient Safety Organization (PSO), which provides health care providers in the U.S. privilege and confidentiality protections for efforts to improve patient safety and the quality of patient care delivery
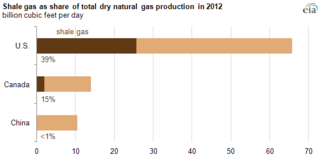
Shale gas is an unconventional natural gas that is found trapped within shale formations. Since the 1990s a combination of horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing has made large volumes of shale gas more economical to produce, and some analysts expect that shale gas will greatly expand worldwide energy supply.

The health and environmental impact of the coal industry includes issues such as land use, waste management, water and air pollution, caused by the coal mining, processing and the use of its products. In addition to atmospheric pollution, coal burning produces hundreds of millions of tons of solid waste products annually, including fly ash, bottom ash, and flue-gas desulfurization sludge, that contain mercury, uranium, thorium, arsenic, and other heavy metals. Coal is the largest contributor to the human-made increase of carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere.
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials into the atmosphere, causing harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or damaging ecosystems. Air pollution can cause health problems including, but not limited to, infections, behavioral changes, cancer, organ failure, and premature death. These health effects are not equally distributed across the U.S population; there are demographic disparities by race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and education. Air pollution can derive from natural sources, or anthropogenic sources. Anthropogenic air pollution has affected the United States since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution.
Respiratory Health Association is a nonprofit organization located on Chicago's Near West Side.
Post Occupancy Evaluation (POE) has its origins in Scotland and the United States and has been used in one form or another since the 1960s. Preiser and colleagues define POE as "the process of evaluating buildings in a systematic and rigorous manner after they have been built and occupied for some time".

Pollution in California relates to the degree of pollution in the air, water, and land of the state of California. Pollution is defined as the addition of any substance or any form of energy to the environment at a faster rate than it can be dispersed, diluted, decomposed, recycled, or stored in some harmless form. The combination of three main factors are the cause of notable unhealthy levels of air pollution in California: the activities of over 39 million people, a mountainous terrain that traps pollution, and a warm climate that helps form ozone and other pollutants. Eight of the ten cities in the US with the highest year-round concentration of particulate matter between 2013 and 2015 were in California, and seven out of the ten cities in the US with the worst ozone pollution were also in California. Studies show that pollutants prevalent in California are linked to several health issues, including asthma, lung cancer, birth complications, and premature death. In 2016, Bakersfield, California recorded the highest level of airborne pollutants of any city in the United States.
The Institute of Occupational Medicine (IOM) was founded in 1969 by the National Coal Board (NCB) as an independent charity in Edinburgh, UK and retains its charitable purpose and status today. The "Institute" has a subsidiary, IOM Consulting Limited, which became fully independent in 1990 and now celebrates its 25th year within the IOM Group as an independent consultancy and also the commercial part of the IOM organization. It specializes in asbestos surveys and services, occupational hygiene services, nanotechnology safety, laboratory analysis and expert witness consulting services. IOM is therefore one of the UK's major independent "not for profit" centres of scientific excellence in the fields of environmental health, occupational hygiene and occupational safety. Its mission is to benefit those at work and in the community by providing quality research, consultancy, surveys, analysis and training and by maintaining an independent, impartial position as an international centre of excellence.

The Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment, commonly referred to as OEHHA, is a specialized department within the cabinet-level California Environmental Protection Agency (CalEPA) with responsibility for evaluating health risks from environmental chemical contaminants.

In the 1950s, the Navajo Nation was situated directly in the uranium mining belt that experienced a boom in production, and many residents found work in the mines. Prior to 1962, the risks of lung cancer due to uranium mining were unknown to the workers, and the lack of a word for radiation in the Navajo language left the miners unaware of the associated health hazards. The cultural significance of water for the Navajo people and the environmental damage to both the land and livestock inhibits the ability of the Navajo people to practice their culture.

Water pollution in the United States is a growing problem that became critical in the 19th century with the development of mechanized agriculture, mining, and industry, although laws and regulations introduced in the late 20th century have improved water quality in many water bodies. Extensive industrialization and rapid urban growth exacerbated water pollution as a lack of regulation allowed for discharges of sewage, toxic chemicals, nutrients and other pollutants into surface water.

Environmental justice and coal mining in Appalachia is the study of environmental justice – the interdisciplinary body of social science literature studying theories of the environment and justice; environmental laws, policies, and their implementations and enforcement; development and sustainability; and political ecology – in relation to coal mining in Appalachia.

Environmental issues in Appalachia, a cultural region in the Eastern United States, include long term and ongoing environmental impact from human activity, and specific incidents of environmental harm such as environmental disasters related to mining. A mountainous area with significant coal deposits, many environmental issues in the region are related to coal and gas extraction. Some extraction practices, particularly surface mining, have met significant resistance locally and at times have received international attention.

The Complex Engineering Systems Institute (ISCI), housed at Universidad de Chile and having Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile as an associate institution, brings together a group of top researchers from eight Chilean universities. Each of the researchers has been invited to join ISCI in view of their academic merit and for their existing or potential synergy with other ISCI members. This is the case with the 58 current ISCI members, who come from the Universidad de Chile, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Universidad de Santiago de Chile, Universidad Diego Portales, Universidad Adolfo Ibáñez, Universidad de los Andes, Universidad de Talca, and Universidad de Concepción.
The Harvard "Six Cities" study was a major epidemiological study of over 8,000 adults in six American cities that helped to establish the connection between fine-particulate air pollution and reduced life expectancy. Widely acknowledged as a landmark piece of public health research, it was initiated by Benjamin G. Ferris, Jr at Harvard School of Public Health and carried out by Harvard's Douglas Dockery, C. Arden Pope of Brigham Young University, Ferris himself, Frank E. Speizer, and four other collaborators, and published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 1993. Following a lawsuit by The American Lung Association, the study, and its various follow-ups, led to a tightening of pollution standards by the US Environmental Protection Agency. This prompted an intense backlash from industry groups in the late 1990s, culminating in a Supreme Court case, in what Science magazine termed "the biggest environmental fight of the decade".
Environmental racism is a form of institutional racism, in which people of colour bear a disproportionate burden of environmental harms, such as pollution from hazardous waste disposal and the effects of natural disasters. Environmental racism exposes Native Americans, African Americans, Asian Americans, Pacific Islanders, and Hispanic populations to physical health hazards and may negatively impact mental health. It creates disparities in many different spheres of life, such as transportation, housing, and economic opportunity.











