Modoc County is a county in the far northeast corner of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2010 census, the population was 9,686, making it California's third-least populous county. The county seat and only incorporated city is Alturas. Previous county seats include Lake City and Centerville. The county borders Nevada and Oregon.

George R. Crook was a career United States Army officer, most noted for his distinguished service during the American Civil War and the Indian Wars. During the 1880s, the Apache nicknamed Crook Nantan Lupan, which means "Chief Wolf."

The Northern Paiute people are a Numic tribe that has traditionally lived in the Great Basin region of the United States in what is now eastern California, western Nevada, and southeast Oregon. The Northern Paiutes' pre-contact lifestyle was well adapted to the harsh desert environment in which they lived. Each tribe or band occupied a specific territory, generally centered on a lake or wetland that supplied fish and waterfowl. Communal hunt drives, which often involved neighboring bands, would take rabbits and pronghorn from surrounding areas. Individuals and families appear to have moved freely among the bands.
The Modoc War, or the Modoc Campaign, was an armed conflict between the Native American Modoc people and the United States Army in northeastern California and southeastern Oregon from 1872 to 1873. Eadweard Muybridge photographed the early part of the US Army's campaign.

The Modoc are a Native American people who originally lived in the area which is now northeastern California and central Southern Oregon. They are currently divided between Oregon and Oklahoma and are enrolled in either of two federally recognized tribes, the Klamath Tribes in Oregon and the Modoc Tribe of Oklahoma, now known as the Modoc Nation.
The Shoshone or Shoshoni are a Native American tribe with four large cultural/linguistic divisions:

The Warner Mountains are an 85-mile (137 km)-long mountain range running north–south through northeastern California and extending into southern Oregon in the United States. The range lies within the northwestern corner of the Basin and Range Province, extending from the northeastern corner of Lassen County, California, through eastern Modoc County, California, and northward into Lake County, Oregon.
The Snake War (1864–1868) was an irregular war fought by the United States of America against the "Snake Indians," the settlers' term for Northern Paiute, Bannock and Western Shoshone bands who lived along the Snake River. Fighting took place in the states of Oregon, Nevada, and California, and in Idaho Territory. Total casualties from both sides of the conflict numbered 1,762 dead, wounded, or captured.

The 1st Cavalry Regiment is a United States Army regiment that has its antecedents in the early 19th century in the formation of the United States Regiment of Dragoons. To this day, the unit's special designation is "First Regiment of Dragoons". While they were the First Regiment of Dragoons another unit designated the 1st Cavalry Regiment was formed in 1855 and in 1861 was re-designated as the 4th Cavalry Regiment. The First Dragoons became the 1st Cavalry Regiment since they were the oldest mounted regiment.
Fort Bidwell is a census-designated place in Modoc County, California. It is located 32 miles (51 km) northeast of Alturas, at an elevation of 4564 feet. The population was 173 at the 2010 census.
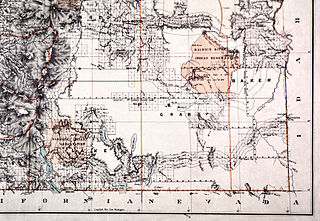
The Malheur Indian Reservation was an Indian reservation established for the Northern Paiute in eastern Oregon and northern Nevada from 1872 to 1879. The federal government discontinued the reservation after the Bannock War of 1878, under pressure from European-American settlers who wanted the land. This negative recommendation against continuing by it’s agent William V. Rinehart, the internment of more than 500 Paiute on the Yakama Indian Reservation, also the reluctance of the Bannock and Paiute to return to the lands after the war.
The 1st Nevada Cavalry Battalion, or the Nevada Territory Cavalry Volunteers, was a unit raised for the Union army during the American Civil War. It remained in the west, garrisoning frontier posts, protecting emigrant routes, and engaged in scouting duties. The unit was disbanded in July 1866.

Camp Warner was a United States Army outpost in south-central Oregon, United States. Camp Warner was located at two different sites approximately 35 miles (56 km) apart. The Army called both sites Camp Warner. However, the first site became known as Old Camp Warner. It was used as winter quarters in 1866–1867 and then abandoned. The second, more developed site is generally known as Fort Warner, although the Army never officially designated it as a fort. Fort Warner was used as a supply depot and administrative headquarters from 1867 to 1874 during a protracted Army campaign against Northern Paiute bands in Eastern Oregon and Northern California. Today, nothing remains of either Old Camp Warner or Fort Warner.

Fort Harney was a United States Army outpost in eastern Oregon in the United States. It was named in honor of Brigadier General William S. Harney. Fort Harney was used as a supply depot and administrative headquarters from 1867 to 1880 during the Army's campaign against Northern Paiute bands in Eastern Oregon and the Bannock uprising in the same area. Today, nothing remains of Fort Harney except a small cemetery.
Billy Chinook was a chief and member of the Wasco tribe. Chinook was a guide for John C. Frémont and Kit Carson, who explored Central Oregon from 1843 to 1844 and from 1845 to 1847. Chinook also served as First Sergeant, U.S. Army Wasco Scouts during the Snake War. Lake Billy Chinook in Oregon is named in his honor.

William Russell Parnell was an Irish-born adventurer and soldier during the mid-to late 19th century. A member of the 17th Lancers during the Crimean War, he was one of the few survivors of the infamous Charge of the Light Brigade.

The Battle of Infernal Caverns was a battle during the Snake War fought between Native Americans and the U.S. Army. The Native American warriors had made a fortress out of lava rocks in the Infernal Caverns of northern California near the town of Likely. From there they were able to pour a steady fire upon the soldiers commanded by Lt. Col. George Crook. Crook's men attacked on the second day. Despite heavy casualties they managed to scale the cliffs and take the fortifications. Colonel Crook reportedly shot down Chief Sieto himself. Fighting continued into the night as the Native warriors withdrew deeper into the caverns. Crook commented, "I never wanted dynamite so bad as I did when we first took the fort and heard the diabolical and defiant yells from down in the rocks". On the third day the Natives had fled the caverns.

Numaga was a Paiute leader during the Paiute War of 1860 that centered on Pyramid Lake in what is now Nevada in the United States. The war was caused by an influx of miners and ranchers after silver was discovered in the Comstock Lode near to Carson City. The newcomers assaulted the Paiutes and destroyed their foods supplies. When the Paiutes responded, the U.S. Army used force to suppress them. Both before and after the war, Numaga was a strong advocate of peace and did much to reduce the violence on both sides. He died of tuberculosis, a "white man's disease", in 1871.
The California Indian Wars were a series of massacres, wars, and battles between the United States Army, and the Indigenous peoples of California. The wars lasted from 1850, immediately after Alta California, acquired during the Mexican–American War, became the state of California, to 1880 when the last minor military operation on the Colorado River ended the Calloway Affair of 1880.

William Horace Warner was an officer in the United States Army's Corps of Topographical Engineers. In 1849, he led an Army survey party north from Sacramento through the uncharted country of northeastern California into south central Oregon. Warner was killed by Native Americans in northeastern California, just south of the Oregon border. In the mid-nineteenth century, two army outposts in southern Oregon were named after Warner. Today, the Warner Mountains, Warner Valley, and a number of other landmarks bear his name.