
The United Nations General Assembly is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as its main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ. Currently in its 78th session, its powers, composition, functions, and procedures are set out in Chapter IV of the United Nations Charter. The UNGA is responsible for the UN budget, appointing the non-permanent members to the Security Council, appointing the UN secretary-general, receiving reports from other parts of the UN system, and making recommendations through resolutions. It also establishes numerous subsidiary organs to advance or assist in its broad mandate. The UNGA is the only UN organ where all member states have equal representation.

The United Nations Economic and Social Council is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations, responsible for coordinating the economic and social fields of the organization, specifically in regards to the fifteen specialised agencies, the eight functional commissions, and the five regional commissions under its jurisdiction.

The member states of the United Nations comprise 193 sovereign states. The United Nations (UN) is the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.
The United Nations General Assembly has granted observer status to international organizations, entities, and non-member states, to enable them to participate in the work of the United Nations General Assembly, though with limitations. The General Assembly determines the privileges it will grant to each observer, beyond those laid down in a 1986 Conference on treaties between states and international organizations. Exceptionally, the European Union (EU) was in 2011 granted the right to speak in debates, to submit proposals and amendments, the right of reply, to raise points of order and to circulate documents, etc. As of May 2011, the EU is the only international organization to hold these enhanced rights, which has been likened to the rights of full membership, short of the right to vote.

Yusril Ihza Mahendra is an Indonesian lawyer, politician and academic, who is currently serving as the leader of the Crescent Star Party (PBB) since 2015. Previously, he served as the leader of the PBB from 1998 until 2005, Minister of Justice and Human Rights from 2004 until 2007, and member of the People's Representative Council from 1999 until 2009.

Dalius Čekuolis is a Lithuanian career diplomat who was Lithuania's Permanent Representative to the UN from 2006 to 2012, and since 2019 is Deputy Minister of Foreign Affairs of Lithuania. Previously, he served as the President of the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC), a primary organ of the United Nations (2007), Chair of the Third Biennial Meeting of States to Consider the Implementation of the United Nations Conference on the Illicit Trade in Small Arms to Prevent, Combat and Eradicate the Illicit Trade in Small Arms and Light Weapons in All its Aspects (2008), Co-Chairman of the Ad Hoc Working Group on the Revitalization of the General Assembly (2010-2011), as well as the Vice-minister of Foreign Affairs and an ambassador of Lithuania to several European countries.
Brazil is a founding member of the United Nations and participates in all of its specialized agencies. Brazil is among the twenty top contributors to United Nations peacekeeping operations, and has participated in peacekeeping efforts in the Middle East, the former Belgian Congo, Cyprus, Mozambique, Angola, and more recently East Timor and Haiti. Brazil has been regularly elected as a non-permanent member to the Security Council since its first session in 1946 and is now among the most elected UN member states to the UNSC. Brazil was voted to become a member of the 15-country UN Security Council for a two-year term, in 2022-23.

Lambertus Nicodemus Palar, also known as Babe Palar, represented the Republic of Indonesia in various diplomatic positions most notably as the first Indonesian representative to the United Nations. He also held ambassadorships in India, West Germany, the Soviet Union, Canada, and the United States. He was the son of Gerrit Palar and Jacoba Lumanauw.
The Holy See is not a member of the United Nations but was granted permanent observer state status on 6 April 1964. In that capacity, it has the right to attend all sessions of the United Nations General Assembly, the United Nations Security Council, and the United Nations Economic and Social Council to observe their work. Accordingly, the Holy See has established permanent observer missions in New York and in Geneva and has been able to influence the decisions and recommendations of the United Nations.
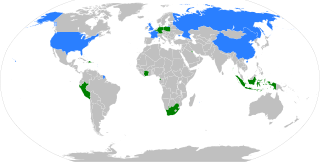
The 2018 United Nations Security Council election was held on 8 June during the 72nd session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections were for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2019.
Malaysia became the 82nd member of the United Nations on 17 September 1957. Malaysia has held a rotational non-permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council for four terms, and has participated in over 30 United Nations peacekeeping missions since October 1960.
The Grand Duchy of Luxembourg is a charter member of the United Nations and served as one of the ten non-permanent members of the UN Security Council (2013–2014).
The People's Socialist Republic of Albania joined the United Nations on 14 December 1955, and has participated in several UN peacekeeping operations. The current Representative of Albania in the UN is Mr. Ferit Hoxha. Albania is a non-permanent member of the 15-country UN Security Council for the two-year term (2022–2023).

Democratic Federal Yugoslavia was a charter member of the United Nations from its establishment in 1945 as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia until 1992 during the Yugoslav Wars. During its existence the country played a prominent role in the promotion of multilateralism and narrowing of the Cold War divisions in which various UN bodies were perceived as important vehicles. Yugoslavia was elected a non-permanent member of the United Nations Security Council on multiple occasions in periods between 1950 and 1951, 1956, 1972–1973, and 1988–1989, which was in total 7 years of Yugoslav membership in the organization. The country was also one of 17 original members of the Special Committee on Decolonization.

Bangladesh and the United Nations have a strong relationship. Bangladesh is one of the largest troop contributing countries in the world.

The president of the United Nations Economic and Social Council is the presiding officer of that body.

Helmi Hasan is an Indonesian politician from the National Mandate Party who is the mayor of the city of Bengkulu.

Bambang Suryadi, also known by his nickname Basur was an Indonesian politician from the Indonesian Democratic Party of Struggle who served as a member of the Central Lampung Regional People's Representative Council from 2004 until 2014, Member of the Lampung Regional People's Representative Council from 2014 until 2019, and Member of the People's Representative Council from 2019 until his death.

The Permanent Mission of Armenia to the United Nations is the diplomatic mission of Armenia to the United Nations.

Wan Abubakar is an Indonesian politician who was a member of the People's Representative Council between 2009 and 2014. He also briefly served as governor of Riau in 2008. He served as the vice governor to Rusli Zainal since 2003, and when Zainal resigned in July 2008, Abubakar was elevated to governor for the rest of his term.



















