


An infrared dark cloud (IRDC) is a cold, dense region of a giant molecular cloud. They can be seen in silhouette against the bright diffuse mid-infrared emission from the galactic plane. [1] [2]



An infrared dark cloud (IRDC) is a cold, dense region of a giant molecular cloud. They can be seen in silhouette against the bright diffuse mid-infrared emission from the galactic plane. [1] [2]
Infrared dark clouds have only been recently discovered in 1996 using the ISO [3] and therefore are in need of further research. [4] The Spitzer Space telescope, created by NASA to detect infrared radiation [5] , assisted in the location and identification of infrared dark clouds. The highly sensitive telescope was used to analyze the Milky Way and create numerous astronomical surveys at wavelengths that allowed for the detailed analysis of IRDCs. Through the use of convolutional neural networks [6] , an IRDC catalog consisting of 18,845 items was created by two astronomers named Jyothish Pari and Joe Hora, who created a computer algorithm which could efficiently scan the images created by the Spitzer telescope’s IRAC camera to find infrared dark clouds. [7]
Astronomers believe that they represent the earliest stage in the formation of high-mass stars [8] and are therefore of great importance for understanding the star formation process as a whole. [9]
| | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2010) |

A proplyd, short for ionized protoplanetary disk, is an externally illuminated photoevaporating protoplanetary disk around a young star. Nearly 180 proplyds have been discovered in the Orion Nebula. Images of proplyds in other star-forming regions are rare, while Orion is the only region with a large known sample due to its relative proximity to Earth.

NGC 2362, also known as Caldwell 64, is an open cluster of stars in the southern constellation of Canis Major. It was discovered by the Italian court astronomer Giovanni Batista Hodierna, who published his finding in 1654. William Herschel called it a "beautiful cluster", while William Henry Smyth said it "has a beautiful appearance, the bright white star being surrounded by a rich gathering of minute companions, in a slightly elongated form, and nearly vertical position". In the past it has also been listed as a nebula, but in 1930 Robert J. Trumpler found no evidence of nebulosity. The brightest member star system is Tau Canis Majoris, and therefore it is sometimes called the Tau Canis Majoris Cluster.

The Carina–Sagittarius Arm is generally thought to be a minor spiral arm of the Milky Way galaxy. Each spiral arm is a long, diffuse curving streamer of stars that radiates from the Galactic Center. These gigantic structures are often composed of billions of stars and thousands of gas clouds. The Carina–Sagittarius Arm is one of the most pronounced arms in our galaxy as many HII regions, young stars and giant molecular clouds are concentrated in it.

35 Aquilae is a star in the equatorial constellation of Aquila. 35 Aquilae is its Flamsteed designation though it also bears the Bayer designation c Aquilae. The apparent visual magnitude of this star is 5.8, which means it is a faint star but visible to the naked eye from dark suburban or rural skies. It has an annual parallax shift of 16.34 mas that is caused by the Earth's orbit around the Sun. This yields a distance estimate of 200 light-years, give or take a 4 light-year margin of error. At this distance, the visual magnitude is diminished by 0.26 from extinction caused by interstellar gas and dust.
GCIRS 13E is an infrared and radio object near the Galactic Center. It is believed to be a cluster of hot massive stars, possibly containing an intermediate-mass black hole (IMBH) at its center.

Sh2-155 is a diffuse nebula in the constellation Cepheus, within a larger nebula complex containing emission, reflection, and dark nebulosity. It is widely known as the Cave Nebula, though that name was applied earlier to Ced 201, a different nebula in Cepheus. Sh2-155 is an ionized H II region with ongoing star formation activity, at an estimated distance of 725 parsecs from Earth.

HR 8799 is a roughly 30 million-year-old main-sequence star located 133.3 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Pegasus. It has roughly 1.5 times the Sun's mass and 4.9 times its luminosity. It is part of a system that also contains a debris disk and at least four massive planets. Those planets, along with Fomalhaut b, were the first exoplanets whose orbital motion was confirmed by direct imaging. The star is a Gamma Doradus variable: its luminosity changes because of non-radial pulsations of its surface. The star is also classified as a Lambda Boötis star, which means its surface layers are depleted in iron peak elements. It is the only known star which is simultaneously a Gamma Doradus variable, a Lambda Boötis type, and a Vega-like star.

