Related Research Articles
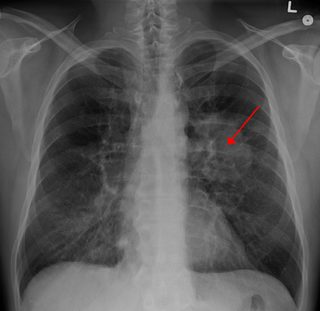
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma, since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas, is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malignant cells that originate as epithelial cells, or from tissues composed of epithelial cells. Other lung cancers, such as the rare sarcomas of the lung, are generated by the malignant transformation of connective tissues, which arise from mesenchymal cells. Lymphomas and melanomas can also rarely result in lung cancer.
Radon is a chemical element with the symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas. It occurs naturally in minute quantities as an intermediate step in the normal radioactive decay chains through which thorium and uranium slowly decay into lead and various other short-lived radioactive elements. Radon itself is the immediate decay product of radium. Its most stable isotope, 222Rn, has a half-life of only 3.8 days, making it one of the rarest elements. Since thorium and uranium are two of the most common radioactive elements on Earth, while also having three isotopes with half-lives on the order of several billion years, radon will be present on Earth long into the future despite its short half-life. The decay of radon produces many other short-lived nuclides, known as "radon daughters", ending at stable isotopes of lead.
Women's health differs from that of men in many unique ways. Women's health is an example of population health, where health is defined by the World Health Organization as "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity". Often treated as simply women's reproductive health, many groups argue for a broader definition pertaining to the overall health of women, better expressed as "The health of women". These differences are further exacerbated in developing countries where women, whose health includes both their risks and experiences, are further disadvantaged.

Passive smoking is the inhalation of tobacco smoke, called secondhand smoke (SHS), or environmental tobacco smoke (ETS), by persons other than the intended "active" smoker. It occurs when tobacco smoke enters an environment, causing its inhalation by people within that environment. Exposure to secondhand tobacco smoke causes disease, disability, and death. The health risks of secondhand smoke are a matter of scientific consensus. These risks have been a major motivation for smoke-free laws in workplaces and indoor public places, including restaurants, bars and night clubs, as well as some open public spaces.

Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, consists of measures taken for disease prevention. Disease and disability are affected by environmental factors, genetic predisposition, disease agents, and lifestyle choices, and are dynamic processes which begin before individuals realize they are affected. Disease prevention relies on anticipatory actions that can be categorized as primal, primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention.

Emergency management is the organization and management of the resources and responsibilities for dealing with all humanitarian aspects of emergencies. The aim is to prevent and reduce the harmful effects of all hazards, including disasters.

Global health is the health of the populations in the worldwide context; it has been defined as "the area of study, research and practice that places a priority on improving health and achieving equity in health for all people worldwide". Problems that transcend national borders or have a global political and economic impact are often emphasized. Thus, global health is about worldwide health improvement, reduction of disparities, and protection against global threats that disregard national borders. Global health is not to be confused with international health, which is defined as the branch of public health focusing on developing nations and foreign aid efforts by industrialized countries. Global health can be measured as a function of various global diseases and their prevalence in the world and threat to decrease life expectancy in the present day. Estimates suggest that in a pre-modern, poor world, life expectancy was around 30 years in all regions of the world.
Mitigation is the reduction of something harmful or the reduction of its harmful effects. It may refer to measures taken to reduce the harmful effects of hazards that remain in potentia, or to manage harmful incidents that have already occurred. It is a stage or component of emergency management and of risk management. The theory of mitigation is a frequently used element in criminal law and is often used by a judge to analyse and conclude on cases such as murder, where a perpetrator is subject to varying degrees of responsibility as a result of ones actions.
Radon mitigation is any process used to reduce radon gas concentrations in the breathing zones of occupied buildings, or radon from water supplies. Radon is a significant contributor to environmental radioactivity.

Radium and radon are important contributors to environmental radioactivity. Radon occurs naturally in the environment as a result of decay of radioactive elements in the soil and it can accumulate in houses built on areas where such decay occurs. Radon is among the major causes of cancer; it is estimated to contribute to about 2% of all cancer related deaths in Europe.

A non-communicable disease (NCD) is a disease that is not transmissible directly from one person to another. NCDs include Parkinson's disease, autoimmune diseases, strokes, most heart diseases, most cancers, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, Alzheimer's disease, cataracts, and others. NCDs may be chronic or acute. Most are non-infectious, although there are some non-communicable infectious diseases, such as parasitic diseases in which the parasite's life cycle does not include direct host-to-host transmission.

