In the context of software engineering, software quality refers to two related but distinct notions:
Quality management ensures that an organization, product or service consistently functions well. It has four main components: quality planning, quality assurance, quality control and quality improvement. Quality management is focused not only on product and service quality, but also on the means to achieve it. Quality management, therefore, uses quality assurance and control of processes as well as products to achieve more consistent quality. Quality control is also part of quality management. What a customer wants and is willing to pay for it, determines quality. It is a written or unwritten commitment to a known or unknown consumer in the market. Quality can be defined as how well the product performs its intended function.
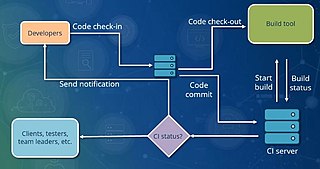
In software engineering, continuous integration (CI) is the practice of merging all developers' working copies to a shared mainline several times a day. Nowadays it is typically implemented in such a way that it triggers an automated build with testing. Grady Booch first proposed the term CI in his 1991 method, although he did not advocate integrating several times a day. Extreme programming (XP) adopted the concept of CI and did advocate integrating more than once per day – perhaps as many as tens of times per day.
Software quality assurance (SQA) is a means and practice of monitoring all software engineering processes, methods, and work products to ensure compliance against defined standards. It may include ensuring conformance to standards or models, such as ISO/IEC 9126, SPICE or CMMI.
Biomedical tissue is biological tissue used for organ transplantation and medical research, particularly cancer research. When it is used for research it is a biological specimen.

Genetic Alliance is a nonprofit organization, founded in 1986 by Joan O. Weiss, working with Victor A. McKusick, to advocate for health benefits in the accelerating field of genomic research. This organization is a network of over 1,000 disease advocacy organizations, universities, government organizations, private companies, and public policy organizations. They aim to advance genetic research agendas toward health benefit by engaging a broad range of stakeholders, including healthcare providers, researchers, industry professionals, public policy leaders, as well as individuals, families and communities. They create programs using a collaborative approach, and aim to increase efficiency and reduce obstacles in genetic research, while ensuring that voices from the involved disease communities are heard. They also promote public policies to advance healthcare. Genetic Alliance provides technical support and informational resources to guide disease-specific advocacy organizations in being their own research advocates. They also maintain a biobank as a central storage facility for several organizations who otherwise would not have the infrastructure to maintain their own repository.

A biobank is a type of biorepository that stores biological samples for use in research. Biobanks have become an important resource in medical research, supporting many types of contemporary research like genomics and personalized medicine.
The College of American Pathologists (CAP) is a member-based physician organization founded in 1946 comprising approximately 18,000 board-certified pathologists. It serves patients, pathologists, and the public by fostering and advocating best practices in pathology and laboratory medicine.
Laboratory quality control is designed to detect, reduce, and correct deficiencies in a laboratory's internal analytical process prior to the release of patient results, in order to improve the quality of the results reported by the laboratory. Quality control (QC) is a measure of precision, or how well the measurement system reproduces the same result over time and under varying operating conditions. Laboratory quality control material is usually run at the beginning of each shift, after an instrument is serviced, when reagent lots are changed, after equipment calibration, and whenever patient results seem inappropriate. Quality control material should approximate the same matrix as patient specimens, taking into account properties such as viscosity, turbidity, composition, and color. It should be simple to use, with minimal vial-to-vial variability, because variability could be misinterpreted as systematic error in the method or instrument. It should be stable for long periods of time, and available in large enough quantities for a single batch to last at least one year. Liquid controls are more convenient than lyophilized (freeze-dried) controls because they do not have to be reconstituted, minimizing pipetting error. Dried Tube Specimen (DTS) is slightly cumbersome as a QC material but it is very low-cost, stable over long periods and efficient, especially useful for resource-restricted settings in under-developed and developing countries. DTS can be manufactured in-house by a laboratory or Blood Bank for its use.
A biorepository is a facility that collects, catalogs, and stores samples of biological material for laboratory research. Biorepositories collect and manage specimens from animals, plants, and other living organisms. Biorepositories store many different types of specimens, including samples of blood, urine, tissue, cells, DNA, RNA, and proteins. If the samples are from people, they may be stored with medical information along with written consent to use the samples in laboratory studies.

P3G (Public Population Project in Genomicsand Society) is a not-for-profit international consortium dedicated to facilitating collaboration between researchers and biobanks working in the area of human population genomics. P3G is member-based and composed of experts from the different disciplines in the areas of and related to genomics, including epidemiology, law, ethics, technology, biomolecular science, etc. P3G and its members are committed to a philosophy of information sharing with the goal of supporting researchers working in areas that will improve the health of people around the world.
The Collaborative Human Tissue Network was established in 1987 by the National Cancer Institute in response to an increase in the demand for high quality biospecimens for cancer research. The purpose of the CHTN is to stimulate, for the good of the public, cooperative efforts to collect and distribute human biospecimens and to thereby facilitate research utilizing those specimens. These activities are expected to encourage basic and developmental studies in many areas of cancer research, including molecular biology, immunology and genetics. The CHTN is not intended to be a human tissue bank, but instead procures tissue at the request of an investigator. Limited banking was to be done as needed to meet specific requests and longer-term banking of targeted specimens to assure availability of rare and hard to obtain materials. It is funded under a UM1 NIH grant.
External quality assessment (EQA) is a challenge of the effectiveness of a laboratory's quality management system, typically referring specifically to medical laboratories. The term external refers to the fact that that the laboratory's results are assessed by a third party. The most common EQA process is proficiency testing, in which an organization sends samples to a group of different laboratories and results are compared among the group. Retesting of the same sample by different laboratories and on-site visits to evaluate laboratory processes may also be part of an EQA scheme.
AstridBio Ltd. is a privately held Biotechnology company with office in Hungary. AstridBio's focus is biobanking software development, data management and analysis for genomics research. Its clients include academic research institutes, pharmaceutical and biotech companies.

A biological specimen is a biological laboratory specimen held by a biorepository for research. Such a specimen would be taken by sampling so as to be representative of any other specimen taken from the source of the specimen. When biological specimens are stored, ideally they remain equivalent to freshly-collected specimens for the purposes of research.
Privacy for research participants is a concept in research ethics which states that a person in human subject research has a right to privacy when participating in research. Some typical scenarios this would apply to include, or example, a surveyor doing social research conducts an interview with a participant, or a medical researcher in a clinical trial asks for a blood sample from a participant to see if there is a relationship between something which can be measured in blood and a person's health. In both cases, the ideal outcome is that any participant can join the study and neither the researcher nor the study design nor the publication of the study results would ever identify any participant in the study. Thus, the privacy rights of these individuals can be preserved.

De-identification is the process used to prevent someone's personal identity from being revealed. For example, data produced during human subject research might be de-identified to preserve the privacy of research participants. Biological data may be de-identified in order to comply with HIPAA regulations that define and stipulate patient privacy laws.
The Coriell Institute for Medical Research is an independent, non-profit biomedical research center dedicated to the study of the human genome. Coriell features programs in biobanking, personalized medicine, cell biology, cytogenetics, genotyping, and induced pluripotent stem cell science. Located in downtown Camden, New Jersey, the Institute has partnered with several prominent state and national health leaders, including Cooper University Hospital, the Cooper Medical School of Rowan University, the United States Air Force, the University of Pennsylvania, and Stanford University.

Marianne Krall Henderson is an American biomedical scientist specialized in biobanks and biorepositories. She is a senior advisor on biospecimen resources at the National Cancer Institute. Henderson was president of the International Society for Biological and Environmental Repositories from 2011 to 2012.





