Related Research Articles

Necrosis is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who is often regarded as one of the founders of modern pathology. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated digestion of cell components. In contrast, apoptosis is a naturally occurring programmed and targeted cause of cellular death. While apoptosis often provides beneficial effects to the organism, necrosis is almost always detrimental and can be fatal.

A gumma is a soft, non-cancerous growth resulting from the tertiary stage of syphilis.

A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious organisms including bacteria and fungi, as well as other materials such as foreign objects, keratin, and suture fragments.

Caseous necrosis or caseous degeneration is a unique form of cell death in which the tissue maintains a cheese-like appearance. It is also a distinctive form of coagulative necrosis. The dead tissue appears as a soft and white proteinaceous dead cell mass.

Necrobiosis lipoidica is a rare, chronic skin condition predominantly associated with diabetes mellitus. It can also occur in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis or without any underlying conditions (idiopathic). It is characterized by hardened, raised areas of the skin, often appearing on the shins, with a yellowish center and a surrounding dark pink area. The lesions are generally asymptomatic but can become tender and ulcerate when injured.
Epulis fissuratum is a benign hyperplasia of fibrous connective tissue which develops as a reactive lesion to chronic mechanical irritation produced by the flange of a poorly fitting denture. More simply, epulis fissuratum is where excess folds of firm tissue form inside the mouth, as a result of rubbing on the edge of dentures that do not fit well. It is a harmless condition and does not represent oral cancer. Treatment is by simple surgical removal of the lesion, and also by adjustment of the denture or provision of a new denture.
Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia (IPH) is a benign lesion of the oral mucosa which is characterized by the growth of one or more nodular lesions, measuring about 2mm or less. The lesion almost exclusively involves the hard palate, and in rare instances, it also has been seen on the mandible. The lesion is mostly asymptomatic and color of the mucosa may vary from pink to red.
Necrobiosis is the physiological death of a cell, and can be caused by conditions such as basophilia, erythema, or a tumor. It is identified both with and without necrosis.

A foreign body reaction (FBR) is a typical tissue response to a foreign body within biological tissue. It usually includes the formation of a foreign body granuloma. Tissue-encapsulation of an implant is an example, as is inflammation around a splinter. Foreign body granuloma formation consists of protein adsorption, macrophages, multinucleated foreign body giant cells, fibroblasts, and angiogenesis. It has also been proposed that the mechanical property of the interface between an implant and its surrounding tissues is critical for the host response.

According to a common point of view epithelioid cells are derivatives of activated macrophages resembling epithelial cells.
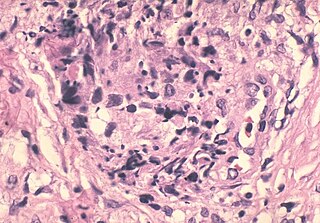
A sperm granuloma is a lump of leaked sperm that appears along the vasa deferentia or epididymides in vasectomized individuals. While the majority of sperm granulomas are present along the vas deferens, the rest of them form at the epididymis. Sperm granulomas range in size, from one millimeter to one centimeter. They consist of a central mass of degenerating sperm surrounded by tissue containing blood vessels and immune system cells. Sperm granulomas may also have a yellow, white, or cream colored center when cut open. While some sperm granulomas can be painful, most of them are painless and asymptomatic. Sperm granulomas can appear as a result of surgery, trauma, or an infection. They can appear as early as four days after surgery and fully formed ones can appear as late as 208 days later.
White dot syndromes are inflammatory diseases characterized by the presence of white dots on the fundus, the interior surface of the eye. The majority of individuals affected with white dot syndromes are younger than fifty years of age. Some symptoms include blurred vision and visual field loss. There are many theories for the etiology of white dot syndromes including infectious, viral, genetics and autoimmune.

Eosinophilic ulcer of the oral mucosa is a condition characterized by an ulcer with an indurated and elevated border. The lesion might be tender, fast-growing and the patient often not be aware of any trauma in the area.

An inflammatory fibroid polyp(IFP) is an uncommon digestive system tumor. J. Vanek initially identified it as a separate pathological entity in 1949 when he reported six case reports of eosinophilic infiltration in gastric submucosal granulomas. It is a single, non-encapsulated polypoid lesion that is typically submucosal. It is characterized by a large number of small blood vessels, oedematous connective tissue, and an inflammatory eosinophilic infiltrate.
Plasma cell granulomas (PCGs) are uncommon, non-neoplastic lesions of unknown etiology and are considered an entity of IgG4-related diseases.

Hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma (HCCC) is a rare malignant salivary gland tumour, with a good prognosis, that is usually found on the tongue or palate.
Smooth muscle tumor of uncertain malignant potential, abbreviated STUMP, is an uncommon tumor of the uterine smooth muscle that may behave like a benign tumor or a cancerous tumor.
The xanthogranulomatous process (XP), is a form of acute and chronic inflammation characterized by an exuberant clustering of foamy macrophages among other inflammatory cells. Localization in the kidney and renal pelvis has been the most frequent and better known occurrence followed by that in the gallbladder but many others have been subsequently recorded. The pathological findings of the process and etiopathogenetic and clinical observations have been reviewed by Cozzutto and Carbone.
Pulmonary hyalinizing granuloma is a lesional pattern of pulmonary inflammatory pseudotumor.

Sclerosing polycystic adenosis is a rare salivary gland tumor first described in 1996 by Dr. Brion Smith. The major salivary glands, specifically the parotid gland and the submandibular gland, are affected most commonly. Patients usually come to clinical attention with a mass or swelling in their salivary glands in the 5th decade of life, with females affected much more commonly than males. Nearly all of the cases reported so far have a benign behavior, although there is a single case that has had an associated malignant transformation.
References
- ↑ Gnepp, Douglas R.; Bishop, Justin A. (5 May 2020). Gnepp's Diagnostic Surgical Pathology of the Head and Neck. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 984. ISBN 978-0-323-54780-2.