
The Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) was a regulatory agency in the United States created by the Interstate Commerce Act of 1887. The agency's original purpose was to regulate railroads to ensure fair rates, to eliminate rate discrimination, and to regulate other aspects of common carriers, including interstate bus lines and telephone companies. Congress expanded ICC authority to regulate other modes of commerce beginning in 1906. Throughout the 20th century, several of ICC's authorities were transferred to other federal agencies. The ICC was abolished in 1995, and its remaining functions were transferred to the Surface Transportation Board.
The Mann–Elkins Act, also called the Railway Rate Act of 1910, was a United States federal law that strengthened the authority of the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) over railroad rates. The law also expanded the ICC's jurisdiction to include regulation of telephone, telegraph and wireless companies, and created a commerce court.
The Transportation Act, 1920, commonly known as the Esch–Cummins Act, was a United States federal law that returned railroads to private operation after World War I, with much regulation. It also officially encouraged private consolidation of railroads and mandated that the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) ensure their profitability. The act was named after Rep. John J. Esch and Sen. Albert B. Cummins.

The Staggers Rail Act of 1980 is a United States federal law that deregulated the American railroad industry to a significant extent, and it replaced the regulatory structure that had existed since the Interstate Commerce Act of 1887.
In the United States government, independent agencies are agencies that exist outside the federal executive departments and the Executive Office of the President. In a narrower sense, the term refers only to those independent agencies that, while considered part of the executive branch, have regulatory or rulemaking authority and are insulated from presidential control, usually because the president's power to dismiss the agency head or a member is limited.
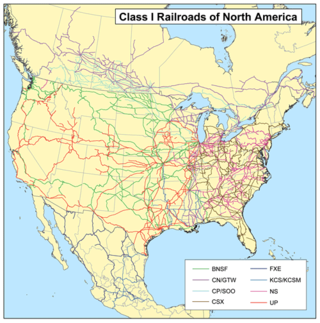
Railroad classes are the system by which freight railroads are designated in the United States. Railroads are assigned to Class I, II or III according to annual revenue criteria originally set by the Surface Transportation Board in 1992. With annual adjustments for inflation, the 2019 thresholds were US$504,803,294 for Class I carriers and US$40,384,263 for Class II carriers.

The Safety Appliance Act is a United States federal law that made air brakes and automatic couplers mandatory on all trains in the United States. It was enacted on March 2, 1893, and took effect in 1900, after a seven-year grace period. The act is credited with a sharp drop in accidents on American railroads in the early 20th century.

The Surface Transportation Board (STB) of the United States is an independent federal agency that serves as an adjudicatory board. The board was created in 1996 following the abolition of the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC), and absorbed regulatory powers relevant to the railroad industry previously under the ICC's purview.

The Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) is an agency in the United States Department of Transportation (DOT). The agency was created by the Department of Transportation Act of 1966. The purpose of the FRA is to promulgate and enforce rail safety regulations, administer railroad assistance programs, conduct research and development in support of improved railroad safety and national rail transportation policy, provide for the rehabilitation of Northeast Corridor rail passenger service, and consolidate government support of rail transportation activities.

The Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act of 1991 is a United States federal law that posed a major change to transportation planning and policy, as the first U.S. federal legislation on the subject in the post-Interstate Highway System era.

The Interstate Commerce Act of 1887 is a United States federal law that was designed to regulate the railroad industry, particularly its monopolistic practices. The Act required that railroad rates be "reasonable and just," but did not empower the government to fix specific rates. It also required that railroads publicize shipping rates and prohibited short haul or long haul fare discrimination, a form of price discrimination against smaller markets, particularly farmers in Western or Southern Territory compared to the Official Eastern states. The Act created a federal regulatory agency, the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC), which it charged with monitoring railroads to ensure that they complied with the new regulations.
Title 49 of the United States Code is a positive law title of the United States Code with the heading "Transportation."

The Western New York and Pennsylvania Railroad is a short-line railroad that operates freight trains in Western New York and Northwest Pennsylvania, United States. The company is controlled by the Livonia, Avon and Lakeville Railroad, with which it does not connect. It started operations in 2001 on the Southern Tier Extension, a former Erie Railroad line between Hornell, NY and Corry, PA, owned by the public Chautauqua, Cattaraugus, Allegany and Steuben Southern Tier Extension Railroad Authority (STERA). Through acquisitions and leases, the line was extended from Corry to Meadville, PA in 2002 and to Oil City, PA in 2006. In 2007, the WNY&P leased and sub-leased portions of the north–south Buffalo Line, a former Pennsylvania Railroad line mostly built by a predecessor of the defunct Western New York and Pennsylvania Railway. The two lines cross at Olean, NY.

Sarah Keys v. Carolina Coach Company, 64 MCC 769 (1955) is a landmark civil rights case in the United States in which the Interstate Commerce Commission, in response to a bus segregation complaint filed in 1953 by a Women's Army Corps (WAC) private named Sarah Louise Keys, broke with its historic adherence to the Plessy v. Ferguson separate but equal doctrine and interpreted the non-discrimination language of the Interstate Commerce Act as banning the segregation of black passengers in buses traveling across state lines.
George W. Bush & Sons Co. v. Malloy, 267 U.S. 317 (1925), was a decision by the United States Supreme Court, which held that the state statute under which the Maryland Public Service Commission (PSC) issued certificates of public convenience and necessity to common carriers engaged in interstate commerce violated the Commerce Clause of the United States Constitution.
The Stony Creek Branch is a railway line in Montgomery County, Pennsylvania. It runs 9.9 miles (15.9 km) from Lansdale, Pennsylvania, to Norristown, Pennsylvania, connecting the Bethlehem and Doylestown Branches with the Norristown Branch. Although SEPTA owns the line, it is freight-only. CSX Transportation, Norfolk Southern Railway, and the Pennsylvania Northeastern Railroad have trackage rights on the branch.

Charles Barnes Goodwin is a United States district judge of the United States District Court for the Western District of Oklahoma. He was formerly a United States magistrate judge of the same court.
Transportation in the United States is governed by laws and regulations of the federal government. The Department of Transportation is responsible for carrying out federal transportation policy, and the Department of Homeland Security is responsible for security in transportation.

The Colebrookdale branch, also known as the Colebrookdale spur, Colebrookdale industrial track or Colebrookdale line, is a railway line in Pennsylvania. It runs 8.6 miles (13.8 km) from a junction with the Harrisburg Line in Pottstown to Boyertown. At its fullest extent, the line continued another 4 miles (6.4 km) to Barto. The line was built between 1868 and 1869 by the Colebrookdale Railroad and part of the Reading Company system until 1976. Berks County has owned the line since 2009. The Eastern Berks Gateway Railroad operates freight service; heritage passenger services are run under the Colebrookdale Railroad name.










