
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy.

Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging is the use of specific MRI sequences as well as software that generates images from the resulting data that uses the diffusion of water molecules to generate contrast in MR images. It allows the mapping of the diffusion process of molecules, mainly water, in biological tissues, in vivo and non-invasively. Molecular diffusion in tissues is not random, but reflects interactions with many obstacles, such as macromolecules, fibers, and membranes. Water molecule diffusion patterns can therefore reveal microscopic details about tissue architecture, either normal or in a diseased state. A special kind of DWI, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), has been used extensively to map white matter tractography in the brain.
Functional imaging is a medical imaging technique of detecting or measuring changes in metabolism, blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption.
Burton Drayer, MD, FACR, FANN, is an American radiologist and nationally recognized authority on the use of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosing neurological disorders. From 2003 to 2008, he served as president, The Mount Sinai Hospital. As of 2020, he is the Charles M. and Marilyn Newman Professor and System Chair, Radiology, for The Mount Sinai Health System and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City.

Mark S. George is a Distinguished University Professor of psychiatry, radiology and neurosciences and is the director of the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) Center for Advanced Imaging Research as well as the Brain Stimulation Laboratory. As of June 2020, his research has been cited over 47,000 times, with an h-index of 113 and i-10 index of 404.

Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to produce high quality two-dimensional or three-dimensional images of the brain and brainstem as well as the cerebellum without the use of ionizing radiation (X-rays) or radioactive tracers.
Mark Steven Cohen is an American neuroscientist and early pioneer of functional brain imaging using magnetic resonance imaging. He currently is a Professor of Psychiatry, Neurology, Radiology, Psychology, Biomedical Physics and Biomedical Engineering at the Semel Institute for Neuroscience and Human Behavior and the Staglin Center for Cognitive Neuroscience. He is also a performing musician.

Zang-Hee Cho is a Korean neuroscientist who developed the first Ring-PET scanner and the scintillation detector BGO. More recently, Cho developed the first PET-MRI fusion molecular imaging device for neuro-molecular imaging.
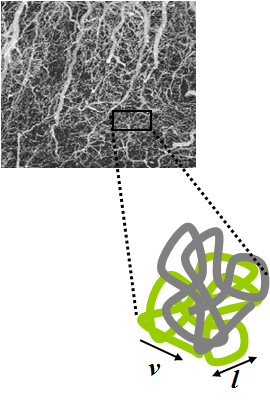
Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging is a concept and a method initially introduced and developed by Le Bihan et al. to quantitatively assess all the microscopic translational motions that could contribute to the signal acquired with diffusion MRI. In this model, biological tissue contains two distinct environments: molecular diffusion of water in the tissue, and microcirculation of blood in the capillary network (perfusion). The concept introduced by D. Le Bihan is that water flowing in capillaries mimics a random walk (Fig.1), as long as the assumption that all directions are represented in the capillaries is satisfied.

Val Murray Runge is an American and Swiss professor of radiology and the editor-in-chief of Investigative Radiology. Runge was one of the early researchers to investigate the use of gadolinium-based contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), giving the first presentation in this field, followed two years later by the first presentation of efficacy. His research also pioneered many early innovations in MRI, including the use of tilted planes and respiratory gating. His publication on multiple sclerosis in 1984 represented the third and largest clinical series investigating the role of MRI in this disease, and the first to show characteristic abnormalities on MRI in patients whose CT was negative.
Bruce Rosen is an American physicist and radiologist and a leading expert in the area of functional neuroimaging. His research for the past 30 years has focused on the development and application of physiological and functional nuclear magnetic resonance techniques, as well as new approaches to combine functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data with information from other modalities such as positron emission tomography (PET), magnetoencephalography (MEG) and noninvasive optical imaging. The techniques his group has developed to measure physiological and metabolic changes associated with brain activation and cerebrovascular insult are used by research centers and hospitals throughout the world.

