
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, commonly known as DDT, is a colorless, tasteless, and almost odorless crystalline chemical compound, an organochloride. Originally developed as an insecticide, it became infamous for its environmental impacts. DDT was first synthesized in 1874 by the Austrian chemist Othmar Zeidler. DDT's insecticidal action was discovered by the Swiss chemist Paul Hermann Müller in 1939. DDT was used in the second half of World War II to limit the spread of the insect-born diseases malaria and typhus among civilians and troops. Müller was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1948 "for his discovery of the high efficiency of DDT as a contact poison against several arthropods".

Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause yellow skin, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria.

Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. The term pesticide includes all of the following: herbicide, insecticides nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, antimicrobial, and fungicide. The most common of these are herbicides which account for approximately 80% of all pesticide use. Most pesticides are intended to serve as plant protection products, which in general, protect plants from weeds, fungi, or insects. As an example, the fungus Alternaria is used to combat the aquatic weed Salvinia.

Plasmodium is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes that are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. The life cycles of Plasmodium species involve development in a blood-feeding insect host which then injects parasites into a vertebrate host during a blood meal. Parasites grow within a vertebrate body tissue before entering the bloodstream to infect red blood cells. The ensuing destruction of host red blood cells can result in disease, called malaria. During this infection, some parasites are picked up by a blood-feeding insect, continuing the life cycle.

A pesticide poisoning occurs when pesticides, chemicals intended to control a pest, affect non-target organisms such as humans, wildlife, plant, or bees. There are three types of pesticide poisoning. The first of the three is a single and short-term very high level of exposure which can be experienced by individuals who commit suicide, as well as pesticide formulators. The second type of poisoning is long-term high-level exposure, which can occur in pesticide formulators and manufacturers. The third type of poisoning is a long-term low-level exposure, which individuals are exposed to from sources such as pesticide residues in food as well as contact with pesticide residues in the air, water, soil, sediment, food materials, plants and animals.

Plasmodium falciparum is a unicellular protozoan parasite of humans, and the deadliest species of Plasmodium that causes malaria in humans. The parasite is transmitted through the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito and causes the disease's most dangerous form, falciparum malaria. It is responsible for around 50% of all malaria cases. P. falciparum is therefore regarded as the deadliest parasite in humans. It is also associated with the development of blood cancer and is classified as Group 2A carcinogen.
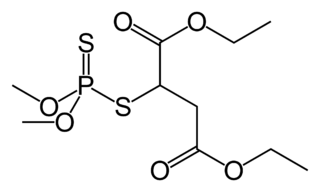
Malathion is an organophosphate insecticide which acts as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. In the USSR, it was known as carbophos, in New Zealand and Australia as maldison and in South Africa as mercaptothion.
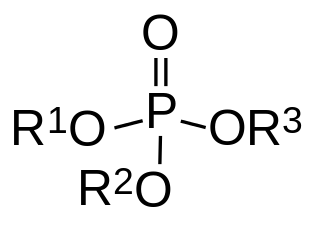
Organophosphates are a class of organophosphorus compounds with the general structure O=P(OR)3, a central phosphate molecule with alkyl or aromatic substituents. They can be considered as esters of phosphoric acid. Like most functional groups organophosphates occur in a diverse range of forms, with important examples including key biomolecules such as DNA, RNA and ATP, as well as many insecticides, herbicides, nerve agents and flame retardants. OPEs have been widely used in various products as flame retardants, plasticizers, and performance additives to engine oil. The popularity of OPEs as flame retardants came as a substitution for the highly regulated brominated flame retardants. The low cost of production and compatibility to different polymers made OPEs to be widely used in different industries including textile, furniture, electronics as plasticizers and flame retardants. These compounds are added to the final product physically rather than by chemical bond. Due to this OPEs leak into the environment more readily through volatilization, leaching, as well as abrasion. OPEs have been detected in different environmental compartments such as air, dust, water, sediment, soil and biota samples at higher frequency and concentration.

