Related Research Articles

Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the gram-staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane.

Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever and difficulty breathing. The severity of the condition is variable. Pneumonia is usually caused by infection with viruses or bacteria, and less commonly by other microorganisms. Identifying the responsible pathogen can be difficult. Diagnosis is often based on symptoms and physical examination. Chest X-rays, blood tests, and culture of the sputum may help confirm the diagnosis. The disease may be classified by where it was acquired, such as community- or hospital-acquired or healthcare-associated pneumonia.
Pontiac fever is an acute, nonfatal respiratory disease caused by various species of Gram-negative bacteria in the genus Legionella. It causes a mild upper respiratory infection that resembles acute influenza. Pontiac fever resolves spontaneously and often goes undiagnosed. Both Pontiac fever and the more severe Legionnaire's disease are caused by the same bacteria, but Pontiac fever does not include pneumonia.
Legionella is a genus of pathogenic Gram-negative bacteria that includes the species L. pneumophila, causing legionellosis including a pneumonia-type illness called Legionnaires' disease and a mild flu-like illness called Pontiac fever.

Legionella pneumophila is a thin, aerobic, pleomorphic, flagellated, non-spore-forming, Gram-negative bacterium of the genus Legionella. L. pneumophila is the primary human pathogenic bacterium in this group and is the causative agent of Legionnaires' disease, also known as legionellosis.

Acid-fastness is a physical property of certain bacterial and eukaryotic cells, as well as some sub-cellular structures, specifically their resistance to decolorization by acids during laboratory staining procedures. Once stained as part of a sample, these organisms can resist the acid and/or ethanol-based decolorization procedures common in many staining protocols, hence the name acid-fast.

The Legionellales are an order of Proteobacteria. Like all Proteobacteria, they are Gram-negative. They comprise two families, typified by Legionella and Coxiella, both of which include notable pathogens. For example, Q fever is caused by Coxiella burnetii and Legionella pneumophila causes Legionnaires' disease and Pontiac fever.
Legionella longbeachae is one species of the family Legionellaceae. It was first isolated from a patient in Long Beach, California. It is found predominantly in potting soil and compost. In humans, the infection is sometimes called Pontiac fever. Human infection from L. longbeachae is particularly common in Australia, but cases have been documented in other countries including the United States, Japan, Greece and the UK.
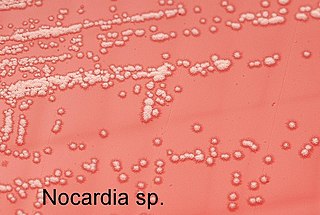
Nocardia is a genus of weakly staining Gram-positive, catalase-positive, rod-shaped bacteria. It forms partially acid-fast beaded branching filaments. It contains a total of 85 species. Some species are nonpathogenic, while others are responsible for nocardiosis. Nocardia species are found worldwide in soil rich in organic matter. In addition, they are oral microflora found in healthy gingiva, as well as periodontal pockets. Most Nocardia infections are acquired by inhalation of the bacteria or through traumatic introduction.
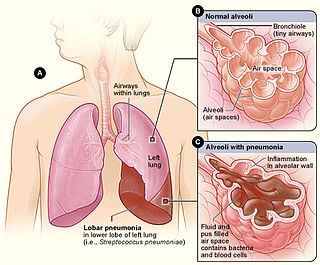
Lobular pneumonia is a form of pneumonia characterized by inflammatory exudate within the intra-alveolar space resulting in consolidation that affects a large and continuous area of the lobe of a lung.

Gemifloxacin mesylate is an oral broad-spectrum quinolone antibacterial agent used in the treatment of acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis and mild-to-moderate pneumonia. Vansen Pharma Inc. has licensed the active ingredient from LG Life Sciences of Korea.

Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) is a form of pneumonia that is caused by the yeast-like fungus Pneumocystis jirovecii. It is also known as PJP, for Pneumocystis jiroveci Pneumonia.

Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article deals with human pathogenic bacteria. Although most bacteria are harmless or often beneficial, some are pathogenic, with the number of species estimated as fewer than a hundred that are seen to cause infectious diseases in humans. By contrast, several thousand species exist in the human digestive system.

The 1976 Legionnaires disease outbreak, occurring in the late summer in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States was the first occasion in which a cluster of a particular type of pneumonia cases were determined to be caused by the Legionella pneumophila bacteria.
Legionella anisa is a Gram-negative bacterium, one of more than 40 species in the family Legionellaceae. After Legionella pneumophila, this species has been isolated most frequently from water samples. This species is also one of the several pathogenic forms of Legionella having been associated with rare clinical cases of illness including Pontiac fever and Legionnaires' disease.
Legionella bozemanae is a Gram-negative bacterium in the family Legionellaceae. Its type strain is WIGA. It is associated with human pneumonia.
Legionella cherrii is an aerobic, flagellated, Gram-negative bacterium from the genus Legionella. It was isolated from a heated water sample in Minnesota. L. cherrii is similar to another Legionella species, L. pneumophila, and is believed to cause major respiratory problems.
Legionella jordanis is a Gram-negative bacterium from the genus Legionella which was isolated from the Jordan River in Bloomington, Indiana and from the sewage in DeKalb County, Georgia. L. jordanis is a rare human pathogen and can cause respiratory tract infections.

Legionnaires' disease is a form of atypical pneumonia caused by any species of Legionella bacteria, quite often Legionella pneumophila. Signs and symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, high fever, muscle pains, and headaches. Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea may also occur. This often begins 2–10 days after exposure.
Legionella clemsonensis was isolated in 2006, but was discovered in 2016 by Clemson University researchers. It is a Gram-negative bacterium.
References
- 1 2 Hébert, G. Ann; Steigerwalt, Arnold G.; Brenner, Don J. (1980-09-01). "Legionella micdadei species nova: Classification of a third species of Legionella associated with human pneumonia". Current Microbiology. 3 (5): 255–257. doi:10.1007/BF02601800. ISSN 0343-8651.
- ↑ McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
| This Legionellales article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |