Related Research Articles
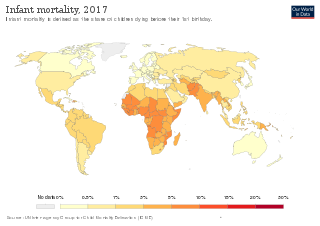
Infant mortality is the death of an infant before the infant's first birthday. The occurrence of infant mortality in a population can be described by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the number of deaths of infants under one year of age per 1,000 live births. Similarly, the child mortality rate, also known as the under-five mortality rate, compares the death rate of children up to the age of five.

Prenatal care, also known as antenatal care, is a type of preventive healthcare. It is provided in the form of medical checkups, consisting of recommendations on managing a healthy lifestyle and the provision of medical information such as maternal physiological changes in pregnancy, biological changes, and prenatal nutrition including prenatal vitamins, which prevents potential health problems throughout the course of the pregnancy and promotes the mother and child's health alike. The availability of routine prenatal care, including prenatal screening and diagnosis, has played a part in reducing the frequency of maternal death, miscarriages, birth defects, low birth weight, neonatal infections and other preventable health problems.
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can often result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. The term is in contrast to miscarriage, which is an early pregnancy loss, and sudden infant death syndrome, where the baby dies a short time after being born alive.

A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders.

Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between 28 and 32 weeks, early preterm birth occurs between 32 and 34 weeks, late preterm birth is between 34 and 36 weeks' gestation. These babies are also known as premature babies or colloquially preemies or premmies. Symptoms of preterm labor include uterine contractions which occur more often than every ten minutes and/or the leaking of fluid from the vagina before 37 weeks. Premature infants are at greater risk for cerebral palsy, delays in development, hearing problems and problems with their vision. The earlier a baby is born, the greater these risks will be.
Environmental toxicants and fetal development is the impact of different toxic substances from the environment on the development of the fetus. This article deals with potential adverse effects of environmental toxicants on the prenatal development of both the embryo or fetus, as well as pregnancy complications. The human embryo or fetus is relatively susceptible to impact from adverse conditions within the mother's environment. Substandard fetal conditions often cause various degrees of developmental delays, both physical and mental, for the growing baby. Although some variables do occur as a result of genetic conditions pertaining to the father, a great many are directly brought about from environmental toxins that the mother is exposed to.

Large for gestational age (LGA) is a term used to describe infants that are born with an abnormally high weight, specifically in the 90th percentile or above, compared to other babies of the same developmental age. Macrosomia is a similar term that describes excessive birth weight, but refers to an absolute measurement, regardless of gestational age. Typically the threshold for diagnosing macrosomia is a body weight between 4,000 and 4,500 grams, or more, measured at birth, but there are difficulties reaching a universal agreement of this definition.

Low birth weight (LBW) is defined by the World Health Organization as a birth weight of an infant of 2,499 g or less, regardless of gestational age. Infants born with LBW have added health risks which require close management, often in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). They are also at increased risk for long-term health conditions which require follow-up over time.

Birth weight is the body weight of a baby at their birth. The average birth weight in babies of European and African descent is 3.5 kilograms (7.7 lb), with the normative range between 2.5 and 4.0 kilograms. On average, babies of Asian descent weigh about 3.25 kilograms (7.2 lb). The prevalence of low birth weight has changed over time. Trends show a slight decrease from 7.9% (1970) to 6.8% (1980), then a slight increase to 8.3% (2006), to the current levels of 8.2% (2016). The prevalence of low birth weights has trended slightly upward from 2012 to the present.
Prenatal development includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal development until birth.
Maternal health is the health of women during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period. In most cases, maternal health encompasses the health care dimensions of family planning, preconception, prenatal, and postnatal care in order to ensure a positive and fulfilling experience. In other cases, maternal health can reduce maternal morbidity and mortality. Maternal health revolves around the health and wellness of pregnant women, particularly when they are pregnant, at the time they give birth, and during child-raising. WHO has indicated that even though motherhood has been considered as a fulfilling natural experience that is emotional to the mother, a high percentage of women develop health problems and sometimes even die. Because of this, there is a need to invest in the health of women. The investment can be achieved in different ways, among the main ones being subsidizing the healthcare cost, education on maternal health, encouraging effective family planning, and ensuring progressive check up on the health of women with children. Maternal morbidity and mortality particularly affects women of color and women living in low and lower-middle income countries.

Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances called pollutants in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. It is also the contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment either by chemical, physical, or biological agents that alters the natural features of the atmosphere. There are many different types of air pollutants, such as gases, particulates, and biological molecules. Air pollution can cause diseases, allergies, and even death to humans; it can also cause harm to other living organisms such as animals and crops, and may damage the natural environment or built environment. Air pollution can be caused by both human activities and natural phenomena.
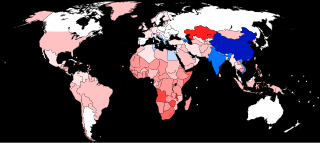
The human sex ratio is the ratio of males to females in a population in the context of anthropology and demography. In humans, the natural sex ratio at birth is slightly biased towards the male sex. It is estimated to be about 1.05 or 1.06 or within a narrow range from 1.03 to 1.06 males per female.
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials into the atmosphere, causing harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or damaging ecosystems. Air pollution can cause health problems including, but not limited to, infections, behavioral changes, cancer, organ failure, and premature death. These health effects are not equally distributed across the U.S. population; there are demographic disparities by race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and education. Air pollution can derive from natural sources, or anthropogenic sources. Anthropogenic air pollution has affected the United States since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution.
Prenatal care in the United States is a health care preventive care protocol recommended to women with the goal to provide regular check-ups that allow obstetricians-gynecologists, family medicine physicians, or midwives to detect, treat and prevent potential health problems throughout the course of pregnancy while promoting healthy lifestyles that benefit both mother and child. Patients are encouraged to attend monthly checkups during the first two trimesters and in the third trimester gradually increasing to weekly visits. Women who suspect they are pregnant can schedule pregnancy tests prior to 9 weeks gestation. Once pregnancy is confirmed an initial appointment is scheduled after 8 weeks gestation. Subsequent appointments consist of various tests ranging from blood pressure to glucose levels to check on the health of the mother and fetus. If not, appropriate treatment will then be provided to hinder any further complications.
The health of a mother directly affects the fetus during pregnancy. High levels of vehicle pollution where pregnant women reside can have adverse health effects on fetuses.
This article summarizes healthcare in Texas. In 2022, the United Healthcare Foundation ranked Texas as the 38th healthiest state in the United States. Obesity, excessive drinking, maternal mortality, infant mortality, vaccinations, mental health, and limited access to healthcare are among the major public health issues facing Texas.
Jeannette R. Ickovics is an American health and social psychologist. She is the inaugural Samuel and Liselotte Herman Professor of Social and Behavioral Sciences at the Yale School of Public Health and Professor of Psychology at the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences at Yale University. She was the Founding Chair of the Social and Behavioral Sciences at the Yale School of Public Health and the Founding Director of Community Alliance for Research and Engagement (CARE). She served as the Dean of Faculty at Yale-NUS College in Singapore from 2018 to 2021.
Black maternal mortality in the United States refers to the death of women, specifically those who identify as Black or African American, during or after child delivery. In general, maternal death can be due to a myriad of factors, such as how the nature of the pregnancy or the delivery itself, but is not associated with unintentional or secondary causes. In the United States, around 700 women die from pregnancy-related illnesses or complications per year. This number does not include the approximately 50,000 women who experience life-threatening complications during childbirth, resulting in lifelong disabilities and complications. However, there are stark differences in maternal mortality rates for Black American women versus Indigenous American, Alaska Native, and White American women.
Maternal health outcomes differ significantly between racial groups within the United States. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists describes these disparities in obstetric outcomes as "prevalent and persistent." Black, indigenous, and people of color are disproportionately affected by many of the maternal health outcomes listed as national objectives in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services's national health objectives program, Healthy People 2030. The American Public Health Association considers maternal mortality to be a human rights issue, also noting the disparate rates of Black maternal death. Race affects maternal health throughout the pregnancy continuum, beginning prior to conception and continuing through pregnancy (antepartum), during labor and childbirth (intrapartum), and after birth (postpartum).
References
- ↑ Rothwell, Charles J. (June 19, 2018), NCHS Update to the Board of Scientific Counselors (PDF), National Center for Health Statistics
- 1 2 Jennifer Parker, University of Maryland School of Public Health , retrieved 2019-01-04
- ↑ Presidents 1971–2017 (PDF), Caucus for Women in Statistics , retrieved 2019-01-04
- ↑ "Many Honored at Presidential Address and Awards Ceremony", AMSTAT News, October 1, 2017