Related Research Articles

A pandemic is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has spread across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. Widespread endemic diseases with a stable number of infected individuals such as recurrences of seasonal influenza are generally excluded as they occur simultaneously in large regions of the globe rather than being spread worldwide.

Measles is a highly contagious, vaccine-preventable infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than 40 °C (104 °F), cough, runny nose, and inflamed eyes. Small white spots known as Koplik's spots may form inside the mouth two or three days after the start of symptoms. A red, flat rash which usually starts on the face and then spreads to the rest of the body typically begins three to five days after the start of symptoms. Common complications include diarrhea, middle ear infection (7%), and pneumonia (6%). These occur in part due to measles-induced immunosuppression. Less commonly seizures, blindness, or inflammation of the brain may occur. Other names include morbilli, rubeola, red measles, and English measles. Both rubella, also known as German measles, and roseola are different diseases caused by unrelated viruses.

The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF), a merging of the William H. Gates Foundation and the Gates Learning Foundation, is an American private foundation founded by Bill Gates and Melinda French Gates. Based in Seattle, Washington, it was launched in 2000 and is reported as of 2020 to be the second largest charitable foundation in the world, holding $69 billion in assets. On his 43rd birthday, Bill Gates gave the foundation $1 billion. The primary stated goals of the foundation are to enhance healthcare and reduce extreme poverty across the world, and to expand educational opportunities and access to information technology in the U.S. Key individuals of the foundation include Bill Gates, Melinda French Gates, Warren Buffett, chief executive officer Mark Suzman, and Michael Larson.
Since October 2018, the Center for Global Infectious Disease Research has been part of the Seattle Children's Research Institute. At the time of the merger, CID Research had 166 scientists. Its mission was to eliminate the world's most devastating infectious diseases through leadership in scientific discovery. The organization's research labs were in the South Lake Union area of Seattle, WA. The institute's research focused on four areas of infectious disease: HIV/AIDS, malaria, tuberculosis (TB), and Emerging & Neglected Diseases (END) like African sleeping sickness, leishmaniasis, Chagas disease, and toxoplasmosis. CID Research was engaged in early stages of the scientific pipeline including bench science and malaria clinical trials and has expertise in immunology, vaccinology, and drug discovery.

William Herbert Foege is an American physician and epidemiologist who is credited with "devising the global strategy that led to the eradication of smallpox in the late 1970s". From May 1977 to 1983, Foege served as the Director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Globalization, the flow of information, goods, capital, and people across political and geographic boundaries, allows infectious diseases to rapidly spread around the world, while also allowing the alleviation of factors such as hunger and poverty, which are key determinants of global health. The spread of diseases across wide geographic scales has increased through history. Early diseases that spread from Asia to Europe were bubonic plague, influenza of various types, and similar infectious diseases.
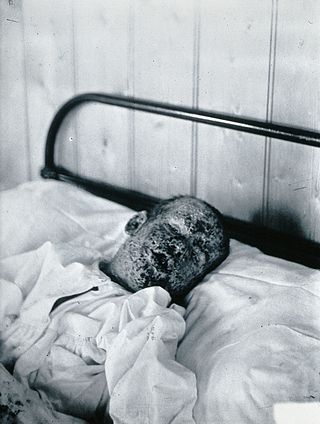
The eradication of infectious diseases is the reduction of an infectious disease's prevalence in the global host population to zero.

The Emerging Pathogens Institute (EPI) is an interdisciplinary research institution associated with the University of Florida. The institute focuses on fusing key disciplines to develop outreach, education, and research capabilities designed to preserve the region's health and economy, as well as to prevent or contain new and re-emerging diseases. Researchers within the institute work in more than 30 different countries around the world, with over 250 affiliated faculty members stemming from 11 University of Florida colleges, centers, and institutes. The 90,000-square-foot building includes laboratories and collaborative space for bioinformatics and mathematical modeling.

Measles vaccine protects against becoming infected with measles. Nearly all of those who do not develop immunity after a single dose develop it after a second dose. When rate of vaccination within a population is greater than 92%, outbreaks of measles typically no longer occur; however, they may occur again if the rate of vaccination decrease. The vaccine's effectiveness lasts many years. It is unclear if it becomes less effective over time. The vaccine may also protect against measles if given within a couple of days after exposure to measles.

The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) is a research institute working in the area of global health statistics and impact evaluation at the University of Washington in Seattle. The Institute is headed by Christopher J.L. Murray, a physician and health economist, and professor at the University of Washington Department of Global Health, which is part of the School of Medicine. IHME conducts research and trains scientists, policymakers, and the public in health metrics concepts, methods, and tools. Its mission includes judging the effectiveness and efficacy of health initiatives and national health systems. IHME also trains students at the post-baccalaureate and post-graduate levels.

The Infectious Disease Research Institute (IDRI) was a non-profit organization based in Seattle, in the United States, and which conducts global health research on infectious diseases. Its new name is Access to Advanced Health Institute (AAHI).

A superspreading event (SSEV) is an event in which an infectious disease is spread much more than usual, while an unusually contagious organism infected with a disease is known as a superspreader. In the context of a human-borne illness, a superspreader is an individual who is more likely to infect others, compared with a typical infected person. Such superspreaders are of particular concern in epidemiology.
This page is a timeline of global health, including major conferences, interventions, cures, and crises.

