Territorial integrity is the principle under international law that gives the right to sovereign states to defend their borders and all territory in them of another state. It is enshrined in Article 2(4) of the UN Charter and has been recognized as customary international law. Conversely it states that imposition by force of a border change is an act of aggression.

Borders are usually defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political borders can be established through warfare, colonization, or mutual agreements between the political entities that reside in those areas; the creation of these agreements is called boundary delimitation.

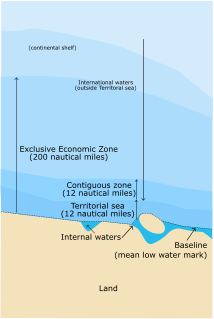
An exclusive economic zone (EEZ), as prescribed by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, is an area of the sea in which a sovereign state has special rights regarding the exploration and use of marine resources, including energy production from water and wind. It stretches from the outer limit of the territorial sea out to 200 nautical miles (nmi) from the coast of the state in question. It is also referred to as a maritime continental margin and, in colloquial usage, may include the continental shelf. The term does not include either the territorial sea or the continental shelf beyond the 200 nautical mile limit. The difference between the territorial sea and the exclusive economic zone is that the first confers full sovereignty over the waters, whereas the second is merely a "sovereign right" which refers to the coastal state's rights below the surface of the sea. The surface waters, as can be seen in the map, are international waters.

The Malaysia–Thailand border divides the countries of Malaysia and Thailand and consists of a land boundary running for 595 km (370 mi) across the Malay Peninsula and maritime boundaries in the Straits of Malacca and the Gulf of Thailand/South China Sea. The Golok River forms the easternmost 95 km stretch of the land border.

The Malaysia–Singapore border is an international maritime border between the Southeast Asian countries of Malaysia, which lies to the north of the border, and Singapore to the south. The boundary is formed by straight lines between maritime geographical coordinates running along or near the deepest channel of the Straits of Johor.
Ewan William Anderson is an English academic expert on geopolitics, economic and social geography. He is also a former English first-class cricketer who played all his games for Oxford University Cricket Club; and has exhibited his drawings of trees in both Britain and the US.

The modern borders of Israel exist as the result both of past wars and of diplomatic agreements between the State of Israel and its neighbours as well as colonial powers. Only two of Israel's five total potential land borders are internationally recognized and uncontested, while the other three remain disputed; the majority of its border disputes are rooted in territorial changes that came about as a result of the 1967 Arab–Israeli War, which saw Israel occupy large swathes of territory from its rivals. Israel's two formally recognized and confirmed borders exist with Egypt and Jordan since the 1979 Egypt–Israel peace treaty and the 1994 Israel–Jordan peace treaty, while its borders with Syria, Lebanon and the Palestinian territories remain internationally recognized as contested.

The Indonesia–Malaysia border consists of a 1,881 km land border that divides the territory of Indonesia and Malaysia on the island of Borneo. It also includes maritime boundaries along the length of the Straits of Malacca, in the South China Sea and in the Celebes Sea.

The Brunei–Malaysia border divides the territory of Brunei and Malaysia on the island of Borneo. It consists of a 266 km (165 mi) land border and substantial lengths of maritime borders stretching from the coastline of the two countries to the edge of the continental shelf in the South China Sea.

Brunei and Malaysia established diplomatic relations in 1984. Brunei has a high commission in Putrajaya, as well as consulate-generals in Kota Kinabalu and Kuching. Malaysia maintains a high commission in Bandar Seri Begawan. Both countries are full members of ASEAN and the Commonwealth of Nations. The two countries share a land border on the island of Borneo.

The Association for Borderlands Studies (ABS) is an international scholarly association dedicated exclusively to the systematic interchange of ideas and information relating to international borders and frontier areas. Founded in 1976 with the original emphasis on the study of the United States-Mexico borderlands region, the association has grown steadily. It now encompasses an interdisciplinary membership of scholars at more than three hundred academic, governmental institutions, and NGOs representing the Americas, Asia, Africa and Europe. The ABS publishes an academic journal Journal of Borderlands Studies and an association newsletter La Frontera, as well as sponsoring an annual meeting.

The Limbang District is one of the two districts of Limbang Division, Malaysia. It has a total area of 3,976.00 square kilometres. The major town is Limbang. It has one sub-district, which is Nanga Medamit Sub-District. It borders Brunei Darussalam to the west and east, Lawas District to the southeast and Miri District at the south and southwest. Due to being squeezed in between Brunei at its north and coastal areas, Limbang is accessible by road only by going through immigration posts.
A maritime boundary is a conceptual division of the Earth's water surface areas using physiographic or geopolitical criteria. As such, it usually bounds areas of exclusive national rights over mineral and biological resources, encompassing maritime features, limits and zones. Generally, a maritime boundary is delineated at a particular distance from a jurisdiction's coastline. Although in some countries the term maritime boundary represents borders of a maritime nation that are recognized by the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, maritime borders usually serve to identify the edge of international waters.
John Robert Victor Prescott FASSA was a British and Australian academic, author, and professor emeritus at the University of Melbourne. A political geographer, most of Prescott's work focused on international boundary issues, particularly maritime boundaries.

The borders of Suriname consist of land borders with three countries: Guyana, Brazil, and France. The borders with Guyana and France are in dispute, but the border with Brazil has been uncontroversial since 1906.
Lee Seokwoo is a Korean academic, author and member of the law faculty at Inha University at Incheon, Korea.

The border between Croatia and Serbia in the area of the Danube is disputed. While Serbia holds the opinion that the thalweg of the Danube valley and the centerline of the river represents the international border between the two countries, Croatia disagrees and claims that the international border lies along the boundaries of the cadastral municipalities located along the river—departing from the course at several points along a 140-kilometre (87 mi) section. The cadastre-based boundary reflects the course of the Danube which existed in the 19th century, before meandering and hydrotechnical engineering works altered its course. The area size of the territory in dispute is reported variously, up to 140 square kilometres.

The Ligitan and Sipadan dispute [2002] ICJ 3 was a territorial dispute between Indonesia and Malaysia over two islands in the Celebes Sea, namely Ligitan and Sipadan. The dispute began in 1969 and was largely resolved by the International Court of Justice (ICJ) in 2002, which opined that both of the islands belonged to Malaysia.
The borders of Indonesia include land and maritime borders with Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, and Timor Leste, as well as shared maritime boundaries with Australia, India, Palau, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.















