Argentina is subdivided into twenty-three provinces and the autonomous city of Buenos Aires, which is the federal capital of the nation as decided by the Argentine Congress. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a federal system.
Most Provinces of Argentina held executive and legislative elections during 2011, electing governors and provincial legislatures. The only exceptions are Santiago del Estero Province, whose executive and legislative elections were elected in 2012; and Corrientes Province, whose governor election was elected in 2013.

The history of the Costa Rican legislature is long and starts from even before its formal independence from the Spanish Empire. Costa Rica is one of the world's oldest democracies, thus, its parliamentary history dates back several centuries.

Alejandro Ariel Vilca is an Argentine activist, garbage worker, trade unionist and politician, active in the Socialist Workers' Party (PTS). A member of the indigenous Qulla people, Vilca was elected to the provincial legislature of Jujuy Province in 2017 on the Workers' Left Front (FIT) list, which won 18% of the vote. In 2021, he was elected to the National Chamber of Deputies.

The Legislature of Catamarca is the local legislature of the Argentinian province of Catamarca. It is a bicameral body, comprising the Chamber of Deputies of Catamarca, and the Senate of Catamarca. It is one of eight bicameral legislatures in the country.

The Legislature of Entre Ríos is the local legislature of the Argentinian province of Entre Ríos. It is a bicameral body, comprising the Chamber of Deputies of Entre Ríos, and the Senate of Entre Ríos. It is one of eight bicameral legislatures in the country.

The Legislature of San Luis is the local legislature of the Argentinian province of San Luis. It is a bicameral body, comprising the 43 members of the Chamber of Deputies of San Luis, and the Senate of San Luis with 9 members. It is one of eight bicameral legislatures in the country.

The Legislature of Córdoba is the unicameral legislative body of Córdoba Province, in Argentina. It comprises 70 legislators, of which 23 are elected directly in each of the 23 departments of Córdoba, while the remaining 44 are elected in a single province-wide district. All legislators serve four-year terms and are elected concurrently.

The Legislature of La Rioja, also sometimes referred to as the Legislative Function, is the unicameral legislative body of La Rioja Province, in Argentina. It comprises 36 legislators, elected in each of the 18 departments of La Rioja. Half of the legislature is renewed every two years.

The Legislature of Tierra del Fuego, Antarctica and South Atlantic Islands is the unicameral legislative body of Tierra del Fuego Province, in Argentina. It comprises 15 legislators, elected in a single province-wide multi-member district that encompasses the entirety of the province's territory.

The Chamber of Deputies of San Juan Province is the unicameral legislative body of San Juan Province, in Argentina. It comprises 36 legislators, 17 of whom are directly elected in single-member districts corresponding to the 19 departments of San Juan, and 17 of whom are elected in a single province-wide multi-member district through proportional representation.

The Legislature of Río Negro Province is the unicameral legislative body of Río Negro Province, in Argentina. It convenes in the provincial capital, Viedma.

The Legislature of Neuquén Province is the unicameral legislative body of Neuquén Province, in Argentina. It convenes in the provincial capital, Neuquén.
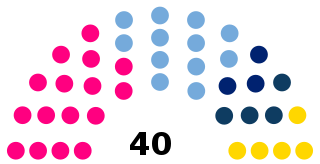
The Chamber of Deputies of Santiago del Estero Province is the unicameral legislative body of Santiago del Estero Province, in Argentina. It comprises 40 legislators, elected in a single province-wide multi-member district through proportional representation using the D'Hondt system.

The Honourable Legislature of Tucumán Province is the unicameral legislative body of Tucumán Province, in Argentina. It convenes in the provincial capital, San Miguel de Tucumán.

The Chamber of Representatives of Misiones Province is the unicameral legislative body of Misiones Province, in Argentina. It convenes in the provincial capital, Posadas.

The Chamber of Deputies of Formosa Province is the unicameral legislative body of Formosa Province, in Argentina. It convenes in the provincial capital, the City of Formosa.

The Chamber of Deputies of Chaco Province, also widely known as the Legislative Power, is the unicameral legislative body of Chaco Province, in Argentina. It convenes in the provincial capital, Resistencia.

The Chamber of Deputies of La Pampa Province is the unicameral legislative body of La Pampa Province, in Argentina. It convenes in the provincial capital, Santa Rosa.

The Legislature of Chubut Province is the unicameral legislative body of Chubut Province, in Argentina. It convenes in the provincial capital, Rawson.





















