The Green Party of the United States (GPUS) is a federation of Green state political parties in the United States. The party promotes green politics, specifically environmentalism; nonviolence; social justice; participatory democracy; grassroots democracy; anti-war; anti-racism; eco-socialism. On the political spectrum, the party is generally seen as left-wing. As of 2023, it is the fourth-largest political party in the United States by voter registration, behind the Libertarian Party.

The Libertarian Party (LP) is a political party in the United States that promotes civil liberties, non-interventionism, laissez-faire capitalism, and limiting the size and scope of government. The party was conceived in August 1971 at meetings in the home of David F. Nolan in Westminster, Colorado, and was officially formed on December 11, 1971, in Colorado Springs. The organizers of the party drew inspiration from the works and ideas of the prominent Austrian school economist Murray Rothbard. The founding of the party was prompted in part due to concerns about the Nixon administration, the Vietnam War, conscription, and the introduction of fiat money.

Andrew Verne Marrou is an American politician who served in the Alaska House of Representatives from the 5th district as a member of the Libertarian Party from 1985 to 1987. He was the Libertarian vice-presidential nominee in the 1988 election and presidential nominee in the 1992 election.
The Oklahoma Libertarian Party is the state affiliate of the Libertarian Party in Oklahoma. It has been active in state politics since the 1970s, but due to Oklahoma's ballot access requirements the party has been an officially recognized party during only portions of the last twenty-five years. In 2016, The Oklahoma Libertarian Party regained ballot access. The state party has secured ballot access through at least 2024.

The Libertarian Party of Washington (LPWA) is the state-affiliate of the national Libertarian Party in the state of Washington, the third-largest political party in the state and country.
The Libertarian National Committee (LNC) controls and manages the affairs, properties, and funds of the United States Libertarian Party. It is composed of the party officers, five at-large representatives elected every two years at the national convention, and a theoretical maximum of 10 regional representatives. The current chair is Angela McArdle, first elected at the 2022 Libertarian National Convention and re-elected at the 2024 Libertarian National Convention. Additional officers will be voted into office at the 2024 Libertarian National Convention in Washington DC between May 24 - 26.

The Libertarian Party of New Hampshire (LPNH) is the New Hampshire affiliate of the national Libertarian Party (LP). Active since its foundation in 1972, it is the third-largest political party in the state having had multiple members elected to the New Hampshire House of Representatives as well as being ballot-qualified multiple times.

The Libertarian Party of Oregon is a political party representing the national Libertarian Party in the U.S. state of Oregon. It is organized as a minor party for state election law, and recognized by the Oregon as a statewide nominating party.
The Libertarian Party of Delaware (LPDE) is the Delaware affiliate of the national Libertarian Party. It was founded in 1975.

The Libertarian Party of North Carolina (LPNC) is the North Carolina affiliate of the Libertarian Party.

Nicholas Joel Sarwark is an American attorney and businessman who served as the 19th chair of the Libertarian National Committee (LNC), the governing body of the Libertarian Party. Prior to his election in 2014, he served on several LP national committees and as chair of the Libertarian Party of Maryland State Committee and vice chair of the Libertarian Party of Colorado State Committee. As of 2020, he is the only LP chair to have served three consecutive terms.

The 2020 Libertarian Party presidential primaries and caucuses were a series of electoral contests to indicate non-binding preferences for the Libertarian Party's presidential candidate in the 2020 United States presidential election. These differ from the Republican or Democratic presidential primaries and caucuses in that they do not appoint delegates to represent a candidate at the party's convention to select the party's presidential nominee.

The 2018 Libertarian National Convention was held from June 30 to July 3, 2018, in New Orleans, Louisiana. According to the Libertarian Party, the 2018 convention was the "biggest Libertarian National Convention ever," breaking previous records in attendance and fundraising.
The Libertarian Party of Wyoming (LPWY) is the affiliate of the US Libertarian Party (LP) in Wyoming, headquartered in Riverton. As of 2021 it was the third-largest political party in Wyoming by voter registration, with a share of votes cast that has exceeded 5%.
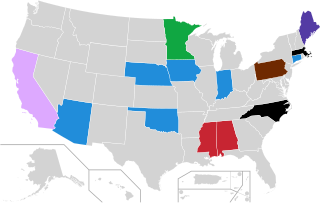
The 2024 Libertarian Party presidential primaries and caucuses are a series of current electoral contests to indicate non-binding preferences for the Libertarian Party (LP) presidential nominee in the 2024 United States presidential election. These differ from the Republican or Democratic presidential primaries and caucuses in that they do not appoint delegates to represent a candidate at the party's convention to select the party's presidential nominee.

The Libertarian Party Mises Caucus (LPMC) is a caucus within the Libertarian Party in the United States that promotes paleolibertarianism, as well as a more radical version of American libertarianism associated with the presidential campaigns of former U.S. congressman Ron Paul. It was founded in 2017 by Michael Heise, mainly in opposition to Nicholas Sarwark's position as party chairman and the pragmatic faction of the party associated with the presidential campaigns of former New Mexico Governor Gary Johnson. It is named after economist Ludwig von Mises.

Angela Elise McArdle is an American politician from Texas and California who was elected on May 28, 2022 as the 22nd and current chair of the Libertarian National Committee. She was also the Secretary of the Libertarian Party of California from April 2018 to April 2019, and was a board member of the Mises Caucus.

The Liberal Party of Pennsylvania is a third party in Pennsylvania founded as the Keystone Party of Pennsylvania in 2022, rebranding to the Liberal moniker in 2024, with a focus on political solutions through the electoral process and Classical Liberalism.
The Unified Libertarians of Massachusetts (ULM), also known as the Libertarian Party of Massachusetts, is a libertarian political party in Massachusetts. It is affiliated with the national Libertarian Party. The party, which was formed in June 2022, claims the lineage and history of the Libertarian Party of Massachusetts, which continues to operate.

Liberal Party USA is a liberal political party in the United States that is affiliated with multiple state parties. In 2022, the state libertarian parties from Massachusetts and New Mexico disaffiliated from the national United States Libertarian Party and affiliated with one another. The Libertarian Party of Virginia also split, with some members leaving to form a new party, the Virginia Classical Liberal Party that affiliated with Liberal Party USA. Additionally, the Liberal Party of Pennsylvania is associated with the organization.