Neil Morris Ferguson is a British epidemiologist and professor of mathematical biology, who specialises in the patterns of spread of infectious disease in humans and animals. He is the director of the Jameel Institute, and of the MRC Centre for Global Infectious Disease Analysis, and head of the Department of Infectious Disease Epidemiology in the School of Public Health and Vice-Dean for Academic Development in the Faculty of Medicine, all at Imperial College London.

Caitlin M. Rivers is an American epidemiologist who as Senior Scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security and assistant professor at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, specializing on improving epidemic preparedness. Rivers is currently working on the American response to the COVID-19 pandemic with a focus on the incorporation of infectious disease modeling and forecasting into public health decision making.
Yvonne "Bonnie" Maldonado is an American physician, pediatrician, and Professor of Pediatrics and of Health Research and Policy at Stanford University, with a focus on Infectious Diseases. She founded Stanford's pediatric HIV Clinic and now serves as Stanford University School of Medicine's Senior Associate Dean of Faculty Development and Diversity.

The COVID-19 pandemic has had many impacts on global health beyond those caused by the COVID-19 disease itself. It has led to a reduction in hospital visits for other reasons. There have been 38 per cent fewer hospital visits for heart attack symptoms in the United States and 40 per cent fewer in Spain. The head of cardiology at the University of Arizona said, "My worry is some of these people are dying at home because they're too scared to go to the hospital." There is also concern that people with strokes and appendicitis are not seeking timely treatment. Shortages of medical supplies have impacted people with various conditions.

The Seattle Coronavirus Assessment Network (SCAN) is a public health surveillance program established in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. SCAN originated in March 2020 as a partnership between the Public Health department of Seattle and King County in Washington, USA and the Seattle Flu Study. SCAN's predecessor, the Seattle Flu Study, reported the first known case of community transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in the United States.
Ann Marie Kimball is an American physician. She is known for being the pioneer of electronic disease surveillance for infectious disease outbreaks and pandemics. She is currently a Professor Emerita in the Department of Epidemiology at the University of Washington, a Consulting Fellow at the Chatham House Royal Institute of Foreign Affairs, and was a Strategic Consultant in Global Health at the Rockefeller Foundation. Kimball served as a technical and strategic lead for the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation infectious disease surveillance strategy formation.

Kayla F. Laserson is an American epidemiologist serving as the director of the Global Health Center at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) since July 2023. She was previously the deputy director for Infectious Diseases and Vaccine Delivery, India Office of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. Laserson served as a commander in the United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps until 2007.
References
- ↑ Cheney, Catherine (3 December 2020). "The Gates Foundation leans into disease modeling". Devex. Retrieved 30 December 2020.
- 1 2 Sandi Doughton (March 15, 2020). "How big will the coronavirus outbreak get? This Bellevue scientist is figuring that out". The Seattle Times.
- ↑ Eaton et al. 2015.
- ↑ Ross Reynolds (March 14, 2014). "Improving The Battle Against Infectious Diseases" (audio). Seattle: KUOW-FM.
- ↑ Bershteyn et al. 2018.
- ↑ Tess Riski (March 31, 2020). "How Bad Will Oregon's Outbreak Get? It Depends on Which Experts You Ask". Willamette Week .
Two reliable studies show divergent COVID-19 outcomes in Oregon.
- ↑ Todd Bishop; Taylor Soper (April 15, 2020), "As Washington state COVID cases keep falling, here's the data driving the ongoing 'stay home' order", Geekwire
- ↑ Gillian Friedman (April 3, 2020). "Coronavirus: How the West Coast is winning, and what Utah can learn". Deseret News . Salt Lake City.
- ↑ Kerr, Cliff; Mistry, Dina; et al. (2021). "Covasim: an agent-based model of COVID-19 dynamics and interventions". medRxiv 10.1101/2020.05.10.20097469v1 .
Sources
- Jeffrey W Eaton; Nicolas Bacaër; Anna Bershteyn; Valentina Cambiano; Anne Cori; Rob E Dorrington; et al. (October 2015), "Assessment of epidemic projections using recent HIV survey data in South Africa: a validation analysis of ten mathematical models of HIV epidemiology in the antiretroviral therapy era", The Lancet, 3 (10): e598–e608, doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(15)00080-7 , PMID 26385301
- Bershteyn, Anna; Gerardin, Jaline; Bridenbecker, Daniel; Lorton, Christopher W; Bloedow, Jonathan; Baker, Robert S; Chabot-Couture, Guillaume; Chen, Ye; Fischle, Thomas; Frey, Kurt; Gauld, Jillian S; Hu, Hao; Izzo, Amanda S; Klein, Daniel J; Lukacevic, Dejan; McCarthy, Kevin A; Miller, Joel C; Ouedraogo, Andre Lin; Perkins, T Alex; Steinkraus, Jeffrey; ten Bosch, Quirine A; Ting, Hung-Fu; Titova, Svetlana; Wagner, Bradley G; Welkhoff, Philip A; Wenger, Edward A; Wiswell, Christian N (2018), "Implementation and applications of EMOD, an individual-based multi-disease modeling platform", Pathogens and Disease , 76 (5), doi: 10.1093/femspd/fty059 , ISSN 2049-632X, PMC 6067119 , PMID 29986020