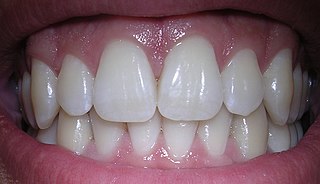
Human teeth function to mechanically break down items of food by cutting and crushing them in preparation for swallowing and digesting. As such, they are considered part of the human digestive system. Humans have four types of teeth: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars, which each have a specific function. The incisors cut the food, the canines tear the food and the molars and premolars crush the food. The roots of teeth are embedded in the maxilla or the mandible and are covered by gums. Teeth are made of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness.
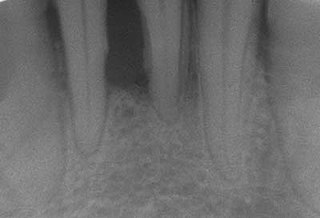
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main cause of tooth loss for adults worldwide. In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or fall out. Halitosis may also occur.

A toothbrush is an oral hygiene tool used to clean the teeth, gums, and tongue. It consists of a head of tightly clustered bristles, atop of which toothpaste can be applied, mounted on a handle which facilitates the cleaning of hard-to-reach areas of the mouth. They should be used in conjunction with something to clean between the teeth where the bristles of the toothbrush cannot reach - for example floss, tape or interdental brushes.
Teeth cleaning is part of oral hygiene and involves the removal of dental plaque from teeth with the intention of preventing cavities, gingivitis, and periodontal disease. People routinely clean their own teeth by brushing and interdental cleaning, and dental hygienists can remove hardened deposits (tartar) not removed by routine cleaning. Those with dentures and natural teeth may supplement their cleaning with a denture cleaner.

Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors, from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty eating. Complications may include inflammation of the tissue around the tooth, tooth loss and infection or abscess formation. Tooth regeneration is an on-going stem cell based field of study that is trying to reverse the effects of decay, unlike most current methods which only try to make dealing with the effects easier.
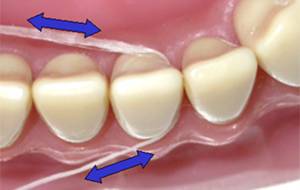
Dental floss is a cord of thin filaments used in interdental cleaning to remove food and dental plaque from between teeth or places a toothbrush has difficulty reaching or is unable to reach. Its regular use as part of oral cleaning is intended to maintain oral health.

A toothpick is a small thin stick of wood, plastic, bamboo, metal, bone or other substance with at least one and sometimes two pointed ends to insert between teeth to remove detritus, usually after a meal. Toothpicks are also used for festive occasions to hold or spear small appetizers or as a cocktail stick, and can be decorated with plastic frills or small paper umbrellas or flags.

The gums or gingiva consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Periodontology or periodontics is the specialty of dentistry that studies supporting structures of teeth, as well as diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting tissues are known as the periodontium, which includes the gingiva (gums), alveolar bone, cementum, and the periodontal ligament. A periodontist is a dentist that specializes in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease and in the placement of dental implants.
Dental plaque is a biofilm of microorganisms that grows on surfaces within the mouth. It is a sticky colorless deposit at first, but when it forms tartar, it is often brown or pale yellow. It is commonly found between the teeth, on the front of teeth, behind teeth, on chewing surfaces, along the gumline (supragingival), or below the gumline cervical margins (subgingival). Dental plaque is also known as microbial plaque, oral biofilm, dental biofilm, dental plaque biofilm or bacterial plaque biofilm. Bacterial plaque is one of the major causes for dental decay and gum disease.
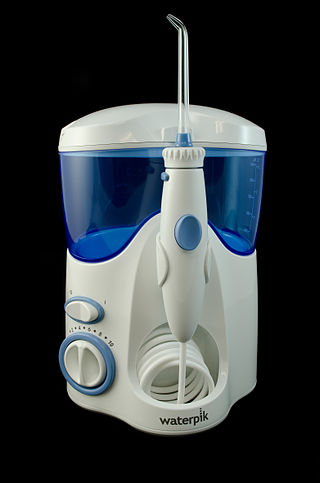
An oral irrigator is a home dental care device which uses a stream of high-pressure pulsating water intended to remove dental plaque and food debris between teeth and below the gum line. Regular use of an oral irrigator is believed to improve gingival health. The devices may also provide easier cleaning for braces and dental implants. However, more research is needed to confirm plaque biofilm removal and effectiveness when used by patients with special oral or systemic health needs.

