
An ecoregion or ecozone is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural communities and species. The biodiversity of flora, fauna and ecosystems that characterise an ecoregion tends to be distinct from that of other ecoregions. In theory, biodiversity or conservation ecoregions are relatively large areas of land or water where the probability of encountering different species and communities at any given point remains relatively constant, within an acceptable range of variation.

The Corn Belt is a region of the Midwestern United States that, since the 1850s, has dominated corn production in the United States. In the United States, "corn" is the common word for "maize". More generally, the concept of the "Corn Belt" connotes the area of the Midwest dominated by farming and agriculture.

The ecology of California can be understood by dividing the state into a number of ecoregions, which contain distinct ecological communities of plants and animals in a contiguous region. The ecoregions of California can be grouped into four major groups: desert ecoregions, Mediterranean ecoregions, forested mountains, and coastal forests.

The tallgrass prairie is an ecosystem native to central North America. Historically, natural and anthropogenic fire, as well as grazing by large mammals provided periodic disturbances to these ecosystems, limiting the encroachment of trees, recycling nutrients soil nutrients, and facilitating seed dispersal and germination. Prior to widespread use of the steel plow, which enabled large scale conversion to agricultural land use, tallgrass prairies extended throughout the American Midwest and smaller portions of southern central Canada, from the transitional ecotones out of eastern North American forests, west to a climatic threshold based on precipitation and soils, to the southern reaches of the Flint Hills in Oklahoma, to a transition into forest in Manitoba.

The Laurentian Mixed Forest Province, also known as the North Woods, is a forested ecoregion in eastern North America. Among others, this terminology has been adopted by the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources. Similar, though not necessarily entirely identical regions, are identified by the United States Environmental Protection Agency as Northern Lakes and Forests, and by the World Wildlife Fund by regions such as the Western Great Lakes forests and Eastern forest-boreal transition.

The term Cross Timbers, also known as Ecoregion 29, Central Oklahoma/Texas Plains, is used to describe a strip of land in the United States that runs from southeastern Kansas across Central Oklahoma to Central Texas. Made up of a mix of prairie, savanna, and woodland, it forms part of the boundary between the more heavily forested eastern country and the almost treeless Great Plains, and also marks the western habitat limit of many mammals and insects.

The natural history of Minnesota covers many plant and animal species in the U.S. state of Minnesota. The continental climate and location of Minnesota at the physiographic intersection of the Laurentian and the Interior Plains influences its plant and animal life. Three of North America's biomes converge in Minnesota: prairie grasslands in the southwestern and western parts of the state, the eastern temperate deciduous forests in the east-central and the southeast, and the coniferous forest in the north-central and northeast.
The Mixed Wood Plains Ecozone is an ecozone of North America that was defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation to reconcile the American and Canadian land classification systems. According to the CEC, the Mixed Wood Plains of North America is a Level II Ecoregion 8.1, which includes the Mixedwood Plains of Canada, and the adjoining areas of the United States such as the Eastern Great Lakes and Hudson Lowlands ecoregion. However, the CEC atlas also includes areas of Wisconsin, Maine and New Brunswick in the Mixed Wood Plain ecoregion.

The Atlantic Maritime Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is an ecozone which covers the Canadian provinces of Prince Edward Island, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick, as well as the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec. It is adjacent to the Atlantic Marine Ecozone to the east, and the Mixedwood Plains to the west. The roughly-corresponding Level I Ecoregion to this ecozone in the United States Environmental Protection Agency's classification, which is also part of the CEC system, is the Northern Forests ecoregion, though that classification includes the woodlands and swamps of northern Michigan and Minnesota, which are adjacent to the Boreal Shield ecozone.

The Eastern Great Lakes and Hudson Lowlands region extends along the south shores of Lake Erie and Lake Ontario and the St. Lawrence River to Lake Champlain, and south down the Hudson River. It is primarily within the state of New York, with smaller portions in Vermont, Pennsylvania, and Ohio. In the north it meets the Mixedwood Plains Ecozone of Canada in eastern Ontario and southern Quebec. It is mostly temperate deciduous forest and agricultural land.

The Mixedwood Plains Ecozone is the Canadian ecozone with the most southern extent, covering all of southwestern Ontario, and parts of central and northeastern Ontario and southern Quebec along the Saint Lawrence River. It was originally dominated by temperate deciduous forest growing mostly on limestone covered by glacial till. It is the smallest ecozone in Canada, but it includes the country's most productive industrial and commercial region, and is home to nearly half of Canada's population, including its two largest cities, Toronto, Ontario and Montreal, Quebec. Hence, little of the original forest cover remains, making protection of the remaining forests a high conservation priority. This ecozone includes two regions described by J.S. Rowe in his classic Forest Regions of Canada: the entire Deciduous Forest Region, and the southern portions of the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Forest Region. In the province of Ontario, the Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources maps this area as Site Regions 6E and 7E.

The North Central Hardwood Forests are a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion in central Minnesota, central Wisconsin, and northwestern Lower Michigan, embedded between (clockwise) the Western Corn Belt Plains in the south, the Northern Glaciated Plains, the Red River Valley, the Northern Minnesota Wetlands, and the Northern Lakes and Forests. It forms the northern part of the upper Midwest forest-savanna transition, which also includes regions 52 and 53.
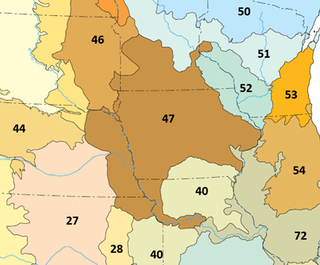
The Western Corn Belt Plains is a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in seven U.S. states, though predominantly in Iowa.












