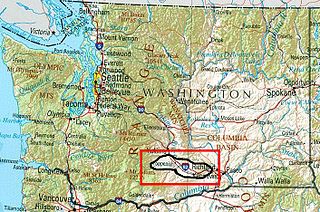
Yakima Valley is the first American Viticultural Area (AVA) established within Washington state, gaining the recognition on May 4, 1983. Within the vast Columbia Valley AVA, Yakima Valley appellation cultivates more than 53,000 acres (21,448 ha) giving the region the largest concentration of wineries and vineyards in the state. The most widely planted varietals in the area are Chardonnay, Riesling, Merlot, Cabernet Sauvignon, Pinot gris, and Syrah. Nearly 40% of Washington's annual wine production is made from Yakima Valley grapes. In addition to grapes, the Yakima Valley is also home to several fruit orchards growing apples, cherries, nectarines, peaches, pears and plums. Around the town of Zillah, there is the Zillah Fruit Loop driving tour through the area's orchards and vineyards. The area is also home to nearly 80% of the US hop production.

Walla Walla Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located within Washington state and extending partly into the northeastern corner of Oregon. The wine region is entirely included within the larger Columbia Valley AVA. In addition to grapes, the area produces sweet onions, wheat and strawberries After the Yakima Valley AVA, the Walla Walla AVA has the second highest concentration of vineyards and wineries in Washington State. Walla Walla hosts about 140 wineries. The area was recognized on March 7, 1984 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury after reviewing the petition submitted by Mr. Richard L Small, President of the Walla Walla Valley Winegrowers Association, for the establishment of a viticultural area in southeast Washington and northeast Oregon, east of Lake Wallula, to be known as "Walls Walls Valley." At the time, Walla Walla Valley viticultural area was approximately 178,560 acres (279 sq mi) with two bonded wineries and about 60 acres (24 ha) from several vineyards.

Horse Heaven Hills is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) in southeastern Washington lying in portions of Klickitat, Yakima, and Benton counties, north and west of the Columbia River and south of the Yakima Valley and lies within the vast Columbia Valley appellation. Horse Heaven Hills was established by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau {TTB), Treasury on June 30, 2005 after reviewing the petition filed by Paul D. Lucas on behalf of regional wine grape growers. Horse Heaven Hills viticultural area is about 60 miles (97 km) long and 22 miles (35 km) wide located 115 miles (185 km) east from Vancouver, Washington. The appellation encompasses 570,000 acres (891 sq mi) with about 6,400 acres (2,590 ha) under vine.

Rattlesnake Hills is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in Yakima County, Washington surrounding the Rattlesnake Hills. The appellation is the state's 9th AVA established on March 20, 2006 by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau {TTB), Treasury after reviewing the petition submitted by Mr. Gail Puryear, Bonair Winery owner, along with 10 other vineyard and winery owners in the region proposing the "Rattlesnake Hills" viticultural area. The 68,500 acres (107 sq mi) Rattlesnake Hills AVA boundaries are within the Yakima Valley AVA as both are encompassed by the vast Columbia Valley AVA. Rattlesnake Hills borders the northern boundary of Yakima Valley including land between the north bank of the Sunnyside Canal and the entire southern boundary slopes are between Outlook and the Wapato Dam. The western boundary meanders on an east-west chain of hills north of I-82 passing through the cities of Parker, Donald, Buena and Zillah while just east of the Yakima River. Rattlesnake Hills rises to the highest point in the Yakima Valley with elevations ranging from 850 to 3,085 feet (259–940 m).

The Augusta AVA was established on June 20, 1980 as the first federally approved American Viticultural Area, eight months before the Napa Valley AVA in northern California. The petition was submitted by Clayton W. Byers and Lucian W. Dressel, representing the local wine industry, to the Director of the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms on October 16, 1978. Located entirely within the state of Missouri, the boundaries of this wine region encompass 15 square miles (39 km2) around the city of Augusta near the intersection of St. Charles County, Warren County and Franklin County.

