
In astronomy and astrobiology, the habitable zone (HZ), or more precisely the circumstellar habitable zone (CHZ), is the range of orbits around a star within which a planetary surface can support liquid water given sufficient atmospheric pressure. The bounds of the HZ are based on Earth's position in the Solar System and the amount of radiant energy it receives from the Sun. Due to the importance of liquid water to Earth's biosphere, the nature of the HZ and the objects within it may be instrumental in determining the scope and distribution of planets capable of supporting Earth-like extraterrestrial life and intelligence.

A Super-Earth is a type of exoplanet with a mass higher than Earth's, but substantially below those of the Solar System's ice giants, Uranus and Neptune, which are 14.5 and 17 times Earth's, respectively. The term "super-Earth" refers only to the mass of the planet, and so does not imply anything about the surface conditions or habitability. The alternative term "gas dwarfs" may be more accurate for those at the higher end of the mass scale, although "mini-Neptunes" is a more common term.

An exoplanet is a planet located outside the Solar System. The first evidence of an exoplanet was noted as early as 1917, but was not recognized as such until 2016; no planet discovery has yet come from that evidence. What turned out to be the first detection of an exoplanet was published among a list of possible candidates in 1988, though not confirmed until 2003. The first confirmed detection came in 1992, with the discovery of terrestrial-mass planets orbiting the pulsar PSR B1257+12. The first confirmation of an exoplanet orbiting a main-sequence star was made in 1995, when a giant planet was found in a four-day orbit around the nearby star 51 Pegasi. Some exoplanets have been imaged directly by telescopes, but the vast majority have been detected through indirect methods, such as the transit method and the radial-velocity method. As of 1 January 2024, there are 5,576 confirmed exoplanets in 4,113 planetary systems, with 887 systems having more than one planet. This is a list of the most notable discoveries.
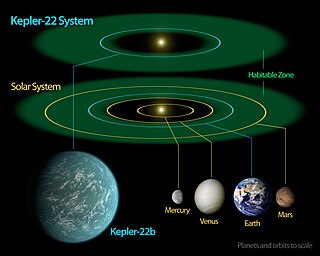
Kepler-22b is an exoplanet orbiting within the habitable zone of the Sun-like star Kepler-22. It is located about 640 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Cygnus. It was discovered by NASA's Kepler Space Telescope in December 2011 and was the first known transiting planet to orbit within the habitable zone of a Sun-like star, where liquid water could exist on the planet's surface. Kepler-22 is too dim to be seen with the naked eye.

Kepler-69c is a confirmed super-Earth extrasolar planet, likely rocky, orbiting the Sun-like star Kepler-69, the outermore of two such planets discovered by NASA's Kepler spacecraft. It is located about 2,430 light-years from Earth.

Kepler-62e is a super-Earth exoplanet discovered orbiting within the habitable zone of Kepler-62, the second outermost of five such planets discovered by NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler-62e is located about 990 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Lyra. The exoplanet was found using the transit method, in which the dimming effect that a planet causes as it crosses in front of its star is measured. Kepler-62e may be a terrestrial or ocean-covered planet; it lies in the inner part of its host star's habitable zone.

Kepler-62f is a super-Earth exoplanet orbiting within the habitable zone of the star Kepler-62, the outermost of five such planets discovered around the star by NASA's Kepler spacecraft. It is located about 980 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Lyra.
Kepler-61b is a super-Earth exoplanet orbiting within parts of the habitable zone of the K-type main-sequence star Kepler-61. It is located about 1,100 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Cygnus. It was discovered in 2013 using the transit method, in which the dimming effect that a planet causes as it crosses in front of its star is measured, by NASA's Kepler spacecraft.

Kepler-438b is a confirmed near-Earth-sized exoplanet. It is likely rocky. It orbits on the inner edge of the habitable zone of a red dwarf, Kepler-438, about 472.9 light-years from Earth in the constellation Lyra. It receives 1.4 times our solar flux. The planet was discovered by NASA's Kepler spacecraft using the transit method, in which the dimming effect that a planet causes as it crosses in front of its star is measured. NASA announced the confirmation of the exoplanet on 6 January 2015.

Kepler-442b is a confirmed near-Earth-sized exoplanet, likely rocky, orbiting within the habitable zone of the K-type main-sequence star Kepler-442, about 1,206 light-years (370 pc) from Earth in the constellation of Lyra.
Kepler-440b is a confirmed super-Earth exoplanet orbiting within the habitable zone of Kepler-440, about 850 light-years (261 pc) from Earth. The planet was discovered by NASA's Kepler spacecraft using the transit method, in which the dimming effect that a planet causes as it crosses in front of its star is measured. NASA announced the confirmation of the exoplanet on 6 January 2015.

Kepler-452b is a super-Earth exoplanet orbiting within the inner edge of the habitable zone of the sun-like star Kepler-452 and is the only planet in the system discovered by Kepler. It is located about 1,800 light-years (550 pc) from Earth in the constellation of Cygnus.
Kepler-419c is a super-Jupiter exoplanet orbiting within the habitable zone of the star Kepler-419, the outermost of two such planets discovered by NASA's Kepler spacecraft. It is located about 3,400 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cygnus. The exoplanet was found by using the transit timing variation method, in which the variations of transit data from an exoplanet are studied to reveal a more distant companion.

Kepler-1229b is a confirmed super-Earth exoplanet, likely rocky, orbiting within the habitable zone of the red dwarf Kepler-1229, located about 870 light years from Earth in the constellation of Cygnus. It was discovered in 2016 by the Kepler space telescope. The exoplanet was found by using the transit method, in which the dimming effect that a planet causes as it crosses in front of its star is measured.
Kepler-442 is a K-type main-sequence star approximately 1,206 light years from Earth in the constellation Lyra. It is located within the field of vision of the Kepler spacecraft, the satellite that NASA's Kepler Mission used to detect planets that may be transiting their stars. On January 6, 2015, along with the notable stars of Kepler-438 and Kepler-440, it was announced that the star has an extrasolar planet orbiting within the habitable zone, named Kepler-442b.
Kepler-1652b is a super-Earth exoplanet, orbiting within the habitable zone of the red dwarf Kepler-1652 about 822 light-years away in the Cygnus constellation. Discovered by NASA's Kepler spacecraft, Kepler-1652b was first announced as a candidate in 2013, but wasn't validated until four years later in 2017. It is a potential super-Earth with 160% Earth's radius. The planet orbits well within the habitable zone of its system, the region where liquid water can exist on a planet's surface. The planet is an eyeball planet candidate.

Kepler-1649c is an Earth-sized exoplanet, likely rocky, orbiting within the habitable zone of the red dwarf star Kepler-1649, the outermost planet of the planetary system discovered by Kepler’s space telescope. It is located about 301 light-years (92 pc) away from Earth, in the constellation of Cygnus.
Kepler-1544b is a potentially habitable exoplanet announced in 2016 and located 1138 light years away, in the constellation of Cygnus.
Kepler-737b is a super-Earth exoplanet 669 light years away. There is a chance it could be on the inner edge of the habitable zone.












