
The Apple II series is a family of home computers, one of the first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products, designed primarily by Steve Wozniak, manufactured by Apple Computer, and launched in 1977 with the original Apple II.

The Apple IIGS, the fifth and most powerful of the Apple II family, is a 16-bit personal computer produced by Apple Computer. While featuring the Macintosh look and feel, and resolution and color similar to the Amiga and Atari ST, it remains compatible with earlier Apple II models. The "GS" in the name stands for "Graphics and Sound," referring to its enhanced multimedia hardware, especially its state-of-the-art audio.

Deluxe Paint, often referred to as DPaint, is a bitmap graphics editor series created by Dan Silva for Electronic Arts. The original Deluxe Paint was written for the Commodore Amiga 1000 and released in November 1985. It was eventually ported to other platforms, including an MS-DOS version which became the standard for pixel graphics in video games in the 1990s, the only competitor being Autodesk Animator Pro.

One on One: Dr. J vs. Larry Bird, commonly known as One on One, is a basketball video game written by Eric Hammond for the Apple II and published by Electronic Arts in 1983. It was initially ported to the Atari 8-bit family, ColecoVision, Commodore 64, and IBM PC. Versions followed for the TRS-80 Color Computer, Macintosh, Amiga, and ZX Spectrum. In Europe, the publisher was Ariolasoft. Atari Corporation released an Atari 7800 port in 1987.

Will Harvey's Music Construction Set (MCS) is a music composition notation program designed by Will Harvey for the Apple II and published by Electronic Arts in 1983. Harvey wrote the original Apple II version in assembly language when he was 15 and in high school. MCS was conceived as a tool to add music to his previously published game, an abstract shooter called Lancaster for the Apple II.
Will Harvey is an American software developer and Silicon Valley entrepreneur. He wrote Music Construction Set (1984) for the Apple II, the first commercial sheet music processor for home computers. Music Construction Set was ported to other systems by its publisher, Electronic Arts. He wrote two games for the Apple IIGS: Zany Golf (1988) and The Immortal (1990). Harvey founded two consumer virtual world Internet companies: IMVU, an instant messaging company, and There, Inc., an MMOG company.

Joseph Paul Montgomery was an American entrepreneur and inventor. In the mid 1980s, he was among the first to see the potential of personal computer technology in the field of video production and 3D animation. As Vice President of NewTek and Co-Founder and President of Play, Inc., Montgomery drove the creation of the first widely-successful digital video products, including the Emmy-award-winning Video Toaster and the Snappy Video Snapshot.

Tass Times in Tonetown is an adventure game published by Activision in 1986. It was designed by Michael Berlyn and Muffy McClung Berlyn and programmed by Rebecca Heineman of Interplay in cooperation with Brainwave Creations.
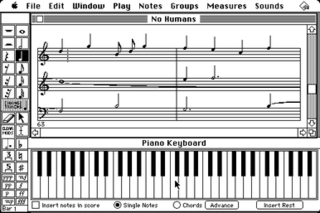
Deluxe Music Construction Set (DMCS) is a 1986 music composition, notation and playback program for the Amiga and Macintosh. The program was originally released as Will Harvey's Music Construction Set for the Apple II and other computers, but was redesigned for the deluxe version. DMCS was created by Geoff Brown and published by Electronic Arts (EA). Ariolasoft published the program in Europe under license from EA.

8 Bit Weapon is an American chiptune music band formed in Ventura County, California, by Seth and Michelle Sternberger. It was originally created by Seth Sternberger around 1998. Its instruments consists primarily of old 8-bit and 16-bit computers such as the Commodore VIC-20, Commodore 64, Commodore 128, Commodore Amiga 500, and the Apple II, as well as game consoles such as the Nintendo Entertainment System, Game Boy, Atari 2600, and an Intellivision synthesizer.
Jam Session is the 1988 successor to Studio Session, a 1986 software program for Macintosh computers, for music creation and playback. It was created by Macintosh and Newton pioneer Steve Capps and musician Ed Bogas. Jam Session was published by Broderbund Software. Studio Session was published by Bogas Productions.
The Amiga is a family of home computers that were designed and sold by the Amiga Corporation from 1985 to 1994.

Starglider is a 3D video game published in 1986 by Rainbird. It was developed by Jez San under his company name Argonaut Software. The game is a fast-moving, first-person combat flight simulator, rendered with colourful wireframe vector graphics inspired by San's love of the 1983 Atari coin-op Star Wars.

The Commodore A1060 Sidecar is an expansion hardware device developed by Commodore and released in 1986 for the Amiga 1000 computer. It features a complete PC XT-clone system mounted in an expansion case which connected to the expansion bus on the right side of the Amiga 1000 computer, sitting beside it similar to a motorcycle's sidecar, hence the name.

World Tour Golf is a 1986 video game by Evan and Nicky Robinson, Paul Reiche III and published by Electronic Arts for Commodore 64, Amiga, Apple IIGS, and DOS.
Manley & Associates was an independent video game developer founded in 1982, which developed over 70 titles for video game publishers, including Electronic Arts, Activision, Disney, GameTek, Publishing International, and Spectrum HoloByte. Many of the company's early titles were one or two person projects created in founder Ivan Manley's house, but eventually it grew to roughly 60 people working from an office park in Issaquah, Washington. Hometown U.S.A. won the Software Publishers' Association's award for the Best Creativity Program, Educational Category, 1988.

GBA Championship Basketball: Two-on-Two is a 1986 computer basketball game for the PC, Amiga, Apple II, Apple IIGS, Amstrad CPC, Atari ST, ZX Spectrum and Commodore 64. It was developed by Dynamix and published by Activision.

Keef the Thief: A Boy and His Lockpick is a video game developed by Naughty Dog and published by Electronic Arts. It was released in 1989 for the Apple IIGS and then later ported to the Amiga and MS-DOS. Keef the Thief is a comedic sword and sorcery role-playing game.

Home computers were a class of microcomputers that entered the market in 1977 and became common during the 1980s. They were marketed to consumers as affordable and accessible computers that, for the first time, were intended for the use of a single nontechnical user. These computers were a distinct market segment that typically cost much less than business, scientific or engineering-oriented computers of the time such as those running CP/M or the IBM PC, and were generally less powerful in terms of memory and expandability. However, a home computer often had better graphics and sound than contemporary business computers. Their most common uses were playing video games, but they were also regularly used for word processing and programming.
Throughout its lengthy, multi-model lifespan, the Apple II series computers lacked any serious built-in sound capabilities. At the time of its release in 1977, this did not distinguish it from its contemporaries, but by 1982, it shared the market with several sound-equipped competitors such as the Commodore 64, whose SID chip could produce sophisticated multi-timbral music and sound effects.