Temecula Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) in the Temecula Valley, located in southwestern Riverside County, California against the eastern slopes of the Santa Ana Mountains. It was initially established by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury as "Temecula" on October 23, 1984 based on submitted petitions from by the Rancho Califomia/Temecula Winegrowers Association and Callaway Vineyard and Winery, Temecula, California in 1982. It was renamed "Temecula Valley" by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) in 2004, approving the 2001 petition by Temecula Valley Winegrowers Association. The petition stated the name change would provide a more accurate description of the Temecula geography and greater clarity as to its location for wine consumers and the public. The petition did not request any change to the established AVA boundaries. This was the first American Viticultural Area to change its name after the initial approval. Temecula Valley encompasses 33,000 acres (52 sq mi) and 5,000 acres (8 sq mi) is located in a "protected" area referred to as the Citrus/Vineyard Zone. This area is generally located in and around the Rancho California Road area with Riverside County. County guidelines strictly enforce the number of acres needed to build a winery, lodging and other limited housing and commercial ventures.

Sonoma County wine is wine made in Sonoma County, California, in the United States.

Paso Robles is the third American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in San Luis Obispo (SLO) County, California. It was established by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury on November 3, 1983 based on a petition submitted by Martin Brothers Winery. The area encompasses 609,673 acres (953 sq mi) with approximately 18,500 acres (7,487 ha) cultivated with wine grapes known for their heritage varietal Zinfandel, Cabernet Sauvignon, and Rhône-style wines.
The Ohio River Valley AVA is an American Viticultural Area centered on the Ohio River and surrounding areas. It is the second largest wine appellation of origin in the United States with 16,640,000 acres (26,000 sq mi) (67,300 km2) in portions of the states of Indiana, Kentucky, Ohio and West Virginia. The area is mostly planted with hybrid grapes like Baco noir, Marechal Foch, Seyval blanc and Vidal. Of the Vitis vinifera found in the area Cabernet Franc, Cabernet Sauvignon, Chardonnay, Petit Manseng and Riesling are the most common. The AVA size was decreased by approximately 1,530 square miles when the Indiana Uplands AVA was established in 2013 composed of the bordering area in Indiana.
Arroyo Grande Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in San Luis Obispo County, California approximately 12 miles (19 km) southeast of the county seat San Luis Obispo. Arroyo Grande Valley was recognized on February 5, 1990 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF) as the state's 60th AVA based on the petition filed in 1987 by Don Talley of Talley Vineyards and William S. Greenough of Saucelito Canyon Vineyard for the establishment of the "Arroyo Grande Valley" viticultural area in San Luis Obispo County. The 16 miles (26 km) long, approximately 67 square miles valley appellation benefits from its east-northeast orientation allowing the breeze from the Pacific Ocean to moderate the climate of the area. The valley is divided by a fog line produced by the cool maritime layer where Zinfandel, Petite Sirah and Rhône varietals are grown on the higher elevations near Lopez Lake and the cooler mid-valley vineyards being home to Chardonnay and Pinot noir. On April 8, 2022, the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) approved the designation of the expansive San Luis Obispo (SLO) Coast AVA overlapping the boundaries of Edna Valley and Arroyo Grande Valley viticultural areas because they share common features. However, these two previously established areas still have unique characteristics to retain their viticultural area distinctions within SLO Coast. Edna Valley lies immediately to the northwest, the Los Padres National Forest straddles the north leg boundary, the Santa Maria Valley AVA lies to the southeast of Arroyo Grande Valley, and the Pacific Ocean communities of Oceano, Grover City and Arroyo Grande abut its southwestern border.

Sierra Foothills is a vast American Viticultural Area (AVA) encompassing the foothill "belt" of the Sierra Nevada in north-central California, United States. It was established on December 18, 1987 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury after evaluating the petition filed by the Sierra Foothills Winery Association of Somerset, California for the establishment of a "Sierra Foothills" viticultural area in portions of Yuba, Nevada, Placer, El Dorado, Amador, Calaveras, Tuolumne and Mariposa Counties. Wine grapes were introduced to the area in the nineteenth century during the California Gold Rush. Over 280 vineyards/wineries are located within its boundaries.

California wine production has a rich viticulture history since 1680 when Spanish Jesuit missionaries planted Vitis vinifera vines native to the Mediterranean region in their established missions to produce wine for religious services. In the 1770s, Spanish missionaries continued the practice under the direction of the Father Junípero Serra who planted California's first vineyard at Mission San Juan Capistrano.

