
A corona is the outermost layer of a star's atmosphere. It is a hot but relatively dim region of plasma populated by intermittent coronal structures known as solar prominences or filaments.
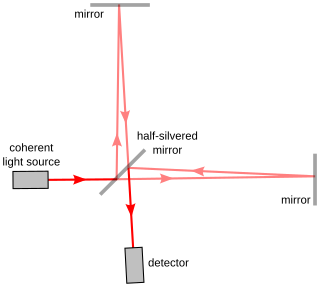
Interferometry is a technique which uses the interference of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy, quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms.

A coronal mass ejection (CME) is a significant ejection of magnetic field and accompanying plasma mass from the Sun's corona into the heliosphere. CMEs are often associated with solar flares and other forms of solar activity, but a broadly accepted theoretical understanding of these relationships has not been established.

The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) is a European Space Agency (ESA) spacecraft built by a European industrial consortium led by Matra Marconi Space that was launched on a Lockheed Martin Atlas IIAS launch vehicle on 2 December 1995, to study the Sun. It has also discovered over 5,000 comets. It began normal operations in May 1996. It is a joint project between the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA. SOHO was part of the International Solar Terrestrial Physics Program (ISTP). Originally planned as a two-year mission, SOHO continues to operate after over 25 years in space; the mission has been extended until the end of 2025, subject to review and confirmation by ESA's Science Programme Committee.

A coronagraph is a telescopic attachment designed to block out the direct light from a star or other bright object so that nearby objects – which otherwise would be hidden in the object's bright glare – can be resolved. Most coronagraphs are intended to view the corona of the Sun, but a new class of conceptually similar instruments are being used to find extrasolar planets and circumstellar disks around nearby stars as well as host galaxies in quasars and other similar objects with active galactic nuclei (AGN).
The Extreme ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (EIT) is an instrument on the SOHO spacecraft used to obtain high-resolution images of the solar corona in the ultraviolet range. The EIT instrument is sensitive to light of four different wavelengths: 17.1, 19.5, 28.4, and 30.4 nm, corresponding to light produced by highly ionized iron (XI)/(X), (XII), (XV), and helium (II), respectively. EIT is built as a single telescope with a quadrant structure to the entrance mirrors: each quadrant reflects a different colour of EUV light, and the wavelength to be observed is selected by a shutter that blocks light from all but the desired quadrant of the main telescope.

The Solar Orbiter (SolO) is a Sun-observing probe developed by the European Space Agency (ESA) with a National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) contribution. Solar Orbiter, designed to obtain detailed measurements of the inner heliosphere and the nascent solar wind, will also perform close observations of the polar regions of the Sun which is difficult to do from Earth. These observations are important in investigating how the Sun creates and controls its heliosphere.

The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) is a NASA mission which has been observing the Sun since 2010. Launched on 11 February 2010, the observatory is part of the Living With a Star (LWS) program.

A Moreton wave, Solar Tsunami, or Moreton-Ramsey wave is the chromospheric signature of a large-scale solar corona shock wave. Described as a kind of solar "tsunami", they are generated by solar flares. They are named for American astronomer Gail Moreton, an observer at the Lockheed Solar Observatory in Burbank, and Harry E. Ramsey, an observer who spotted them in 1959 at The Sacramento Peak Observatory. He discovered them in time-lapse photography of the chromosphere in the light of the Balmer alpha transition.

Comet McNaught, also known as the Great Comet of 2007 and given the designation C/2006 P1, is a non-periodic comet discovered on 7 August 2006 by British-Australian astronomer Robert H. McNaught using the Uppsala Southern Schmidt Telescope. It was the brightest comet in over 40 years, and was easily visible to the naked eye for observers in the Southern Hemisphere in January and February 2007.

Comet 96P/Machholz or 96P/Machholz 1 is a short-period sungrazing comet discovered on May 12, 1986, by amateur astronomer Donald Machholz on Loma Prieta peak, in central California using 130 millimetres (5.1 in) binoculars. On June 6, 1986, 96P/Machholz passed 0.404 AU from the Earth. 96P/Machholz last came to perihelion on January 31, 2023. The comet has an estimated diameter of around 6.4 km (4.0 mi).

In solar physics, a coronal loop is a well-defined arch-like structure in the Sun's atmosphere made up of relatively dense plasma confined and isolated from the surrounding medium by magnetic flux tubes. Coronal loops begin and end at two footpoints on the photosphere and project into the transition region and lower corona. They typically form and dissipate over periods of seconds to days and may span anywhere from 1 to 1,000 megametres in length.
The Sun Watcher using Active Pixel System Detector and Image Processing (SWAP) telescope is a compact extreme-ultraviolet (EUV) imager on board the PROBA-2 mission. SWAP provides images of the solar corona at a temperature of roughly 1 million degrees. the instrument was built upon the heritage of the Extreme ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (EIT) which monitored the solar corona from the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory from 1996 until after the launch of the Solar Dynamics Observatory in 2010.

Helmet streamers, also known as coronal streamers, are elongated cusp-like structures in the Sun's corona which are often visible in white-light coronagraphs and during solar eclipses. They are closed magnetic loops which lie above divisions between regions of opposite magnetic polarity on the Sun's surface. The solar wind elongates these loops to pointed tips which can extend a solar radius or more into the corona.

Proba-3 is a dual probe technological demonstration mission by the European Space Agency devoted to high precision formation flying to achieve scientific coronagraphy. It is part of the series of PROBA satellites that are being used to validate new spacecraft technologies and concepts while also carrying scientific instruments.

The Bastille Day solar storm was a powerful solar storm on 14-16 July 2000 during the solar maximum of solar cycle 23. The storm began on the national day of France, Bastille Day. It involved a solar flare, a solar particle event, and a coronal mass ejection which caused a severe geomagnetic storm.

Supra-arcade downflows (SADs) are sunward-traveling plasma voids that are sometimes observed in the Sun's outer atmosphere, or corona, during solar flares. In solar physics, arcade refers to a bundle of coronal loops, and the prefix supra indicates that the downflows appear above flare arcades. They were first described in 1999 using the Soft X-ray Telescope (SXT) on board the Yohkoh satellite. SADs are byproducts of the magnetic reconnection process that drives solar flares, but their precise cause remains unknown.

The Vigil mission, formerly known as Lagrange, is a Space weather weather mission developed by European Space Agency. The mission will provide the ESA Space Weather Office with instruments able to monitor the Sun, its solar corona and interplanetary medium between the Sun and Earth, to provide early warnings of increased solar activity, to identify and mitigate potential threats to society and ground, airborne and space based infrastructure as well as to allow 4 to 5 days space weather forecasts. To this purpose the Vigil mission will place for the first time a spacecraft at Sun-Earth Lagrange point 5 (L5) from where it would get a 'side' view of the Sun, observing regions of solar activity on the solar surface before they turn and face Earth.

The Wide-Field Imager for Solar Probe (WISPR) is an imaging instrument of the Parker Solar Probe mission to the Sun, launched in August 2018. Imaging targets include visible light images of the corona, solar wind, shocks, solar ejecta, etc. Development of WISPR was led by the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory. The Parker Solar Probe with WISPR on board was launched by a Delta IV Heavy on 12 August 2018 from Cape Canaveral, Florida. WISPR is intended take advantage of the spacecraft's proximity to the Sun by taking coronagraph-style images of the solar corona and features like coronal streamers, plumes, and mass ejections. One of the goals is to better understand the structure of the solar corona near the Sun.

Dr Natchimuthuk "Nat" Gopalswamy is an Indian American Solar physicist. He is currently a staff scientist at the Heliophysics Division of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center.















