The Bell AH-1 Cobra is a single-engined attack helicopter developed and manufactured by the American rotorcraft manufacturer Bell Helicopter. A member of the prolific Huey family, the AH-1 is also referred to as the HueyCobra or Snake.

The Bell UH-1 Iroquois is a utility military helicopter designed and produced by the American aerospace company Bell Helicopter. It is the first member of the prolific Huey family, as well as the first turbine-powered helicopter in service with the United States military.

The Royal New Zealand Air Force is the aerial service branch of the New Zealand Defence Force. It was formed initially in 1923 as a branch of the New Zealand Army, being known as the New Zealand Permanent Air Force, becoming an independent air force on 1 April 1937.

The Bell CH-146 Griffon is a multi-role utility helicopter designed by Bell Helicopter Textron as a variant of the Bell 412EP for the Canadian Armed Forces. It is used in a wide variety of roles, including aerial firepower, reconnaissance, search and rescue and aero-mobility tasks. The CH-146 has a crew of three, can carry up to ten troops and has a cruising speed of 220–260 km/h.

The Kenya Air Force (KAF) or Swahili: Jeshi la Wanahewa is the national aerial warfare service branch of the Republic of Kenya.

No. 3 Squadron RNZAF is a unit of the Royal New Zealand Air Force (RNZAF). It currently operates NHIndustries NH90 and Agusta A109 helicopters. The squadron was initially formed as a territorial unit of the New Zealand Permanent Air Force in Christchurch in 1930. During World War II, the squadron served in the Pacific, undertaking patrol operations. In the early post war period, the squadron was converted to a Territorial formation flying fixed wing aircraft, but later converted to rotary wing aircraft, and returning to permanent status. Since then, personnel from the squadron have served in the Vietnam War, East Timor, Singapore, the Sinai, and the Solomon Islands.

The Bell 412 is a utility helicopter of the Huey family manufactured by Bell Helicopter. It is a development of the Bell 212, with the major difference being the composite four-blade main rotor. It is twin-turbine helicopter that has been popular on the civilian and military markets, and major users include Canada, Italy, and Japan. Several hundred have been produced since its introduction in 1979, and several iterations of upgrades and variations have been produced such as with upgraded cockpit electronics.

The 5th Aviation Regiment is an Australian Army aviation unit. Formed in 1987 after the Army took over responsibility for operating helicopters from the Royal Australian Air Force, the regiment is based at RAAF Base Townsville, in Queensland. It currently forms part of the 16th (Aviation) Brigade and it operates the majority of the Army's transport helicopters. Throughout its existence, the regiment has been deployed overseas numerous times, supporting both peacekeeping and warlike operations. Since its formation elements of the regiment have made operational deployments to Cambodia, Papua New Guinea, East Timor, Iraq, Indonesia and Pakistan.

Oakey Army Aviation Centre is situated approximately 3 km (1.9 mi) from the town centre of Oakey in Queensland, Australia. It provides a training establishment for Australian Army Aviation, and also hosts the Republic of Singapore Air Force's "Cougar" 126 Squadron. The Defence name for the facility is Swartz Barracks, named for prominent politician, Army Aviation advocate, and ex-POW Sir Reginald Swartz.

The Army Airmobile Force is the army aviation branch of the Spanish Army. An Independent Army Aviation force was formed in 1965 as Aviación Ligera del Ejército de Tierra and renamed FAMET in 1973.

No. 9 Squadron is a unit of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). The squadron was formed in early 1939 and saw active service in World War II as a fleet co-operation unit providing aircrews for seaplanes operating off Royal Australian Navy cruisers. It was disbanded in late 1944, but was re-raised in 1962 and later became an Army co-operation unit, flying helicopters in support of Australian troops during the Vietnam War. The squadron was disbanded in 1989 when the RAAF transferred its battlefield helicopters to the Australian Army's aviation regiments. It was re-raised in June 2023 to operate Northrop Grumman MQ-4C Tritons.

ANZUK was a tripartite force formed by Australia, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom to defend the Asian Pacific region after the United Kingdom withdrew forces from the east of Suez in the early 1970s. The ANZUK force was formed in Singapore on 1 November 1971 under Rear Admiral David Wells and disbanded on 31 January 1974.
Tactical Transport Group was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) group. It was established on 1 June 1988 as part of a broad-ranging reform of the RAAF's organisation.

No. 35 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) transport unit. Formed in 1942, No. 35 Squadron operated during World War II, transporting cargo and passengers around Australia, New Guinea and the Netherlands East Indies, equipped with a variety of aircraft including the Douglas Dakota. It was disbanded after the war, but was re-raised in the 1960s for service during the Vietnam War, flying transportation and resupply operations with DHC-4 Caribous in support of Australian and US forces. The squadron was subsequently augmented with rotary-wing aircraft, operating UH-1 Iroquois in both the transportation and gunship roles. In the late 1980s, the squadron returned to a solely fixed-wing transport role. It ceased operations in 2000, but was re-raised in January 2013. It began re-equipping with C-27 Spartan transports in 2015.

The Bell 214 is a medium-lift helicopter derived from Bell Helicopter's ubiquitous UH-1 Huey series. The Bell 214ST shares the same model number, but is a larger, much-modified twin-engine derivative.

The Bell 204 and 205 are the civilian versions of the UH-1 Iroquois single-engine military helicopter of the Huey family of helicopters. They are type-certificated in the transport category and are used in a wide variety of applications, including crop dusting, cargo lifting, Forestry Operations, and aerial firefighting.

The Bell UH-1N Twin Huey is a medium military helicopter designed and produced by the American aerospace manufacturer Bell Helicopter. It is a member of the extensive Huey family, the initial version was the CUH-1N Twin Huey, which was first ordered by the Canadian Forces in 1968.

The Bell UH-1 Iroquois military helicopter, first introduced in 1959, is the first production member of the prolific Huey family of helicopters, and was itself developed in over twenty variants, which are listed below.

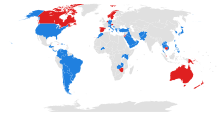
The Bell Huey family of helicopters includes a wide range of civil and military aircraft produced since 1956 by Bell Helicopter. This H-1 family of aircraft includes the utility UH-1 Iroquois and the derivative AH-1 Cobra attack helicopter series and ranges from the XH-40 prototype, first flown in October 1956 to the 21st-century UH-1Y Venom and AH-1Z Viper. Although not flown in military service in the USA, the Bell 412 served in Canada and Japan, and like the UH-1Y is a twin engine four rotor design based on the Bell 212.