
A registered nurse (RN) is a nurse who has graduated or successfully passed a nursing program from a recognized nursing school and met the requirements outlined by a country, state, province or similar government-authorized licensing body to obtain a nursing license. An RN's scope of practice is determined by legislation, and is regulated by a professional body or council.

The Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) is the regulator for nursing and midwifery professions in the UK. The NMC maintains a register of all nurses, midwives and specialist community public health nurses and nursing associates eligible to practise within the UK. It sets and reviews standards for their education, training, conduct and performance. The NMC also investigates allegations of impaired fitness to practise.
Nurse education consists of the theoretical and practical training provided to nurses with the purpose to prepare them for their duties as nursing care professionals. This education is provided to student nurses by experienced nurses and other medical professionals who have qualified or experienced for educational tasks, traditionally in a type of professional school known as a nursing school of college of nursing. Most countries offer nurse education courses that can be relevant to general nursing or to specialized areas including mental health nursing, pediatric nursing, and post-operative nursing. Nurse education also provides post-qualification courses in specialist subjects within nursing.
Nursing in the United Kingdom is the largest health care profession in the country. It has evolved from assisting doctors to encompass a variety of professional roles. Over 700,000 nurses practice, working in settings such as hospitals, health centres, nursing homes, hospices, communities, military, prisons, and academia. Most are employed by the National Health Service (NHS).

The Medical Council of India (MCI) was a statutory body for establishing uniform and high standards of medical education in India until its dissolution on 25 September 2020 when it was replaced by National Medical Commission. The Council granted recognition of medical qualifications, gave accreditation to medical schools, granted registration to medical practitioners, and monitored medical practice in India. The MCI faced persistent criticism for corruption.

Nursing in Australia is a health care profession. Nurses and midwives form the majority (54%) of Australian health care professionals. Nurses are either registered or enrolled. Registered nurses have broader and deeper education than enrolled nurses. Nurse practitioners complete a yet higher qualification. Nurses are not limited to working in hospitals, instead working in a variety of settings. Australian nurses are in demand as traveling nurses, particularly those with advanced qualifications.

Services Hospital, located on Jail Road, Lahore, in Punjab, Pakistan, is the teaching hospital for the Services Institute of Medical Sciences (SIMS).

Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences (SGPGI) is a medical Institute under the State Legislature Act in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, 14 km (8.7 mi) south of Hazratganj on Raebareli Road. It was established in 1983 and is named after Sanjay Gandhi.

The Veterinary Council of India (VCI) is a statutory body which regulates veterinary practice in India. Established under the Ministry of Agriculture of the Government of India in 1984, and based in New Delhi, the council is governed by the Indian Veterinary Council Act, 1984. The first members were nominated in 1989. The first elections to the council took place in 1999. Since May 2019 after the creation of Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying the Veterinary Council of India is functional as a statutory body under this ministry.

College of Physicians & Surgeons of Mumbai or CPS Mumbai or CPS Bombay, established in 1912, is an autonomous body imparting Postgraduate Medical Education and offers 10 Fellowship & 17 Diploma Courses. It is located in Mumbai near KEM Hospital and it caters to doctors from all over India. The qualifications granted by CPS Mumbai allow the Practitioner to register themselves as specialists in the specialty concerned, upon duly completing the tenure of 2 years Diploma or 3 years Fellowship and passing the exit examination prescribed.

Health professional requisites refer to the regulations used by countries to control the quality of health workers practicing in their jurisdictions and to control the size of the health labour market. They include licensure, certification and proof of minimum training for regulated health professions.
Nursing in India is the practice of providing care for patients, families, and communities in that nation to improve health and quality of life.
Higher education accreditation is a type of quality assurance process under which services and operations of post-secondary educational institutions or programs are evaluated to determine if applicable standards are met. If standards are met, accredited status is granted by the agency.

A paraveterinary worker is a professional of veterinary medicine who performs procedures autonomously or semi-autonomously, as part of a veterinary assistance system. The job role varies throughout the world, and common titles include veterinary nurse, veterinary technician, and veterinary assistant, and variants with the prefix of "animal health".
In India, the Kerala Nurses and Midwives Council was established in 1953 under the provisions of Nurses and Midwives Act and works as an autonomous body under the Government of Kerala, Department of Health and Family Welfare. It is a regulatory body for nurses and education in nursing in Kerala and It is monitored by Indian Nursing Council.

Assam Down Town University was established through the Assam Down Town University Act, 2010 in the state of Assam, India in 2010. The university is located in Panikhaiti, Guwahati, the capital of Assam. The campus is based out of a 42 acres campus overlooking the Brahmaputra River, only 12 km from the Assam State Secretariat, Dispur; the capital complex of the state of Assam.
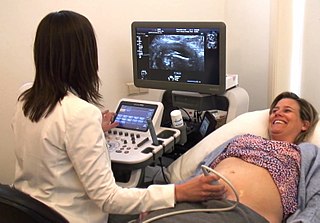
A midwife is a health professional who cares for mothers and newborns around childbirth, a specialization known as midwifery.
Auxiliary nurse midwife or nurse hybrids commonly known as ANM, is a village-level female health worker in India who is known as the first contact person between the community and the health services. ANMs are regarded as the grass-roots workers in the health organisation pyramid. Their services are considered important to provide safe and effective care to village communities. The role may help communities achieve the targets of national health programmes.
Midwives in South Africa are nurses who focus on the care of pregnant women and the delivery of babies. Midwives have the ability to work independently in cases of healthy pregnancies and problem-free deliveries; however, they can refer patients to gynaecologists or obstetricians when complications are diagnosed. The majority of pregnant women in South Africa use the public healthcare system, and most of this care is provided by midwives.












