Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are an immune cell or some types of venom, e.g. from the puff adder or brown recluse spider.

A biogenic substance is a product made by or of life forms. While the term originally was specific to metabolite compounds that had toxic effects on other organisms, it has developed to encompass any constituents, secretions, and metabolites of plants or animals. In context of molecular biology, biogenic substances are referred to as biomolecules. They are generally isolated and measured through the use of chromatography and mass spectrometry techniques. Additionally, the transformation and exchange of biogenic substances can by modelled in the environment, particularly their transport in waterways.
The lignans are a large group of low molecular weight polyphenols found in plants, particularly seeds, whole grains, and vegetables. The name derives from the Latin word for "wood". Lignans are precursors to phytoestrogens. They may play a role as antifeedants in the defense of seeds and plants against herbivores.

Ferulic acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid, an organic compound. It is an abundant phenolic phytochemical found in plant cell walls, covalently bonded as side chains to molecules such as arabinoxylans. As a component of lignin, ferulic acid is a precursor in the manufacture of other aromatic compounds. The name is derived from the genus Ferula, referring to the giant fennel.

Secoisolariciresinol is an organic compound. It is classified as a lignan, i.e., a type of phenylpropanoid. It is present in some cereals, e.g. rye, and together with matairesinol, has attracted much attention for its beneficial nutritional effects.
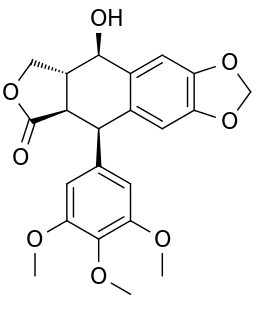
Podophyllotoxin (PPT) is the active ingredient in Podofilox, which is a medical cream that is used to treat genital warts and molluscum contagiosum. It is not recommended in HPV infections without external warts. It can be applied either by a healthcare provider or the person themselves.

Safranal is an organic compound isolated from saffron, the spice consisting of the stigmas of crocus flowers. It is the constituent primarily responsible for the aroma of saffron.

The complex-toothed flying squirrel occurs in the southern Chinese provinces Hubei, Hunan, Guizhou, Sichuan, and Yunnan. The common name refers to the teeth, which differ from those of other species of flying squirrels.
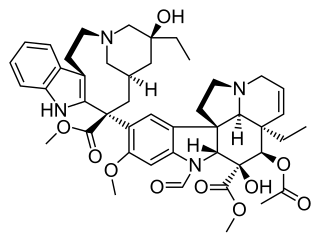
Vinca alkaloids are a set of anti-mitotic and anti-microtubule alkaloid agents originally derived from the periwinkle plant Catharanthus roseus and other vinca plants. They block beta-tubulin polymerization in a dividing cell.

Honokiol is a lignan isolated from the bark, seed cones, and leaves of trees belonging to the genus Magnolia. It has been identified as one of the chemical compounds in some traditional eastern herbal medicines along with magnolol, 4-O-methylhonokiol, and obovatol.

Magnolol is an organic compound that is classified as lignan. It is a bioactive compound found in the bark of the Houpu magnolia or in M. grandiflora. The compound exists at the level of a few percent in the bark of species of magnolia, the extracts of which have been used in traditional Chinese and Japanese medicine. In addition to magnolol, related lignans occur in the extracts including honokiol, which is an isomer of magnolol.

Natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCR3 gene. NCR3 has also been designated as CD337 and as NKp30.

Herbacetin is a flavonol, a type of flavonoid.

Enterolactone is a organic compound classified as an enterolignan. It is formed by the action of intestinal bacteria on plant lignan precursors present in the diet.
![Enterodiol Lignan formed by the action of intestinal bacteria on lignan precursors found in plants.[1]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/eb/Enterodiol.png/320px-Enterodiol.png)
Enterodiol is an organic compound with the formula [HOC6H4CH2CH(CH2OH)]2.
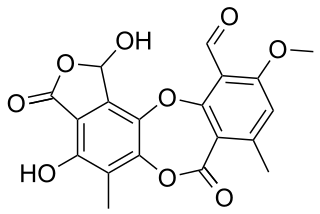
Stictic acid is an aromatic organic compound, a product of secondary metabolism in some species of lichens.

Coumarinolignoids are phenolic compounds formed from a lignan structure with a coumarin formed in place of one of the two phenylpropanoids.
1,7-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,4,6-heptatrien-3-one is a natural product, a curcuminoid antioxidant found in turmeric and torch ginger.

Dichapetalins are a small class of triterpenoid compounds found primarily in the Dichapetalaceae family but also reportedly in Phyllanthus (Euphorbiaceae). They are structural derivatives of dammarene characterized by a C6C2 unit connected to a dammarene or a 13,30-cyclodammarane skeleton with variable C-17 side chains containing actone, spirolactone, lactol, acetal, or furan moieties. They have been found to display cytotoxicity against several cancer cell lines.
Hinokinin is a dibenzylbutyrolactone lignan, derived from various species of plants. It is a potential antichagonistic agent and has shown to possess neuroprotective effects as well. It is also found to have anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, antiviral and antifungal properties.













![Enterodiol Lignan formed by the action of intestinal bacteria on lignan precursors found in plants.[1]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/eb/Enterodiol.png/320px-Enterodiol.png)


