
Ethernet is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 1983 as IEEE 802.3. Ethernet has since been refined to support higher bit rates, a greater number of nodes, and longer link distances, but retains much backward compatibility. Over time, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies such as Token Ring, FDDI and ARCNET.

3Com Corporation was an American digital electronics manufacturer best known for its computer network products. The company was co-founded in 1979 by Robert Metcalfe, Howard Charney and others. Bill Krause joined as President in 1981. Metcalfe explained the name 3Com was a contraction of "Computer Communication Compatibility", with its focus on Ethernet technology that he had co-invented, which enabled the networking of computers.
A network switch is networking hardware that connects devices on a computer network by using packet switching to receive and forward data to the destination device.

Cisco Systems, Inc., commonly known as Cisco, is an American-based multinational digital communications technology conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develops, manufactures, and sells networking hardware, software, telecommunications equipment and other high-technology services and products. Cisco specializes in specific tech markets, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), domain security, videoconferencing, and energy management with leading products including Webex, OpenDNS, Jabber, Duo Security, and Jasper. Cisco is one of the largest technology companies in the world ranking 74 on the Fortune 100 with over $51 billion in revenue and nearly 80,000 employees.

Andreas Maria Maximilian Freiherr von Mauchenheim genannt Bechtolsheim is a German electrical engineer, entrepreneur and investor. He co-founded Sun Microsystems in 1982 and was its chief hardware designer. His net worth reached $7 billion in September 2018.
In computer networking, cut-through switching, also called cut-through forwarding is a method for packet switching systems, wherein the switch starts forwarding a frame before the whole frame has been received, normally as soon as the destination address and outgoing interface is determined. Compared to store and forward, this technique reduces latency through the switch and relies on the destination devices for error handling. Pure cut-through switching is only possible when the speed of the outgoing interface is at least equal or higher than the incoming interface speed.

Power over Ethernet, or PoE, describes any of several standards or ad hoc systems that pass electric power along with data on twisted-pair Ethernet cabling. This allows a single cable to provide both a data connection and enough electricity to power devices such as wireless access points (WAPs), Internet Protocol (IP) cameras and voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) phones.

Foundry Networks, Inc. was a networking hardware vendor selling high-end Ethernet switches and routers. The company was acquired by Brocade Communications Systems on December 18, 2008.

Cabletron Systems was a manufacturer of networking computer equipment throughout the 1980s and 1990s primarily based in Rochester, New Hampshire, in the United States. They also had manufacturing facilities in Ironton, Ohio, and in Ireland.
Bay Networks, Inc., was a network hardware vendor formed through the merger of Santa Clara, California, based SynOptics Communications and Billerica, Massachusetts based Wellfleet Communications on July 6, 1994. SynOptics was an important early innovator of Ethernet products, having developed a pre-standard twisted pair 10Mbit/s Ethernet product and a modular Ethernet hub product that dominated the enterprise networking market. Wellfleet was an important competitor to Cisco Systems in the router market, ultimately commanding up to a 20% market share of the network router business worldwide. The combined company was renamed Bay Networks as a nod to the legacy that SynOptics was based in the San Francisco area and Wellfleet was based in the Boston area, two cities well known for their bays.

Catalyst is the brand for a variety of network switches, wireless controllers, and wireless access points sold by Cisco Systems. While commonly associated with Ethernet switches, a number of different types of network interfaces have been available throughout the history of the brand. Cisco acquired several different companies and rebranded their products as different versions of the Catalyst product line. The original Catalyst 5000 and 6000 series were based on technology acquired from Crescendo Communications. The 1700, 1900, and 2800 series Catalysts came from Grand Junction Networks, and the Catalyst 3000 series came from Kalpana in 1994.

EtherChannel is a port link aggregation technology or port-channel architecture used primarily on Cisco switches. It allows grouping of several physical Ethernet links to create one logical Ethernet link for the purpose of providing fault-tolerance and high-speed links between switches, routers and servers. An EtherChannel can be created from between two and eight active Fast, Gigabit or 10-Gigabit Ethernet ports, with an additional one to eight inactive (failover) ports which become active as the other active ports fail. EtherChannel is primarily used in the backbone network, but can also be used to connect end user machines.

The 10 Gigabit Ethernet Alliance (10GEA) was an independent organization which aimed to further 10 Gigabit Ethernet development and market acceptance. Founded in February 2000 by a consortium of companies, the organization provided IEEE with technology demonstrations and specifications. Its efforts bore fruit with the IEEE Standards Association (IEEE-SA) Standards Board's approval in June 2002 of the IEEE 802.3 standard.
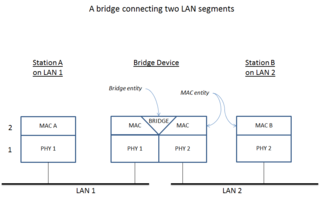
A network bridge is a computer networking device that creates a single, aggregate network from multiple communication networks or network segments. This function is called network bridging. Bridging is distinct from routing. Routing allows multiple networks to communicate independently and yet remain separate, whereas bridging connects two separate networks as if they were a single network. In the OSI model, bridging is performed in the data link layer. If one or more segments of the bridged network are wireless, the device is known as a wireless bridge.
40 Gigabit Ethernet (40GbE) and 100 Gigabit Ethernet (100GbE) are groups of computer networking technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at rates of 40 and 100 gigabits per second (Gbit/s), respectively. These technologies offer significantly higher speeds than 10 Gigabit Ethernet. The technology was first defined by the IEEE 802.3ba-2010 standard and later by the 802.3bg-2011, 802.3bj-2014, 802.3bm-2015, and 802.3cd-2018 standards.
Cortina Systems, Inc. is a supplier of integrated circuits (ICs) for broadband communications founded in 2001. It is based in California.
TRILL is an Internet Standard implemented by devices called TRILL switches. TRILL combines techniques from bridging and routing, and is the application of link-state routing to the VLAN-aware customer-bridging problem. Routing bridges (RBridges) are compatible with and can incrementally replace previous IEEE 802.1 customer bridges. TRILL Switches are also compatible with IPv4 and IPv6, routers and end systems. They are invisible to current IP routers, and like conventional routers, RBridges terminate the broadcast, unknown-unicast and multicast traffic of DIX Ethernet and the frames of IEEE 802.2 LLC including the bridge protocol data units of the Spanning Tree Protocol.

FORE Systems was a computer network switching equipment company based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Founded in 1990 to supply Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) cards for workstation computers, it soon branched out to become a major supplier in the ATM switch market and the extended those product lines to add Internet Protocol switching and other devices.
Arista Networks is an American computer networking company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. The company designs and sells multilayer network switches to deliver software-defined networking (SDN) for large datacenter, cloud computing, high-performance computing, and high-frequency trading environments. These products include 10/25/40/50/100 Gigabit Ethernet/200/400/800 low-latency cut-through switches, including the 7124SX, which remained the fastest switch using SFP+ optics through September 2012 with its sub-500 nanosecond (ns) latency, and the 7500 series, Arista's modular 10G/40G/100Gbit/s switch. Arista's Linux-based network operating system, Extensible Operating System (EOS), runs on all Arista products.

Ethernet Routing Switch 3500 series and Ethernet Routing Switch 2500 series or ERS 3500 and ERS 2500 in data computer networking terms are stackable routing switches designed and manufactured by Avaya.













