Related Research Articles

Populism is a range of political stances that emphasize the idea of "the people" and often juxtapose this group with "the elite". It is frequently associated with anti-establishment and anti-political sentiment. The term developed in the late 19th century and has been applied to various politicians, parties and movements since that time, often as a pejorative. Within political science and other social sciences, several different definitions of populism have been employed, with some scholars proposing that the term be rejected altogether.

Self-Defence of the Republic of Poland is a nationalist, socialist, populist, and agrarian political party and trade union in Poland. The party promotes agrarian socialist and Catholic socialist economic policies combined with a left-wing populist, anti-globalization and anti-neoliberal rhetoric. The party describes itself as left-wing, although it stresses that it belongs to the "patriotic left" and follows Catholic social teaching. The party is sympathetic to Communist Poland, which led political scientists to label the party as neocommunist, post-communist, and far-left.

Law and Justice is a right-wing populist and national-conservative political party in Poland. Its chairman is Jarosław Kaczyński.

Order and Justice, formerly the Liberal Democratic Party was a right-wing national-conservative political party in Lithuania that self-identified as "left-of-centre", at least on economic matters. It had eight members in the Seimas, the unicameral Lithuanian parliament, as of the last election it participated in (2016).

The Alternative Democratic Reform Party is a conservative and mildly populist political party in Luxembourg. It has five seats in the sixty-seat Chamber of Deputies, making it the fourth-largest party.

Right-wing populism, also called national populism and right-wing nationalism, is a political ideology that combines right-wing politics and populist rhetoric and themes. Its rhetoric employs anti-elitist sentiments, opposition to the Establishment, and speaking to or for the "common people". Recurring themes of right-wing populists include neo-nationalism, social conservatism, economic nationalism and fiscal conservatism. Frequently, they aim to defend a national culture, identity, and economy against perceived attacks by outsiders. Right-wing populism has remained the dominant political force in the Republican Party in the United States since the 2010s.
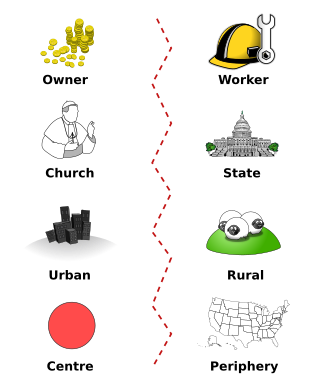
In political science and sociology, a cleavage is a historically determined social or cultural line which divides citizens within a society into groups with differing political interests, resulting in political conflict among these groups. Social or cultural cleavages thus become political cleavages once they get politicized as such. Cleavage theory accordingly argues that political cleavages predominantly determine a country's party system as well as the individual voting behavior of citizens, dividing them into voting blocs. These blocs are distinguished by similar socio-economic characteristics, who vote and view the world in a similar way. It is distinct from other common political theories on voting behavior in the sense that it focuses on aggregate and structural patterns instead of individual voting behaviors.

Patriotic Self-Defence was a minor political party in Poland. The party was founded in September 2006 by former members of the Self-Defence of the Republic of Poland, who left the party following an argument with the leader of Self-Defence Andrzej Lepper. The party ran in the 2007 Polish parliamentary election, where it tried to take votes from their former party by using a similar name, logo and political program. Ultimately, the party's electoral lists were only accepted in one electoral district. The party won 0.02% of the nationwide vote. It disbanded in 2013.
Far-left politics, also known as the radical left or extreme left, are politics further to the left on the left–right political spectrum than the standard political left. The term does not have a single, coherent definition; some scholars consider it to represent the left of social democracy, while others limit it to the left of communist parties. In certain instances—especially in the news media—far left has been associated with some forms of authoritarianism, anarchism, communism, and Marxism, or are characterized as groups that advocate for revolutionary socialism and related communist ideologies, or anti-capitalism and anti-globalization. Far-left terrorism consists of extremist, militant, or insurgent groups that attempt to realize their ideals through political violence rather than using democratic processes.
A valence issue is an issue where there is a broad amount of consensus among voters. As valence issues are representative of a goal or quality, voters use valence issues to evaluate a political party’s effectiveness in producing this particular goal or quality.

