Related Research Articles

Niger–Congo is a hypothetical language family spoken over the majority of sub-Saharan Africa. It unites the Mande languages, the Atlantic-Congo languages, and possibly several smaller groups of languages that are difficult to classify. If valid, Niger-Congo would be the world's largest in terms of member languages, the third-largest in terms of speakers, and Africa's largest in terms of geographical area. It is generally considered to be the world's largest language family in terms of the number of distinct languages, just ahead of Austronesian, although this is complicated by the ambiguity about what constitutes a distinct language; the number of named Niger–Congo languages listed by Ethnologue is 1,540.

Benue–Congo is a major branch of the Volta-Congo languages which covers most of Sub-Saharan Africa.
The Adamawa languages are a putative family of 80–90 languages scattered across the Adamawa Plateau in Central Africa, in northern Cameroon, north-western Central African Republic, southern Chad, and eastern Nigeria, spoken altogether by only one and a half million people. Joseph Greenberg classified them as one branch of the Adamawa–Ubangi family of Niger–Congo languages. They are among the least studied languages in Africa, and include many endangered languages; by far the largest is Mumuye, with 400,000 speakers. A couple of unclassified languages—notably Laal and Jalaa—are found along the fringes of the Adamawa area.

Southern Bantoid is a branch of the Bantoid language family. It consists of the Bantu languages along with several small branches and isolates of eastern Nigeria and west-central Cameroon. Since the Bantu languages are spoken across most of Sub-Saharan Africa, Southern Bantoid comprises 643 languages as counted by Ethnologue, though many of these are mutually intelligible.
Tiv is a Tivoid language spoken in some states in North Central Nigeria, with some speakers in Cameroon. It had over 5 million speakers in 2020. The largest population of Tiv speakers are found in Benue state in Nigeria. The language is also widely spoken in the Nigerian states of Plateau, Taraba, Nasarawa, Cross River, Adamawa, Kaduna, and Abuja. It is by far the largest of the Tivoid languages, a group of languages belonging to the Southern Bantoid languages
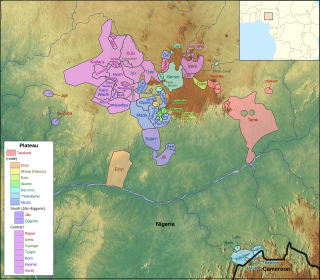
The forty or so Plateau languages are a tentative group of Benue–Congo languages spoken by 15 million people on the Jos Plateau, Southern Kaduna, Nasarawa State and in adjacent areas in central Nigeria.

There are over 525 native languages spoken in Nigeria. The official language and most widely spoken lingua franca is English, which was the language of Colonial Nigeria. Nigerian Pidgin – an English-based creole – is spoken by 30 million people in Nigeria.

The Beboid languages are any of several groups of languages spoken principally in southwest Cameroon, although two languages are spoken over the border in Nigeria. They are probably not most closely related to each other. The Eastern Beboid languages may be most closely related to the Tivoid and Momo groups, though some of the geographical Western Beboid grouping may be closer to Ekoid and Bantu.

The Ekoid languages are a dialect cluster of Southern Bantoid languages spoken principally in southeastern Nigeria and in adjacent regions of Cameroon. They have long been associated with the Bantu languages, without their status being precisely defined. Crabb (1969) remains the major monograph on these languages, although regrettably, Part II, which was to contain grammatical analyses, was never published. Crabb also reviews the literature on Ekoid up to the date of publication.
"Ekoi" or "Ejagham" may refer to:

Ekoi people, also known as Ejagham, are an ethnic group in southeastern Nigeria and extending eastward into the southwest region of Cameroon. They speak the Ejagham language. Other Ekoi languages are spoken by related groups, including the Etung, some groups in Ikom, some groups in Ogoja, Ufia, and Yakö. The Ekoi have lived closely with the nearby Efik, Annang, Ibibio, and Igbo people of southeastern Nigeria. The Ekoi are best known for their Ekpe headdresses and the Nsibidi text. The Ejagham are the original creators of the Nsibidi ideograms and still use them as a part of tradition.
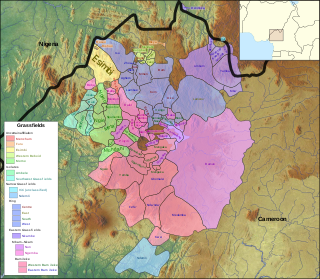
The Grassfields languages are a branch of the Southern Bantoid languages spoken in the Western High Plateau of Cameroon and some parts of Taraba state, Nigeria. Better known Grassfields languages include the Eastern Grassfields languages, Bamun, Yamba, Bali, and Bafut and the Ring languages, Kom, Nso, and Oku. Almost all of these languages are closely related, sharing approximately half of their vocabulary.
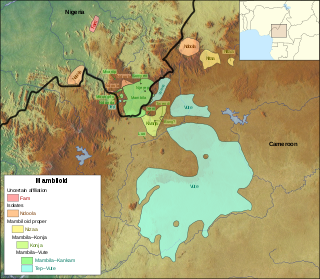
The twelve Mambiloid languages are languages spoken by the Mambila and related peoples mostly in eastern Nigeria and in Cameroon. In Nigeria the largest group is Mambila. In Cameroon the largest group is Vute.
Ukaan is a poorly described Niger–Congo language or dialect cluster of uncertain affiliation. Roger Blench suspects, based on wordlists, that it might be closest to the (East) Benue–Congo languages. Blench (2012) states that "noun-classes and concord make it look Benue-Congo, but evidence is weak."
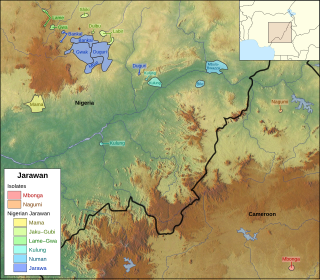
Jarawan is a group of languages spoken mostly in Bauchi State, Nigeria, with some also scattered in Plateau State, Taraba State, and Adamawa State in the same country. Two related languages formerly spoken in Cameroon are now extinct but are believed to have belonged to the group. This connection between Nigerian and Cameroonian Jarawan is attributed to Thomas (1925). Whether Jarawan languages are best classified alongside other Bantu languages or among non-Bantu Bantoid languages is a matter of ongoing debate. A number of descriptions and classifications in the early 20th century suggest that they be may historically related to Bantu languages but not necessarily Bantu themselves. Other perspectives based on lexicostatistic modeling and other phylogenetic techniques for language comparison argue instead that Jarawan languages are properly classified alongside Zone A Bantu languages (A31-A40-A60). For classifications based on these more recent studies, see for example Blench (2006), Piron (1997), and Grollemund (2012).

The Bendi languages are a small group of languages spoken in Cross River State, southeastern Nigeria. Bokyi is one of the Bendi languages having some speakers in Cameroon. Once counted among the Cross River languages, they may be a branch of Southern Bantoid, with observed similarities especially with the Ekoid languages.

The Kwasio language, also known as Ngumba / Mvumbo, Bujeba, and Gyele / Kola, is a language of Cameroon, spoken in the south along the coast and at the border with Equatorial Guinea by some 70,000 members of the Ngumba, Kwasio, Gyele and Mabi peoples. Many authors view Kwasio and the Gyele/Kola language as distinct. In the Ethnologue, the languages therefore receive different codes: Kwasio has the ISO 639-3 code nmg, while Gyele has the code gyi. The Kwasio, Ngumba, and Mabi are village farmers; the Gyele are nomadic Pygmy hunter-gatherers living in the rain forest.
Iyasa is a Bantu language spoken in Cameroon and Equatorial Guinea by the Iyasa and Ndowe coastal fishing peoples. It is also spoken by Pygmies, perhaps Babongo, in Gabon. Approximately 3,000 people speak Iyasa, though some note that this number may be an overestimation.
Mbe is a language spoken by the Mbube people of the Ogoja, Cross River State region of Nigeria, numbering about 65,000 people in 2011. As the closest relative of the Ekoid family of the Southern Bantoid languages, Mbe is fairly close to the Bantu languages. It is tonal and has a typical Niger–Congo noun-class system.
Izere is a dialect continuum of Plateau languages in Nigeria. According to Blench (2008), it is four languages, though Ethnologue does not distinguish NW and NE Izere. The Cen and Ganang varieties are spoken by only 2000 each. Cen has added Berom noun-class prefixes and consonant alternation to an Izere base.
References
- ↑ Ekoi at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Tadadjeu 1993, p. 73.
- ↑ Blench, Roger. "Ekoid: Bantoid languages of the Nigeria-Cameroun borderland" (PDF). p. 1.
- ↑ Blench, Roger (2019). An Atlas of Nigerian Languages (4th ed.). Cambridge: Kay Williamson Educational Foundation.
Works cited
- Tadadjeu, Maurice (1993). "Cameroun". In Rhonda L. Hartell (ed.). Alphabets des langues africaines. Dakar: Unesco et Société internationale de linguistique.