HAT-P-14b, officially named Sissi also known as WASP-27b, is an extrasolar planet located approximately 224.2 ± 0.6 parsecs (731.2 ± 2.0 ly) away in the constellation of Hercules, orbiting the 10th magnitude F-type main-sequence star HAT-P-14. This planet was discovered in 2010 by the HATNet Project using the transit method. It was independently detected by the SuperWASP project.
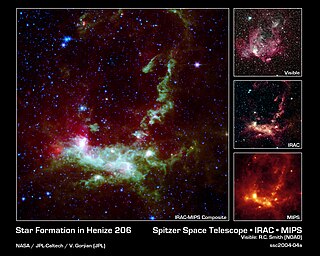
Henize 206 is a nebula in the Large Magellanic Cloud. This luminous cloud of gas and dust houses a cluster of newborn stars. Although Henize 206 was first catalogued in the 1950s, it was reported in NASA press releases in March 2004, for showing several example images generated from the various infrared cameras on the Spitzer Space Telescope launched in August 2003.

VFTS 102 is a star located in the Tarantula nebula, a star forming region in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way.

WISE 0855−0714 is a sub-brown dwarf 2.28±0.01 parsecs from Earth, therefore the fourth-closest star or (sub-) brown dwarf system to the Sun, the discovery of which was announced in April 2014 by Kevin Luhman using data from the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE). As of 2014, WISE 0855−0714 has the third-highest proper motion after Barnard's Star and Kapteyn's Star and the fourth-largest parallax of any known star or brown dwarf. It is also the coldest object of its type found in interstellar space, having a temperature of about 285 K.

NGC 4102 is an intermediate barred spiral galaxy located in the northern constellation of Ursa Major. It is visible in a small telescope and has an apparent visual magnitude of 11.2. The galaxy was discovered April 12, 1789 by William Herschel. J. L. E. Dreyer described it as "bright, pretty small, round, brighter middle and bright nucleus". This galaxy is located at a distance of 60 million light years and is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 837 km/s. It is a member of the Ursa Major group of galaxies.

Westerhout 40 or W40 is a star-forming region in the Milky Way located in the constellation Serpens. In this region, interstellar gas forming a diffuse nebula surrounds a cluster of several hundred new-born stars. The distance to W40 is 436 ± 9 pc, making it one of the closest sites of formation of high-mass O-type and B-type stars. The ionizing radiation from the massive OB stars has created an H II region, which has an hour-glass morphology.

The Serpens–Aquila Rift (also known as the Aquila Rift) is a region of the sky in the constellations Aquila, Serpens Cauda, and eastern Ophiuchus containing dark interstellar clouds. The region forms part of the Great Rift, the nearby dark cloud of cosmic dust that obscures the middle of the galactic plane of the Milky Way, looking inwards and towards its other radial sectors. The clouds that form this structure are called "molecular clouds", constituting a phase of the interstellar medium which is cold and dense enough for molecules to form, particularly molecular hydrogen (H2). These clouds are opaque to light in the optical part of the spectrum due to the presence of interstellar dust grains mixed with the gaseous component of the clouds. Therefore, the clouds in the Serpens-Aquila Rift block light from background stars in the disk of the Galaxy, forming the dark rift. The complex is located in a direction towards the inner Galaxy, where molecular clouds are common, so it is possible that not all components of the rift are at the same distance and physically associated with each other.

V4650 Sagittarii (qF362) is a luminous blue variable star (LBV) in the constellation of Sagittarius. Located some 25,000 light years away, the star is positioned on the edge of a starburst cluster known as the Quintuplet cluster.

NGC 4636 is an elliptical galaxy located in the constellation Virgo. It is a member of the NGC 4753 Group of galaxies, which is a member of the Virgo II Groups, a series of galaxies and galaxy clusters strung out from the southern edge of the Virgo Supercluster. It is located at a distance of about 55 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 4636 is about 105,000 light years across.

NGC 3511 is an intermediate spiral galaxy located in the constellation Crater. It is located at a distance of circa 45 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 3511 is about 70,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on December 21, 1786. It lies two degrees west of Beta Crateris.
2MASS J10475385+2124234 is a brown dwarf of spectral class T6.5, in the constellation Leo about 34 light-years from Earth, hence in galactic topographical and interstellar medium study terms being in the Local Bubble and very nearby in the Orion Arm. It is the first brown dwarf to have an inferred range of its typical wind speeds computed.
Thushara Pillai is an Indian astrophysicist and astronomer with a senior research scientist position at Boston University's Institute for Astrophysical Research and MIT Haystack Observatory. Her research interests have included molecular clouds, high-mass star formation, magnetic fields, astrochemistry, and the Galactic Center. She is known for her work that looked to understand star formation by observing magnetized interstellar clouds, and Pillai is the first astronomer to capture images of magnetic fields reorienting near areas of star formation.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link){{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link){{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)