The Freedom Party of Austria is a national-conservative and right-wing populist political party in Austria. It has been led by Herbert Kickl since 2021. It is the third largest of five parties in the National Council, with 30 of the 183 seats, and won 16.2% of votes cast in the 2019 legislative election and it is represented in all nine state legislatures. On a European level, the FPÖ is a founding member of the Identity and Democracy Party and its three MEPs sit with the Identity and Democracy (ID) group.

Left-wing populism, also called social populism, is a political ideology that combines left-wing politics with populist rhetoric and themes. Its rhetoric often includes elements of anti-elitism, opposition to the Establishment, and speaking for the "common people". Recurring themes for left-wing populists include economic democracy, social justice, and scepticism of globalization. Socialist theory plays a lesser role than in traditional left-wing ideologies.

The Radical Party of Oleh Liashko and formerly known as the Ukrainian Radical-Democratic Party, is a political party in Ukraine that was registered in September 2010. It was primarily known for its radical populism, especially in the 2014 Ukrainian parliamentary election when it gained its largest support.

Alternative for Germany is a right-wing populist political party in Germany. AfD is known for its Euroscepticism, as well as for opposing immigration to Germany. Described as a party of the far-right, the AfD is commonly positioned on the radical right, a subset of the far-right within the family of European political parties that generally does not reject democracy.

Roger Eatwell is a British academic currently an Emeritus Professor of Politics at the University of Bath.
In political science, the terms reactionary right and populist right have been used to refer to the range of nationalist, right-wing to far-right parties that have grown in support since the late 1970s in Europe. Populist right groups have shared a number of causes, which typically include opposition to globalisation and immigration, criticism of multiculturalism, and opposition to the European Union, but do not oppose democracy.
Populism exists in Europe.
Techno-populism is either a populism in favor of technocracy or a populism concerning certain technology – usually information technology – or any populist ideology conversed using digital media. It can be employed by single politicians or whole political movements respectively. Neighboring terms used in a similar way are technocratic populism, technological populism, and cyber-populism. Italy's Five Star Movement and France's La République En Marche! have been described as technopopulist political movements.
Populism in the United States reaches back to the Presidency of Andrew Jackson in the 1830s and to the People's Party in the 1890s. It has made a resurgence in modern-day politics in not only the United States but also democracies around the world. Populism is an approach to politics which views "the people" as being opposed to "the elite" and is often used as a synonym of anti-establishment; as an ideology, it transcends the typical divisions of left and right and has become more prevalent in the US with the rise of disenfranchisement and apathy toward the establishment. The definition of populism is a complex one as due to its mercurial nature; it has been defined by many different scholars with different focuses, including political, economic, social, and discursive features. Populism is often split into two variants in the US, one with a focus on culture and the other that focuses on economics.

Elections to the European Parliament saw declining voter turnout between 1979 and 2014. However, voter turnout in 2019 European elections increased by 8 points compared to 2014. In spite of this exception for all Member States, the electoral mobilization remains weak compared to the national parliamentary elections. Moreover, turnout significantly differs from one country to another in Europe and across a time: in 2019 Belgium citizens participated the most with 88.47% and Slovakians the less with 22.74%. The potential factors that might influence these trends and their implications have attracted great scholarly attention. Identifying and analysing the factors that determine the relative low turnout at European elections is therefore critical, as it is one element that weakens the democratic legitimacy of the European Parliament.
References
- ↑ "Univ.-Prof. Dr. Kai Arzheimer | German Politics and Political Sociology". German.politics.uni-mainz.de. Retrieved 2017-12-21.
- ↑ "Prof. Dr. Kai Arzheimer | SoCuM" (in German). Retrieved 2023-12-15.
- ↑ "CV - kai arzheimer". 2012-05-04. Retrieved 2023-12-15.