Tooth brushing is the act of scrubbing teeth with a toothbrush equipped with toothpaste. Interdental cleaning can be useful with tooth brushing, and together these two activities are the primary means of cleaning teeth, one of the main aspects of oral hygiene. The recommended amount of time for tooth brushing is two minutes.

Gingival and periodontal pockets are dental terms indicating the presence of an abnormal depth of the gingival sulcus near the point at which the gingival tissue contacts the tooth.
Bleeding on probing (BoP) which is also known as bleeding gums or gingival bleeding is a term used by dentists and dental hygienists when referring to bleeding that is induced by gentle manipulation of the tissue at the depth of the gingival sulcus, or interface between the gingiva and a tooth. BoP is a sign of periodontal inflammation and indicates some sort of destruction and erosion to the lining of the sulcus or the ulceration of sulcular epithelium. The blood comes from lamina propria after the ulceration of the lining. BoP seems to be correlated with Periodontal Inflamed Surface Area (PISA).

Scaling and root planing, also known as conventional periodontal therapy, non-surgical periodontal therapy or deep cleaning, is a procedure involving removal of dental plaque and calculus and then smoothing, or planing, of the (exposed) surfaces of the roots, removing cementum or dentine that is impregnated with calculus, toxins, or microorganisms, the agents that cause inflammation. It is a part of non-surgical periodontal therapy. This helps to establish a periodontium that is in remission of periodontal disease. Periodontal scalers and periodontal curettes are some of the tools involved.

Oral hygiene is the practice of keeping one's oral cavity clean and free of disease and other problems by regular brushing of the teeth and adopting good hygiene habits. It is important that oral hygiene be carried out on a regular basis to enable prevention of dental disease and bad breath. The most common types of dental disease are tooth decay and gum diseases, including gingivitis, and periodontitis.

A tongue cleaner is an oral hygiene device designed to clean the coating on the upper surface of the tongue. While there is tentative benefit from the use of a tongue cleaner it is insufficient to draw clear conclusions regarding bad breath.

Gingivitis is a non-destructive disease that causes inflammation of the gums; ulitis is an alternative term. The most common form of gingivitis, and the most common form of periodontal disease overall, is in response to bacterial biofilms that are attached to tooth surfaces, termed plaque-induced gingivitis. Most forms of gingivitis are plaque-induced.
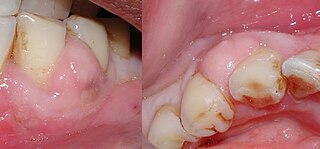
A periodontal abscess, is a localized collection of pus within the tissues of the periodontium. It is a type of dental abscess. A periodontal abscess occurs alongside a tooth, and is different from the more common periapical abscess, which represents the spread of infection from a dead tooth. To reflect this, sometimes the term "lateral (periodontal) abscess" is used. In contrast to a periapical abscess, periodontal abscesses are usually associated with a vital (living) tooth. Abscesses of the periodontium are acute bacterial infections classified primarily by location.
Periodontal surgery is a form of dental surgery that prevents or corrects anatomical, traumatic, developmental, or plaque-induced defects in the bone, gingiva, or alveolar mucosa. The objectives of this surgery include accessibility of instruments to root surface, elimination of inflammation, creation of an oral environment for plaque control, periodontal diseases control, oral hygiene maintenance, maintain proper embrasure space, address gingiva-alveolar mucosa problems, and esthetic improvement. The surgical procedures include crown lengthening, frenectomy, and mucogingival flap surgery.


