Disease burden is the impact of a health problem as measured by financial cost, mortality, morbidity, or other indicators. It is often quantified in terms of quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) or disability-adjusted life years (DALYs). Both of these metrics quantify the number of years lost due to disability (YLDs), sometimes also known as years lost due to disease or years lived with disability/disease. One DALY can be thought of as one year of healthy life lost, and the overall disease burden can be thought of as a measure of the gap between current health status and the ideal health status. According to an article published in The Lancet in June 2015, low back pain and major depressive disorder were among the top ten causes of YLDs and were the cause of more health loss than diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and asthma combined. The study based on data from 188 countries, considered to be the largest and most detailed analysis to quantify levels, patterns, and trends in ill health and disability, concluded that "the proportion of disability-adjusted life years due to YLDs increased globally from 21.1% in 1990 to 31.2% in 2013." The environmental burden of disease is defined as the number of DALYs that can be attributed to environmental factors. Similarly, the work-related burden of disease is defined as the number of deaths and DALYs that can be attributed to occupational risk factors to human health. These measures allow for comparison of disease burdens, and have also been used to forecast the possible impacts of health interventions. By 2014 DALYs per head were "40% higher in low-income and middle-income regions."

R. William Field is an academic scholar and Professor in the Department of Occupational and Environmental Health and Department of Epidemiology within the College of Public Health at the University of Iowa. He received a BS and MS degree in Biology from Millersville University of Pennsylvania and a PhD in Preventive Medicine from the College of Medicine at the University of Iowa in 1994. Field is currently an occupational and environmental epidemiologist as well as an internationally recognized expert on the measurement and health effects of radon gas.

Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types of air pollutants, such as gases, particulates, and biological molecules. Air pollution can cause diseases, allergies, and even death to humans; it can also cause harm to other living organisms such as animals and food crops, and may damage the natural environment or built environment. Both human activity and natural processes can generate air pollution.

Household air pollution (HAP) is a significant form of indoor polluted air mostly relating to cooking and heating methods used in developing countries.
Radon, a radioactive, colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas, has been studied by a number of scientific and medical bodies for its effects on health. A naturally-occurring gas formed as a decay product of radium, radon is one of the densest substances that remains a gas under normal conditions, and is considered to be a health hazard due to its radioactivity. Its most stable isotope, radon-222, has a half-life of 3.8 days. Due to its high radioactivity, it has been less well-studied by chemists, but a few compounds are known.
Exposure to ionizing radiation is known to increase the future incidence of cancer, particularly leukemia. The mechanism by which this occurs is well understood, but quantitative models predicting the level of risk remain controversial. The most widely accepted model posits that the incidence of cancers due to ionizing radiation increases linearly with effective radiation dose at a rate of 5.5% per sievert; if correct, natural background radiation is the most hazardous source of radiation to general public health, followed by medical imaging as a close second. Additionally, the vast majority of non-invasive cancers are non-melanoma skin cancers caused by ultraviolet radiation. Non-ionizing radio frequency radiation from mobile phones, electric power transmission, and other similar sources have been described as a possible carcinogen by the WHO's International Agency for Research on Cancer, but the link remains unproven.
The United Nations Interagency Task Force on the Prevention and Control of Non-communicable Diseases (UNIATF), hereafter referred to as the Task Force, was established by the United Nations Secretary-General in 2013. Non-communicable diseases (NCDs), also known as chronic diseases, include cardiovascular diseases, cancers, chronic respiratory diseases and diabetes. The role of the Task Force is to bring relevant actors from across the United Nations (UN) system and national governments together to develop whole-of-government, whole-of-society approaches for the prevention and control of NCDs. Following the establishment of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development in 2015, the Task Force's scope of work was expanded to include “NCD related Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)” such as addressing mental health conditions, violence, injuries, nutrition and environmental issues that contribute to the global burden of NCDs. The Task Force promotes multisectoral action for the prevention and control of NCDs, supports countries to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and supports countries to move towards Universal Health Coverage (UHC). The work of the Task Force includes implementing the Global Joint Programme to conduct investment cases, coordinating interagency joint programmes and facilitating thematic working groups. The World Health Organization acts as a Secretariat for the Task Force.
Environmental health policy is the interplay between the environment and health, and how the environment can affect human health. Policies are created by governments and organizations where they see the issues arising in the health of their jurisdiction related to the environment, and enforced by environmental health officers.

Lung cancer in Australia has killed more than 9,000 people and there are estimated to be over 12,500 new cases as of 2018. Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in Australia and is responsible for one fifth of cancer diagnosis in the nation. It is differentiated into two different types: Non-small cell lung cancer and small cell-lung cancer. There are a range of diagnostic and treatment options available to treat both disease types. Smoking tobacco cigarettes is considered the leading risk factor of lung cancer in Australia, and Government-led public health schemes have aimed to reduce smoking and minimise its lung cancer risk. There has been relative success in these campaigns, and in treatment, as survival rates have improved from 9.2% to 17% as of 2014.Attitudes towards habitual smoking in youth and young adult groups have also subsequently changed in response to this. However, there is a growing stigma surrounding people living with Lung Cancer, and a large portion of work conducted by the Lung Foundation Australia is directed towards supporting the health and welfare of those affected.