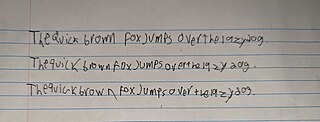Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by executive dysfunction occasioning symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and otherwise age-inappropriate.

Homework is a set of tasks assigned to students by their teachers to be completed at home. Common homework assignments may include required reading, a writing or typing project, mathematical exercises to be completed, information to be reviewed before a test, or other skills to be practiced.
Developmental disorders comprise a group of psychiatric conditions originating in childhood that involve serious impairment in different areas. There are several ways of using this term. The most narrow concept is used in the category "Specific Disorders of Psychological Development" in the ICD-10. These disorders comprise developmental language disorder, learning disorders, motor disorders, and autism spectrum disorders. In broader definitions ADHD is included, and the term used is neurodevelopmental disorders. Yet others include antisocial behavior and schizophrenia that begins in childhood and continues through life. However, these two latter conditions are not as stable as the other developmental disorders, and there is not the same evidence of a shared genetic liability.
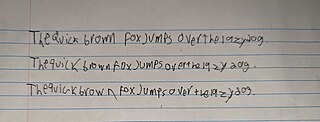
Dysgraphia is a neurological disorder and learning disability that concerns written expression, which affects the ability to write, primarily handwriting, but also coherence. It is a specific learning disability (SLD) as well as a transcription disability, meaning that it is a writing disorder associated with impaired handwriting, orthographic coding and finger sequencing. It often overlaps with other learning disabilities and neurodevelopmental disorders such as speech impairment, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or developmental coordination disorder (DCD).

Hyperfocus is an intense form of mental concentration or visualization that focuses consciousness on a subject, topic, or task. In some individuals, various subjects or topics may also include daydreams, concepts, fiction, the imagination, and other objects of the mind. Hyperfocus on a certain subject can cause side-tracking away from assigned or important tasks.
Adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is the neurological condition of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults. About one-third to two-thirds of children with symptoms from early childhood continue to demonstrate ADHD symptoms throughout life.
Child psychopathology refers to the scientific study of mental disorders in children and adolescents. Oppositional defiant disorder, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, and autism spectrum disorder are examples of psychopathology that are typically first diagnosed during childhood. Mental health providers who work with children and adolescents are informed by research in developmental psychology, clinical child psychology, and family systems. Lists of child and adult mental disorders can be found in the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Edition (ICD-10), published by the World Health Organization (WHO) and in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). In addition, the Diagnostic Classification of Mental Health and Developmental Disorders of Infancy and Early Childhood is used in assessing mental health and developmental disorders in children up to age five.
Cognitive disengagement syndrome (CDS) is an attention syndrome characterised by prominent dreaminess, mental fogginess, hypoactivity, sluggishness, slow reaction time, staring frequently, inconsistent alertness, and a slow working speed.
Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) is listed in the DSM-5 under Disruptive, impulse-control, and conduct disorders and defined as "a pattern of angry/irritable mood, argumentative/defiant behavior, or vindictiveness". This behavior is usually targeted toward peers, parents, teachers, and other authority figures. Unlike conduct disorder (CD), those with ODD do not show patterns of aggression towards people or animals, destruction of property, theft, or deceit. One half of children with ODD also fulfill the diagnostic criteria for ADHD.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder predominantly inattentive, is one of the three presentations of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). In 1987–1994, there were no subtypes and thus it was not distinguished from hyperactive ADHD in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-III-R).

Despite the scientifically well-established nature of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), its diagnosis, and its treatment, each of these has been controversial since the 1970s. The controversies involve clinicians, teachers, policymakers, parents, and the media. Positions range from the view that ADHD is within the normal range of behavior to the hypothesis that ADHD is a genetic condition. Other areas of controversy include the use of stimulant medications in children, the method of diagnosis, and the possibility of overdiagnosis. In 2009, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, while acknowledging the controversy, states that the current treatments and methods of diagnosis are based on the dominant view of the academic literature.
Emotional and behavioral disorders refer to a disability classification used in educational settings that allows educational institutions to provide special education and related services to students who have displayed poor social and/or academic progress.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder management options are evidence-based practices with established treatment efficacy for ADHD.

Learning disability, learning disorder, or learning difficulty is a condition in the brain that causes difficulties comprehending or processing information and can be caused by several different factors. Given the "difficulty learning in a typical manner", this does not exclude the ability to learn in a different manner. Therefore, some people can be more accurately described as having a "learning difference", thus avoiding any misconception of being disabled with a possible lack of an ability to learn and possible negative stereotyping. In the United Kingdom, the term "learning disability" generally refers to an intellectual disability, while conditions such as dyslexia and dyspraxia are usually referred to as "learning difficulties".
In psychology and neuroscience, executive dysfunction, or executive function deficit, is a disruption to the efficacy of the executive functions, which is a group of cognitive processes that regulate, control, and manage other cognitive processes. Executive dysfunction can refer to both neurocognitive deficits and behavioural symptoms. It is implicated in numerous psychopathologies and mental disorders, as well as short-term and long-term changes in non-clinical executive control.
The Pediatric Attention Disorders Diagnostic Screener (PADDS), created by Dr. Thomas K. Pedigo and Kenneth L. Pedigo, is a suite of computer administered neuropsychological tests of attention and executive functioning. The PADDS is used in the diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children between the ages of 6 and 12 years. The PADDS software program represents a multi-dimensional, evidence-based approach to ADHD assessment, consisting of the Computer Administered Diagnostic Interview (CADI), the Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham—IV (SNAP-IV) Parent and Teacher rating scales, and the three computer-administered objective measures of the Target Tests of Executive Functioning (TTEF). It calculates a diagnostic likelihood ratio, where each data source is allowed to contribute to (or detract from) the prediction of the diagnosis, as well as normalized relative standard scores, t-scores, z-scores, and percentile ranks for comparison to the non-clinical reference group.
Mental disorders diagnosed in childhood can be neurodevelopmental, emotional, or behavioral disorders. These disorders negatively impact the mental and social wellbeing of a child, and children with these disorders require support from their families and schools. Childhood mental disorders often persist into adulthood. These disorders are usually first diagnosed in infancy, childhood, or adolescence, as laid out in the DSM-5 and in the ICD-11.
The Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function (BRIEF) is an assessment of executive function behaviors at home and at school for children and adolescents ages 5–18. It was originally developed by Gerard Gioia, Ph.D., Peter Isquith, Ph.D., Steven Guy, Ph.D., and Lauren Kenworthy, Ph.D.

Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (DMDD) is a mental disorder in children and adolescents characterized by a persistently irritable or angry mood and frequent temper outbursts that are disproportionate to the situation and significantly more severe than the typical reaction of same-aged peers. DMDD was added to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) as a type of depressive disorder diagnosis for youths. The symptoms of DMDD resemble those of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), anxiety disorders, and childhood bipolar disorder.
Ernest "Mark" Mahone is an American pediatric neuropsychologist.