Diazinon, a colorless to dark brown liquid, is a thiophosphoric acid ester developed in 1952 by Ciba-Geigy, a Swiss chemical company. It is a nonsystemic organophosphate insecticide formerly used to control cockroaches, silverfish, ants, and fleas in residential, non-food buildings. Diazinon was heavily used during the 1970s and early 1980s for general-purpose gardening use and indoor pest control. A bait form was used to control scavenger wasps in the western U.S. Diazinon is used in flea collars for domestic pets in Australia and New Zealand. Residential uses of diazinon were outlawed in the U.S. in 2004 because of human health risks but it is still approved for agricultural uses. An emergency antidote is atropine.

Mosquito control manages the population of mosquitoes to reduce their damage to human health, economies, and enjoyment. Mosquito control is a vital public-health practice throughout the world and especially in the tropics because mosquitoes spread many diseases, such as malaria and the Zika virus.

Deltamethrin is a pyrethroid ester insecticide. Deltamethrin plays a key role in controlling malaria vectors, and is used in the manufacture of long-lasting insecticidal mosquito nets; however, resistance of mosquitos and bed bugs to deltamethrin is becoming widespread.

Any cause that reduces or increases reproductive success in a portion of a population potentially exerts evolutionary pressure, selective pressure or selection pressure, driving natural selection. It is a quantitative description of the amount of change occurring in processes investigated by evolutionary biology, but the formal concept is often extended to other areas of research.

Organophosphate poisoning is poisoning due to organophosphates (OPs). Organophosphates are used as insecticides, medications, and nerve agents. Symptoms include increased saliva and tear production, diarrhea, vomiting, small pupils, sweating, muscle tremors, and confusion. While onset of symptoms is often within minutes to hours, some symptoms can take weeks to appear. Symptoms can last for days to weeks.

The history of malaria stretches from its prehistoric origin as a zoonotic disease in the primates of Africa through to the 21st century. A widespread and potentially lethal human infectious disease, at its peak malaria infested every continent, except Antarctica. Its prevention and treatment have been targeted in science and medicine for hundreds of years. Since the discovery of the Plasmodium parasites which cause it, research attention has focused on their biology, as well as that of the mosquitoes which transmit the parasites.

Chrysomya megacephala, more commonly known as the oriental latrine fly, is a member of the family Calliphoridae (blowflies). It is a warm-weather fly with a greenish-blue metallic box-like body. The fly infests corpses soon after death, making it important to forensic science. This fly is implicated in some public health issues; it can cause accidental myiasis, and also infects fish and livestock.

Sentinel Event Notification System for Occupational Risks (SENSOR)-Pesticides is a U.S. state-based surveillance program that monitors pesticide-related illness and injury. It is administered by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), twelve state health agencies participate. NIOSH provides technical support to all participating states. It also provides funding to some states, in conjunction with the US Environmental Protection Agency.

Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase enzyme family.

Anopheles stephensi is a primary mosquito vector of malaria in urban India and is included in the same subgenus as Anopheles gambiae, the primary malaria vector in Africa. A. gambiae consists of a complex of morphologically identical species of mosquitoes, along with all other major malaria vectors; however, A. stephensi has not yet been included in any of these complexes. Nevertheless, two races of A. stephensi exist based on differences in egg dimensions and the number of ridges on the eggs; A. s. stephensisensu stricto, the type form, is a competent malaria vector that takes place in urban areas, and A. s. mysorensis, the variety form, exists in rural areas and exhibits considerable zoophilic behaviour, making it a poor malaria vector. However, A. s. mysorensis is a detrimental vector in Iran. An intermediate form also exists in rural communities and peri-urban areas, though its vector status is unknown. About 12% of malaria cases in India are due to A. stephensi.

The direct and indirect effects of climate change on human health are becoming increasingly obvious. Direct effects include exposure to extreme weather events such as heat waves. Indirect effects include disruption to economic and social activity, which can impact health if for example it reduces people's ability to earn a livelihood. Other health related effects arise from environmental degradation, diseases carried by vectors, food and waterborne infections, changes to food security, and impacts on mental health. In some cases there can be health benefits, but in the clear majority of observed and predicted cases, the health impacts of climate change are negative.
Anopheles funestus is a species of mosquito in the Culicidae family. This species was first described in 1900 by Giles. The female is attracted to houses where it seeks out humans in order to feed on their blood, mostly during the night. This mosquito is a major vector of malaria in sub-Saharan Africa.



