Ferenc Andras Jolesz was a Hungarian-American physician and scientist best known for his research on image guided therapy, the process by which information derived from diagnostic imaging is used to improve the localization and targeting of diseased tissue to monitor and control treatment during surgical and interventional procedures. He pioneered the field of Magnetic Resonance Imaging-guided interventions and introduced of a variety of new medical procedures based on novel combinations of imaging and therapy delivery.
James S. Hyde was an American biophysicist. He held the James S. Hyde chair in Biophysics at the Medical College of Wisconsin (MCW) where he specialized in magnetic resonance instrumentation and methodology development in two distinct areas: electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). He is senior author of the widely cited 1995 paper by B.B. Biswal et al. reporting the discovery of resting state functional connectivity (fcMRI) in the human brain. He also served as Director of the National Biomedical EPR Center, a Research Resource supported by the National Institutes of Health. He was author of more than 400 peer-reviewed papers and review articles and held 35 U.S. Patents. He was recognized by Festschrifts in both EPR and fcMRI.

Ron Kikinis is an American physician and scientist best known for his research in the fields of imaging informatics, image guided surgery, and medical image computing. He is a professor of radiology at Harvard Medical School. Kikinis is the founding director of the Surgical Planning Laboratory in the Department of Radiology at Brigham and Women's Hospital, in Boston, Massachusetts. He is the vice-chair for Biomedical Informatics Research in the Department of Radiology.

Roderic Ivan Pettigrew is an American physicist, engineer, and physician who is CEO of EnHealth and Executive Dean for EnMed at Texas A&M University. From 2002-November 2017, he was the founding director of the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) at the National Institutes of Health (NIH). He is a pioneer and world expert in cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).

An MRI sequence in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a particular setting of pulse sequences and pulsed field gradients, resulting in a particular image appearance.
Denis Le Bihan is a medical doctor, physicist, member of the Institut de France, member of the French Academy of Technologies and director since 2007 of NeuroSpin, an institution of the Atomic Energy and Alternative Energy Commission (CEA) in Saclay, dedicated to the study of the brain by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with a very high magnetic field. Denis Le Bihan has received international recognition for his outstanding work, introducing new imaging methods, particularly for the study of the human brain, as evidenced by the many international awards he has received, such as the Gold Medal of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (2001), the coveted Lounsbery Prize, the Louis D. Prize from the Institut de France, the prestigious Honda Prize (2012), the Louis-Jeantet Prize (2014), the Rhein Foundation Award (2021). His work has focused on the introduction, development and application of highly innovative methods, notably diffusion MRI.
Daniel Kevin Sodickson is an American physicist and an expert in the field of biomedical imaging. A past president and gold medalist of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, he is credited with foundational work in parallel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), in which distributed arrays of detectors are used to gather magnetic resonance images at previously inaccessible speeds. Sodickson is an elected Fellow of the US National Academy of Inventors. He currently serves as Vice-Chair for Research in the Department of Radiology at New York University (NYU) Grossman School of Medicine, as Director of the department's Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, as Principal Investigator of the Center for Advanced Imaging Innovation and Research, and as Co-Director of NYU's Tech4Health Institute.
Karla Loreen Miller is an American neuroscientist and professor of biomedical engineering at the University of Oxford. Her research investigates the development of neuroimaging techniques, with a particular focus on Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), neuroimaging, diffusion MRI and functional magnetic resonance imaging. She was elected a Fellow of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine in 2016.
Amir Amini is the Professor and Endowed Chair in Bioimaging at the University of Louisville. Prior to this, he was the founder of the Cardiovascular Image Analysis Laboratory and associate professor at the Washington University in St. Louis. He was elected a fellow of the IEEE in 2007, the College of Fellows of the American Institute of Medical and Biological Engineering in 2017, the International Society for Optics, Photonics, and Imaging in 2019, and the Asia-Pacific Artificial Intelligence Association in 2021.