El Dorado is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in El Dorado County, California, east of the state’s capital, Sacramento and centered around the county seat of Placerville. It was established on November 14, 1983 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF), Treasury after approving the submitted petition from the El Dorado Wine Grape Growers Association of Camino, California applying to establish a viticultural area named "El Dorado.” The area includes parts of El Dorado County on the north border by the Middle Fork American River and on the south by the South Fork of the Cosumnes River. El Dorado viticultural area lies within the vast 4,062 square miles Sierra Foothills viticultural area, one of the largest appellations in California, which extends about 170 miles (274 km) through portions of Yuba, Nevada, Placer, El Dorado, Amador, Calaveras, Tuolumne and Mariposa Counties. The El Dorado viticultural area encompasses 1,093,120 acres (1,708 sq mi) which entirely includes Fair Play and a small portion of northeastern California Shenandoah Valley AVAs.

Fiddletown is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) in Amador County, California, United States. The area was established on November 3, 1983 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury after reviewing the petition submitted from the Fiddletown Wine Grape Growers in Amador County to establish a viticultural area to be known as "Fiddletown." The region was first settled in 1849, during the California Gold Rush. Settlers who stayed in the area eventually planted grape vines, which became abundant by the end of the nineteenth century. Most of the vineyards in the Fiddletown AVA are located in the south and west portion of the region on Sierra Nevada slopes between 1,500 to 2,500 feet (457–762 m) above sea level. About 20% of the wine produced in Amador County comes from Fiddletown viticultural area.

Lake County wine is an appellation that designates wine made from grapes grown mostly in Lake County, California. The region is located north of Napa County and east of Mendocino County. Although each region within Lake County has unique viticultural attributes, many are influenced by Clear Lake, the largest inland body of water in California.

Sta. Rita Hills is an American Viticultural Area located in Santa Barbara County, California. From its creation in 2001 through 2006, the wine appellation was officially named Santa Rita Hills AVA. The formal name change was the result of a protest by and subsequent negotiations with Vina Santa Rita, a very large Chilean wine producer that was concerned about the AVA name diluting its international brand value. The name change took effect on January 5, 2006, with a yearlong period for producers in the AVA to change their wine labels. In 2016, TTB expanded the approximately 33,380 acres (52 sq mi) “Sta. Rita Hills” viticultural area by approximately 2,296 acres (4 sq mi).

Lake Chelan is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) in Washington state. The appellation lies about 112 miles (180 km) northeast of Seattle located in north-central Washington's Lake Chelan Valley and is a sub-appellation of the vast Columbia Valley AVA. It lies east of the Puget Sound viticultural area and north or west of the other Washington State viticultural areas. It borders the Columbia Valley viticultural area on is eastern side and does not include any portion of other Washington viticultural areas except the Columbia Valley AVA.

Naches Heights is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) in Yakima County, Washington. The AVA was recognized officially by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau {TTB), Treasury on January 13, 2012 after reviewing the petition submitted by R. Paul Beveridge, owner of Wilridge Winery and Vineyard, to establish the viticultural area named "Naches Heights." The AVA is located entirely within the vast Columbia Valley AVA with the city of Yakima to the southeast in a valley at a lower elevation. The Naches Heights appellation encompasses 13,254 acres (21 sq mi) and contains 105 acres (42 ha) of commercial vineyards either producing or expecting to produce wine grapes in the foreseeable future. Additionally, it is the first AVA in Washington state to be fully sustainable, with all 7 vineyards practicing in either biodynamic or LIVE certification. At the recognition date, only 37.2 acres (15 ha) were under vine, making the AVA the smallest planted wine region in Washington.
Los Olivos District AVA is an American Viticultural Area located in Santa Barbara County, California established on January 20, 2016, by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB). It straddles the Santa Ynez Valley, formed by the Santa Ynez River, between the Purisima Hills above Solvang. The area encompasses the townships of Los Olivos, Ballard, Santa Ynez and Solvang. State Route 154, known locally as the San Marcos Pass Road or Chumash Highway, bisects the region accessing many of the wineries and vineyards as it traverses toward its destination in Santa Barbara.

Santa Barbara County wine is an appellation that designates wine made from grapes grown mostly in Santa Barbara County, California which is located approximately 50 miles (80 km) north of Los Angeles County. County names in the United States automatically qualify as legal appellations of origin for wine produced from grapes grown in that county and do not require registration with the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) of the Treasury Department. TTB was created in January 2003, when the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms, or ATF, was extensively reorganized under the provisions of the Homeland Security Act of 2002.
















